- Home
-
Trailers
- Box Trailers >
-
Flat Top/Flat Bed Trailers
>
- Single Axle Flatbed Trailers >
-
Tandem Axle Flatbed Trailers
>
-
 8×5ft ATM 1990KG Flat Top /Flat Bed TrailerTrail...
8×5ft ATM 1990KG Flat Top /Flat Bed TrailerTrail... -
 10×6.3ft ATM 2800KG Flat Top /Flat Bed Tandem TrailerTrail...
10×6.3ft ATM 2800KG Flat Top /Flat Bed Tandem TrailerTrail... -
 10×6ft ATM 3500KG Flat Top /Flat Bed Hydraulic Tipper TrailerTrail...
10×6ft ATM 3500KG Flat Top /Flat Bed Hydraulic Tipper TrailerTrail... -
 12×7ft ATM 3500KG Flat Top /Flat Bed Tandem TrailerTrail...
12×7ft ATM 3500KG Flat Top /Flat Bed Tandem TrailerTrail... -
 14×7ft 3500KG ATM Flat Bed Tandem TrailerTrail...
14×7ft 3500KG ATM Flat Bed Tandem TrailerTrail... -
 12×7ft ATM 3500KG Tandem Flatbed Hydraulic Tipper TrailerTrail...
12×7ft ATM 3500KG Tandem Flatbed Hydraulic Tipper TrailerTrail...
-
- Tri Axle Flatbed Trailers >
- Hydraulic Tippers >
- Cattle/ Livestock Trailers >
-
Boat, Kayak & Jet Ski Trailers
>
-
Single Axle Rollers Boat Trailer
>
-
 4100 Series 750KG ATM Single Axle Rollers Boat TrailerTrail...
4100 Series 750KG ATM Single Axle Rollers Boat TrailerTrail... -
 4500 Series 750KG ATM Single Axle Rollers Boat TrailerTrail...
4500 Series 750KG ATM Single Axle Rollers Boat TrailerTrail... -
 4900 Series 1200KG ATM Single Axle Rollers Boat TrailerTrail...
4900 Series 1200KG ATM Single Axle Rollers Boat TrailerTrail... -
 5700 Series 1500KG ATM Single Axle Rollers Boat TrailerTrail...
5700 Series 1500KG ATM Single Axle Rollers Boat TrailerTrail... -
 6300 Series 1500KG ATM Single Axle Rollers Boat TrailerTrail...
6300 Series 1500KG ATM Single Axle Rollers Boat TrailerTrail...
-
- Single Axle Skid Boat Trailer >
- Tandem Axle Rollers Boat Trailer >
- Kayak & Canoe Trailer >
-
Single Axle Rollers Boat Trailer
>
- Motorcycles, ATV & Buggy Trailers >
- Car & Plant Trailers >
- Gardening & Mowing Trailers >
-
Builders/Tradesman Trailers
>
-
Single Axle Fully Enclosed & Luggage Trailer
>
-
 6×4ft Small Tradesman/ Builders TrailerTrail...
6×4ft Small Tradesman/ Builders TrailerTrail... -
 7×4ft Tradesman/ Builders TrailerTrail...
7×4ft Tradesman/ Builders TrailerTrail... -
 7×5ft Tradesman/ Builders Trailer with Aluminium CanopyTrail...
7×5ft Tradesman/ Builders Trailer with Aluminium CanopyTrail... -
 8×5ft Durable Tradesman/ Builders TrailerTrail...
8×5ft Durable Tradesman/ Builders TrailerTrail... -
 8×6ft ATM 750KG Tradesman/ Builders TrailerTrail...
8×6ft ATM 750KG Tradesman/ Builders TrailerTrail... -
 7×5ft Heavy Duty Tradesman/ Builders TrailerTrail...
7×5ft Heavy Duty Tradesman/ Builders TrailerTrail... -
 8×5ft Heavy Duty ATM 1400KG Tradesman/ Builders TrailerTrail...
8×5ft Heavy Duty ATM 1400KG Tradesman/ Builders TrailerTrail... -
 8×6ft Heavy Duty Enclosed Tradesman/ Builders TrailerTrail...
8×6ft Heavy Duty Enclosed Tradesman/ Builders TrailerTrail...
-
-
Tandem Axle Builders/Tradesman Trailer
>
-
 8×5ft Dual Axle Builders/Tradesman TrailerTrail...
8×5ft Dual Axle Builders/Tradesman TrailerTrail... -
 10×5ft Tandem Builders/Tradesman TrailerTrail...
10×5ft Tandem Builders/Tradesman TrailerTrail... -
 10×6ft Tandem Builders/Tradesman TrailerTrail...
10×6ft Tandem Builders/Tradesman TrailerTrail... -
 8×5ft Tandem Axle Tradesman/ Builders TrailerTrail...
8×5ft Tandem Axle Tradesman/ Builders TrailerTrail... -
 10×5ft Tandem Tradesman/ Builders TrailerTrail...
10×5ft Tandem Tradesman/ Builders TrailerTrail... -
 10×6ft Tandem Tradesman/ Builders Trailer with Aluminium CanopyTrail...
10×6ft Tandem Tradesman/ Builders Trailer with Aluminium CanopyTrail...
-
-
Single Axle Fully Enclosed & Luggage Trailer
>
- Enclosed/Luggage Trailers >
-
Toolboxes
-
Under Tray Toolboxes
>
-
Ute Under Tray Toolboxes
>
-
 580 x 230 x 400mm Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Truck Storage Under Body Tray Storage Strap Tool BoxThickness:...
580 x 230 x 400mm Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Truck Storage Under Body Tray Storage Strap Tool BoxThickness:... -
 600 x 200 x 400mm Aluminium 20L Ute Camping Under Tray Body Box Storage Water TankThickness:...
600 x 200 x 400mm Aluminium 20L Ute Camping Under Tray Body Box Storage Water TankThickness:... -
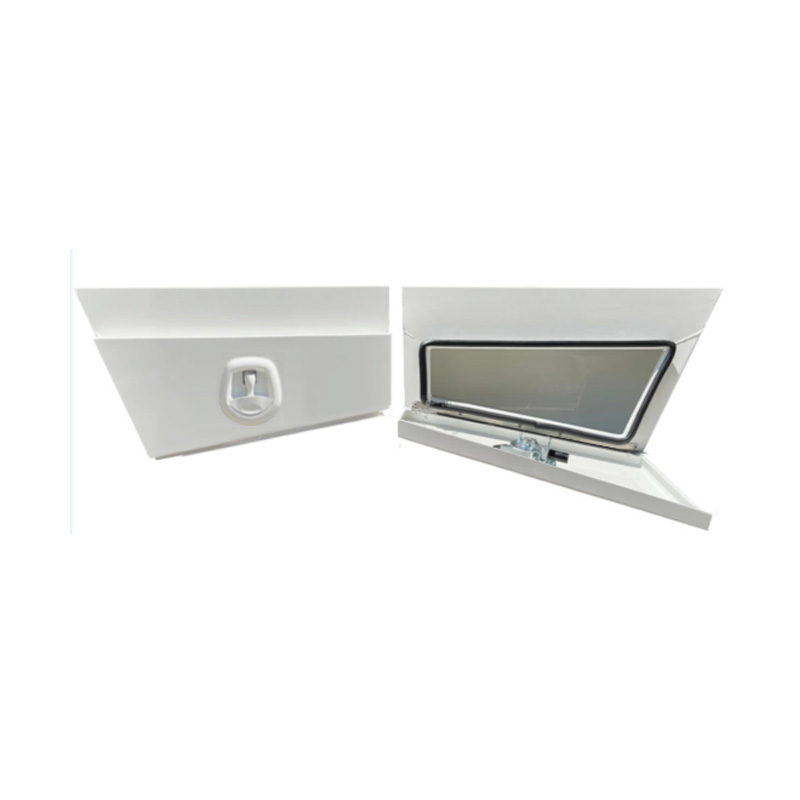
 600 x 230 x 400mm Aluminium Pair Ute Toolbox Truck Storage Under Body Tray Storage Strap Tool Box Off Road TapperThickness:...
600 x 230 x 400mm Aluminium Pair Ute Toolbox Truck Storage Under Body Tray Storage Strap Tool Box Off Road TapperThickness:... -
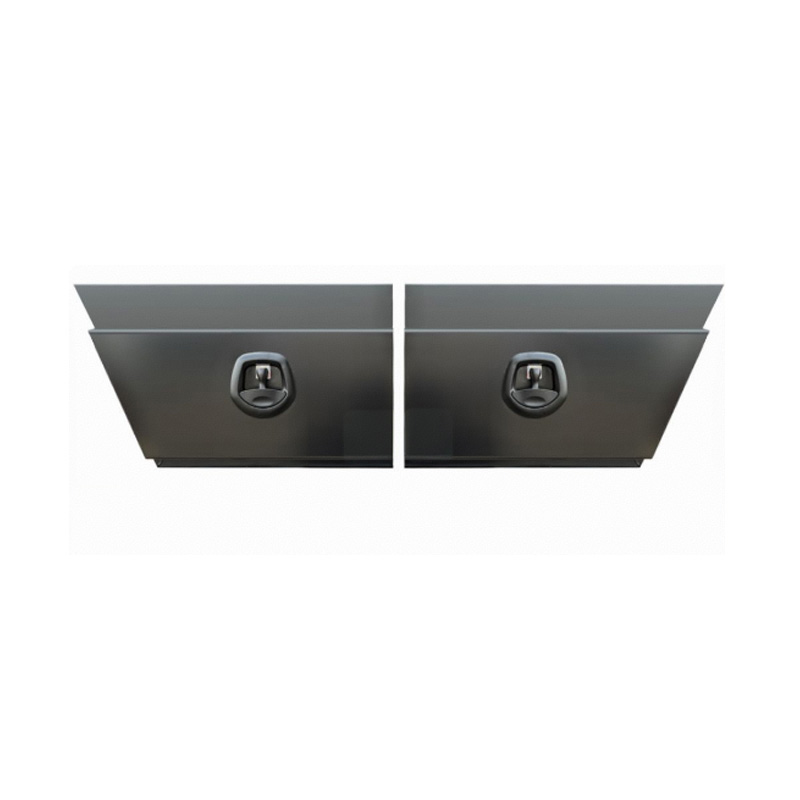
 600 x 230 x 400mm Aluminium Set Pair Ute Toolbox Truck Storage Under Body Tray Storage Strap Tool Box Off Road TapperThickness:...
600 x 230 x 400mm Aluminium Set Pair Ute Toolbox Truck Storage Under Body Tray Storage Strap Tool Box Off Road TapperThickness:... -
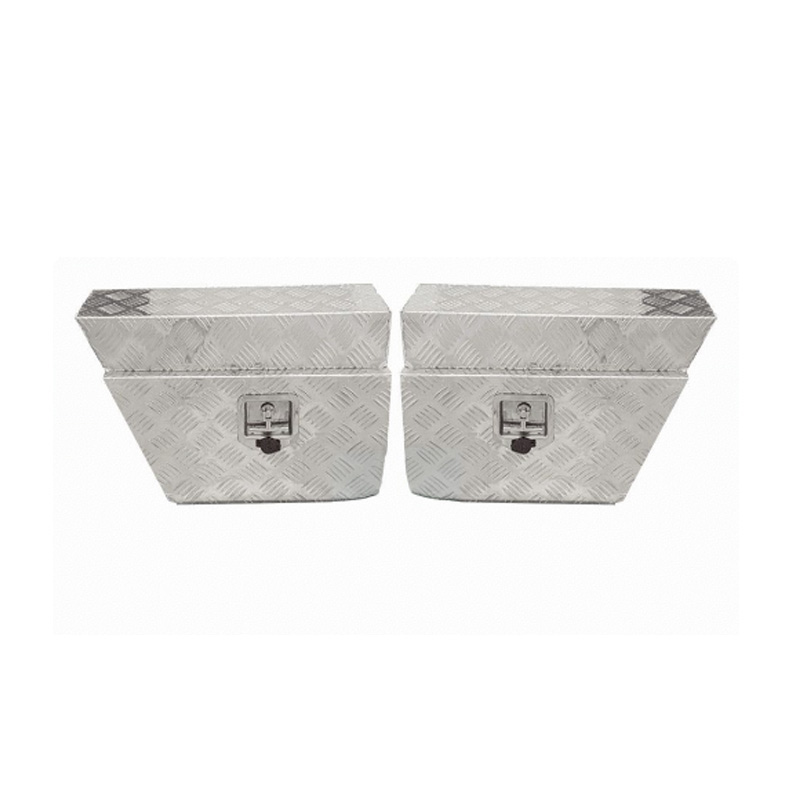
 750 x 230 x 400mm Aluminium SET PAIR Ute Toolbox Truck Storage Under Body Tray Storage Strap Tool Box Off Road TapperThickness:...
750 x 230 x 400mm Aluminium SET PAIR Ute Toolbox Truck Storage Under Body Tray Storage Strap Tool Box Off Road TapperThickness:... -
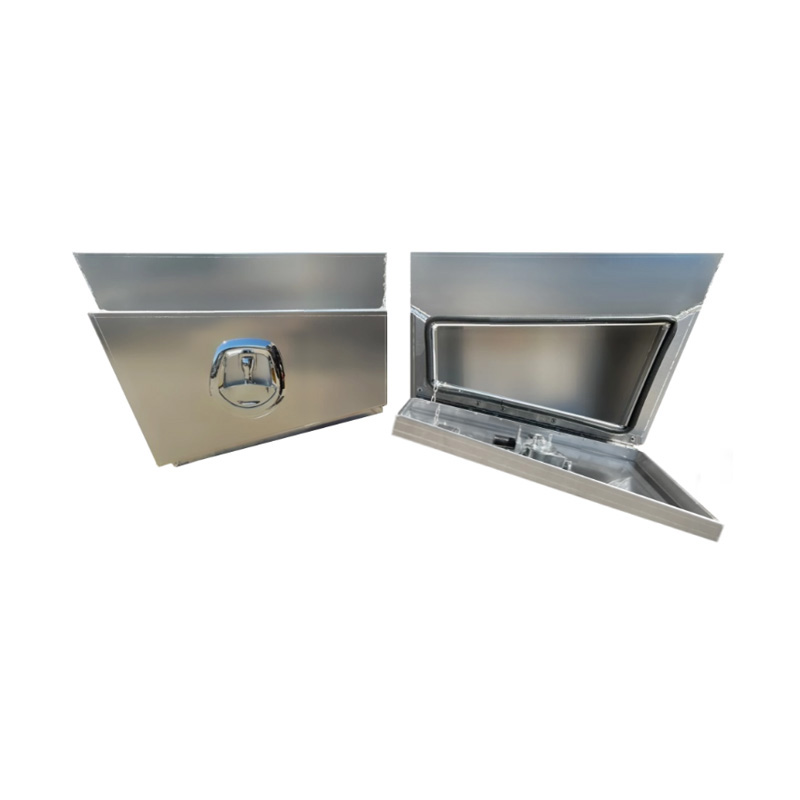
 750 x 230 x 400mm Aluminium SET PAIR Ute Toolbox Truck Storage Under Body Tray Storage Strap Tool Box Off Road TapperThickness:...
750 x 230 x 400mm Aluminium SET PAIR Ute Toolbox Truck Storage Under Body Tray Storage Strap Tool Box Off Road TapperThickness:... -
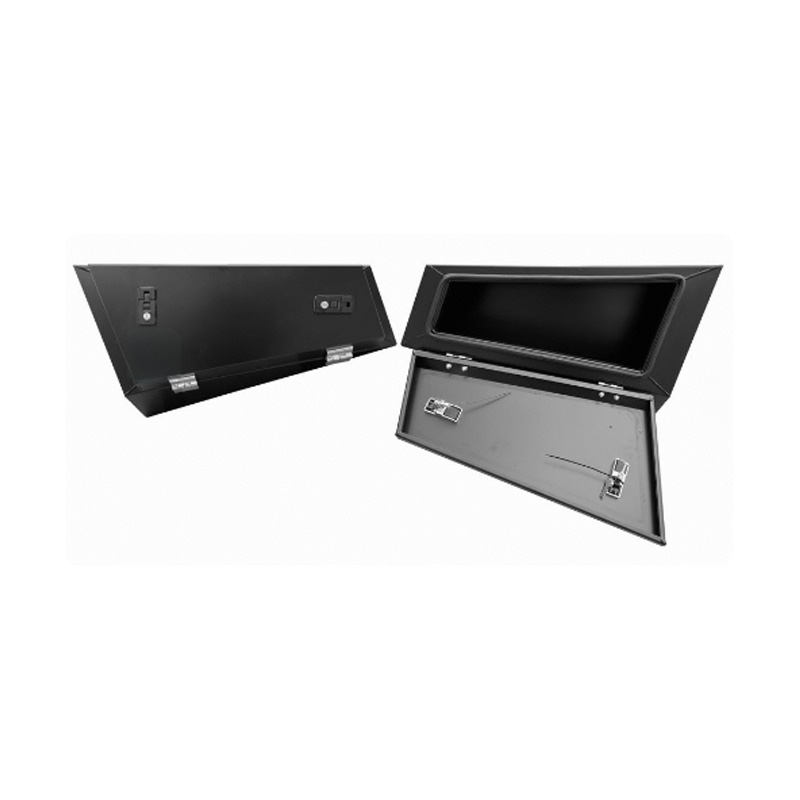 700 x 260 x 400mm (LIMITED EDITION) Under Tray Toolbox TapperedThickness:...
700 x 260 x 400mm (LIMITED EDITION) Under Tray Toolbox TapperedThickness:... -
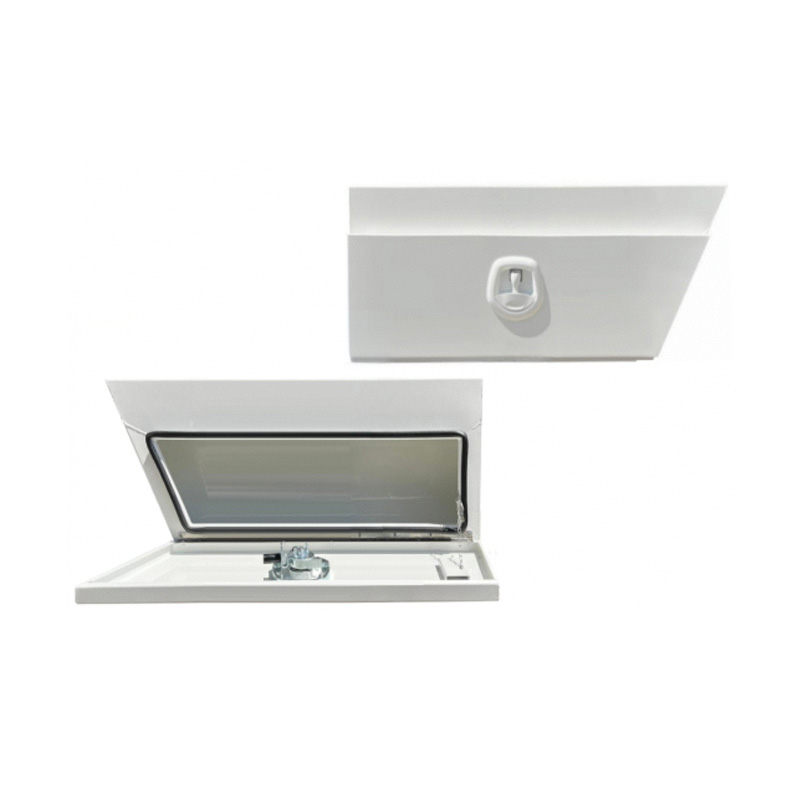 940 x 230 x 400mm Aluminium SET PAIR Ute Toolbox Truck Storage Under Body Tray Storage Strap Tool Box Off Road TapperThickness:...
940 x 230 x 400mm Aluminium SET PAIR Ute Toolbox Truck Storage Under Body Tray Storage Strap Tool Box Off Road TapperThickness:... -
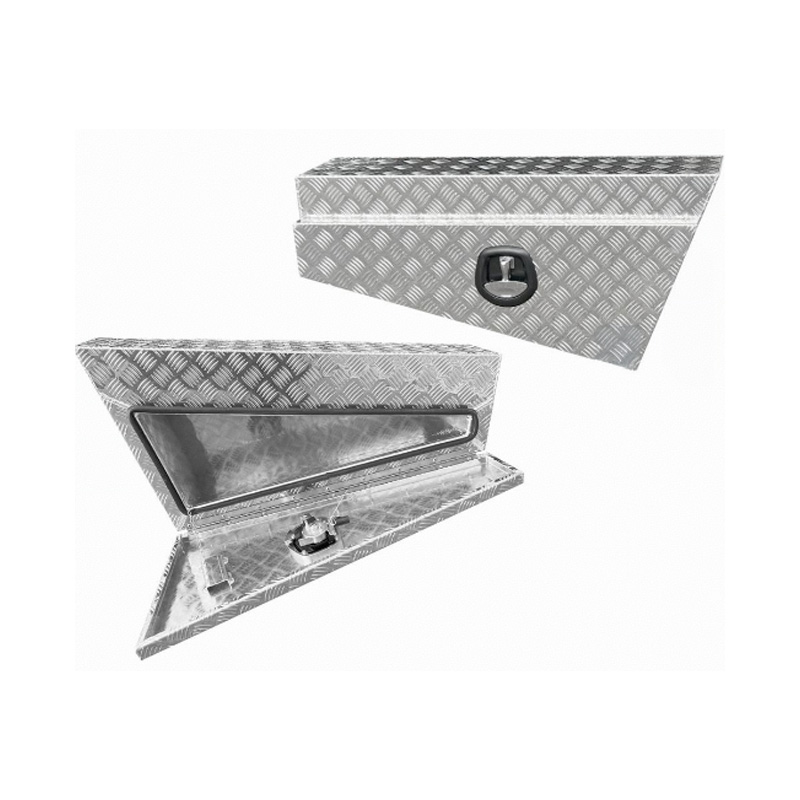 940 x 230 x 400mm Aluminium SET PAIR Ute Toolbox Truck Storage Under Body Tray Storage Strap Tool Box Off Road TapperThickness:...
940 x 230 x 400mm Aluminium SET PAIR Ute Toolbox Truck Storage Under Body Tray Storage Strap Tool Box Off Road TapperThickness:... -
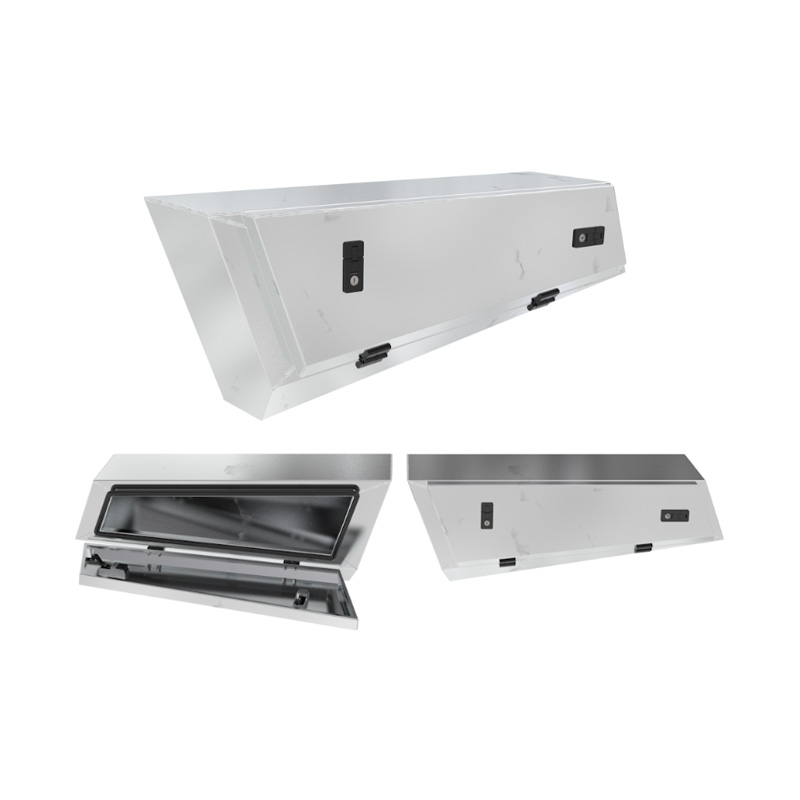 900 x 260 x 400mm (LIMITED EDITION) Under Tray Toolbox TapperedThickness:...
900 x 260 x 400mm (LIMITED EDITION) Under Tray Toolbox TapperedThickness:...
-
-
Truck Under Tray Boxes
>
-
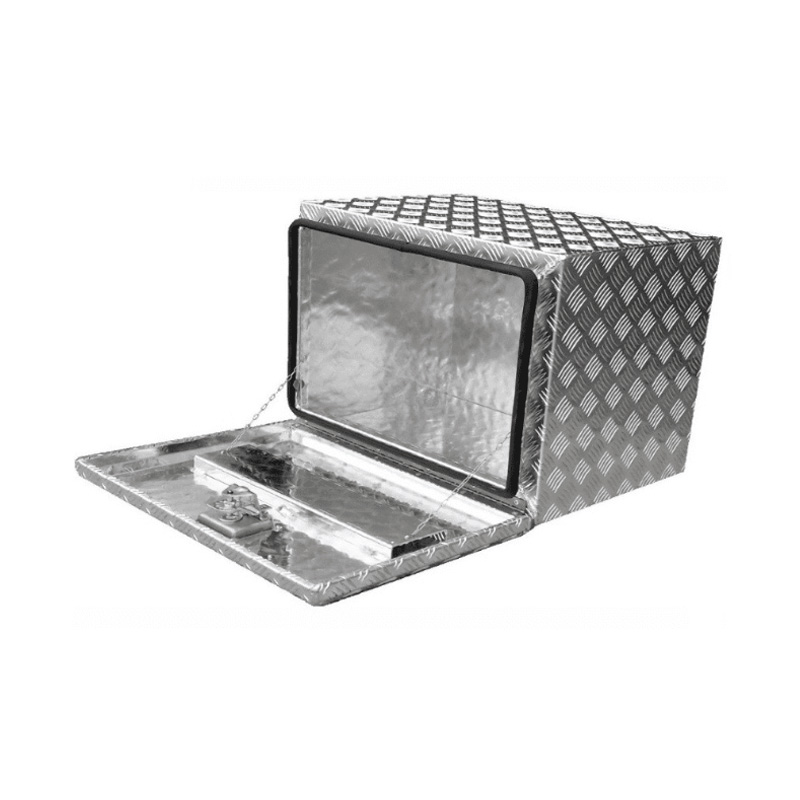 600 x 450 x 450mm Aluminium Checker Under Tray Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:...
600 x 450 x 450mm Aluminium Checker Under Tray Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:... -
 600 x 450 x 450mm Flat Aluminium Under Tray Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:...
600 x 450 x 450mm Flat Aluminium Under Tray Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:... -
 900 x 450 x 450mm Flat Aluminium Under Tray Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:...
900 x 450 x 450mm Flat Aluminium Under Tray Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:... -
 1000 x 450 x 450mm Flat Aluminium Under Tray Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:...
1000 x 450 x 450mm Flat Aluminium Under Tray Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:... -
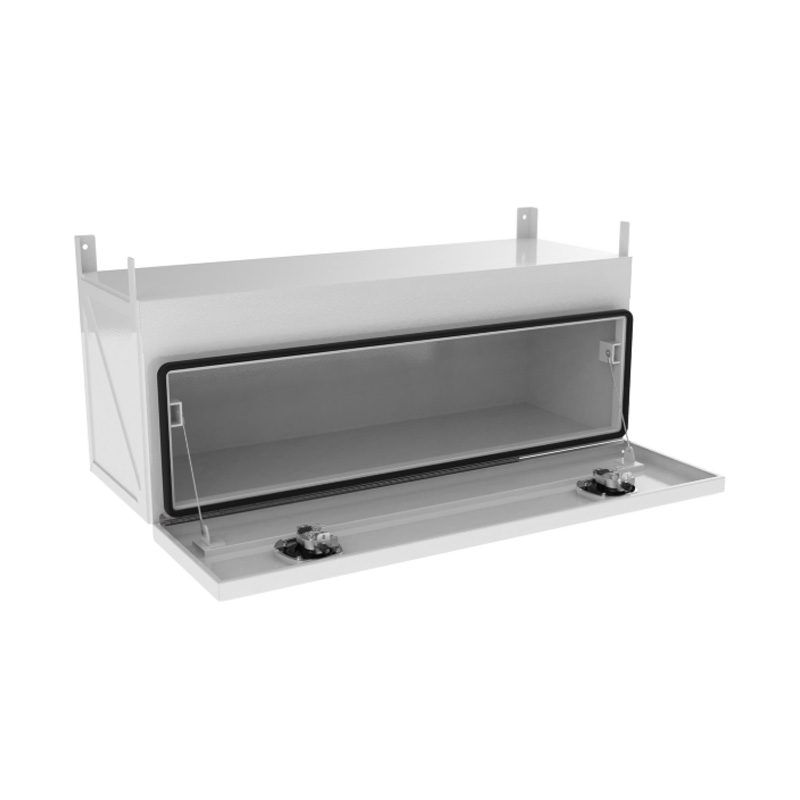 1200 x 450 x 450mm Flat Aluminium Under Tray Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:...
1200 x 450 x 450mm Flat Aluminium Under Tray Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:... -
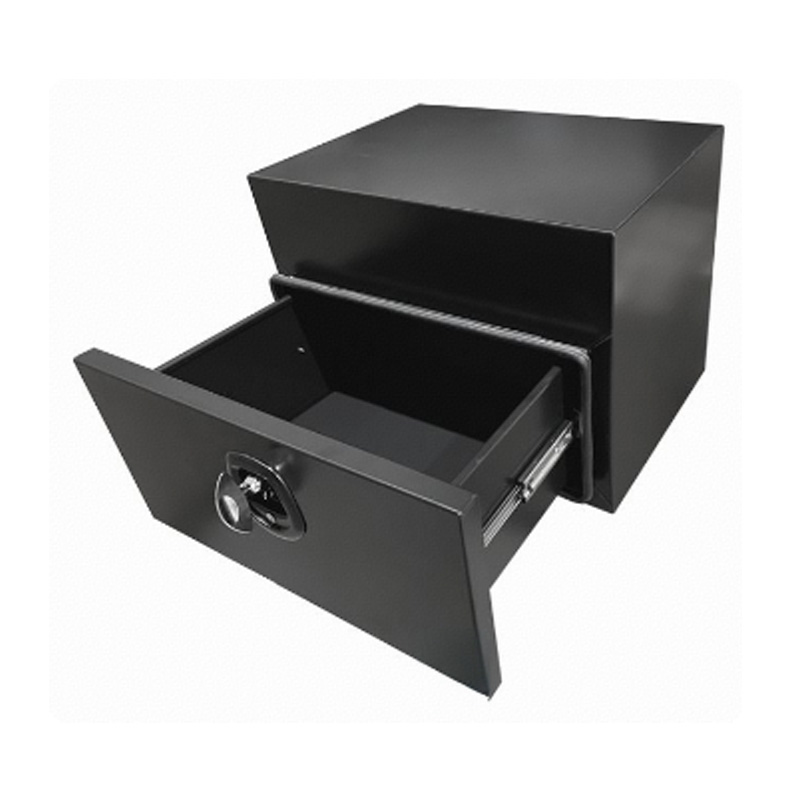 600 x 500 x 500mm Black Aluminium Under Tray Slide Drawer Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:...
600 x 500 x 500mm Black Aluminium Under Tray Slide Drawer Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:... -
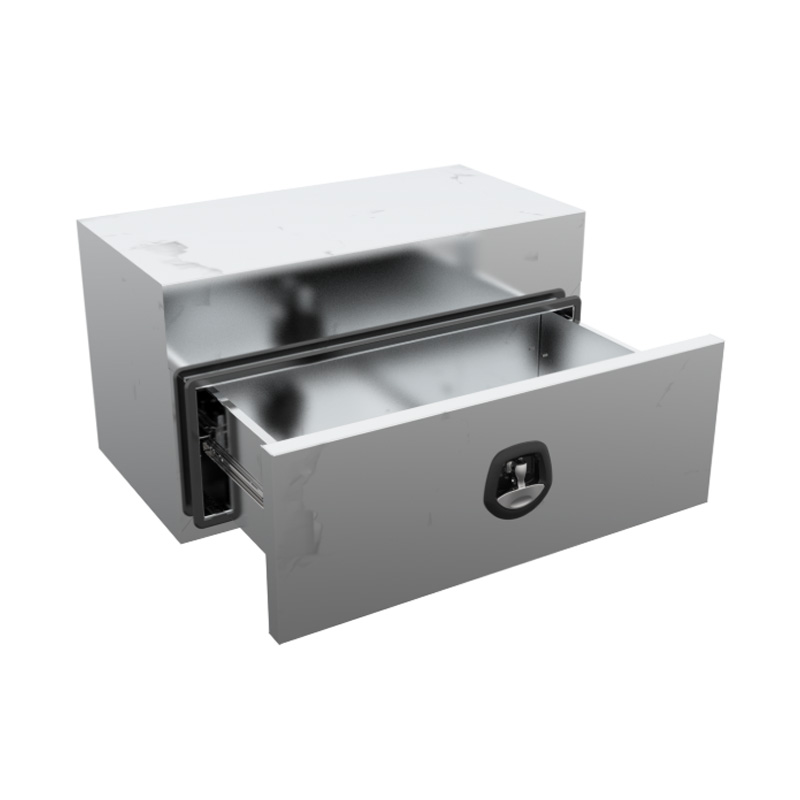 900 x 500 x 500mm Raw Flat Aluminium Under Tray Slide Drawer Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:...
900 x 500 x 500mm Raw Flat Aluminium Under Tray Slide Drawer Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:... -
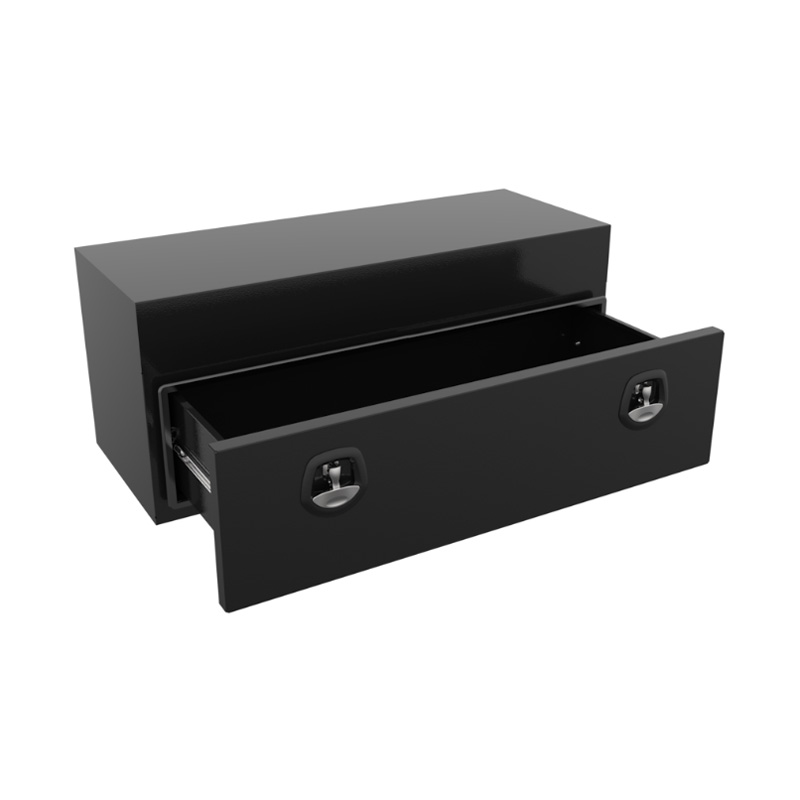 1200 x 500 x 500mm Black Aluminium Under Tray Slide Drawer Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:...
1200 x 500 x 500mm Black Aluminium Under Tray Slide Drawer Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:...
-
-
Trundle-Trays
>
-
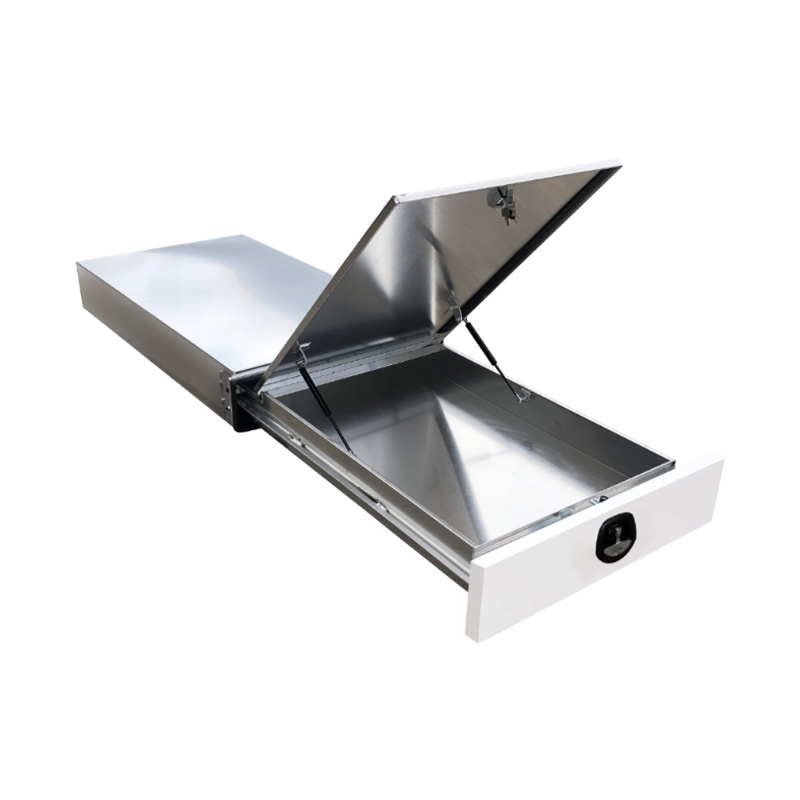 1.4m Aluminium Ute Tool box Under Tray Toolbox Trundle Roller Tray Slide Out Drawer Toolbox Benchtop LidThickness:...
1.4m Aluminium Ute Tool box Under Tray Toolbox Trundle Roller Tray Slide Out Drawer Toolbox Benchtop LidThickness:... -
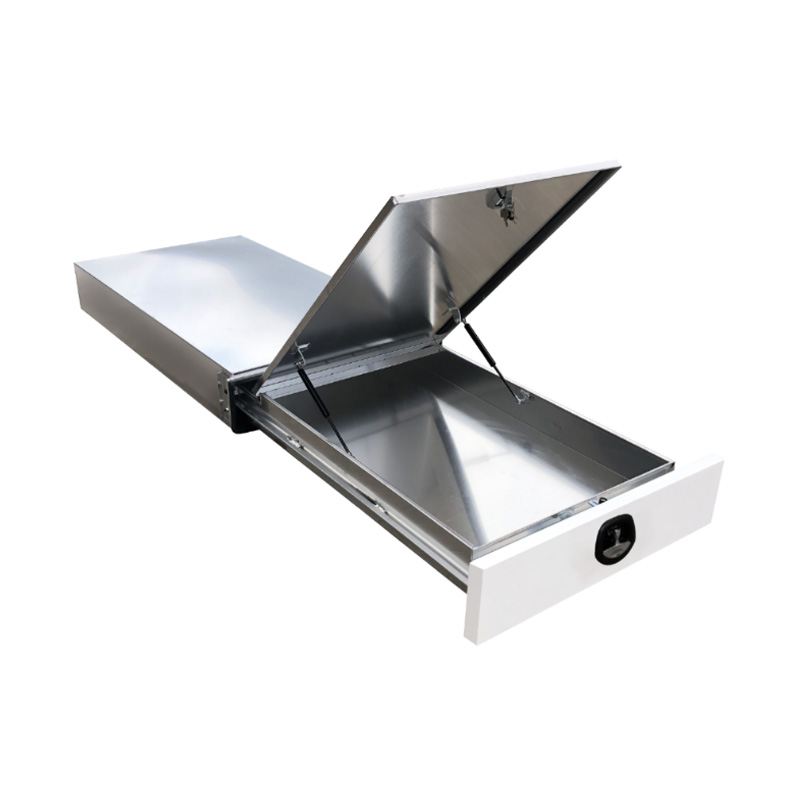 1.6m Aluminium Ute Tool box Under Tray Toolbox Trundle Roller Tray Slide Out Drawer Toolbox Benchtop LidThickness:...
1.6m Aluminium Ute Tool box Under Tray Toolbox Trundle Roller Tray Slide Out Drawer Toolbox Benchtop LidThickness:... -
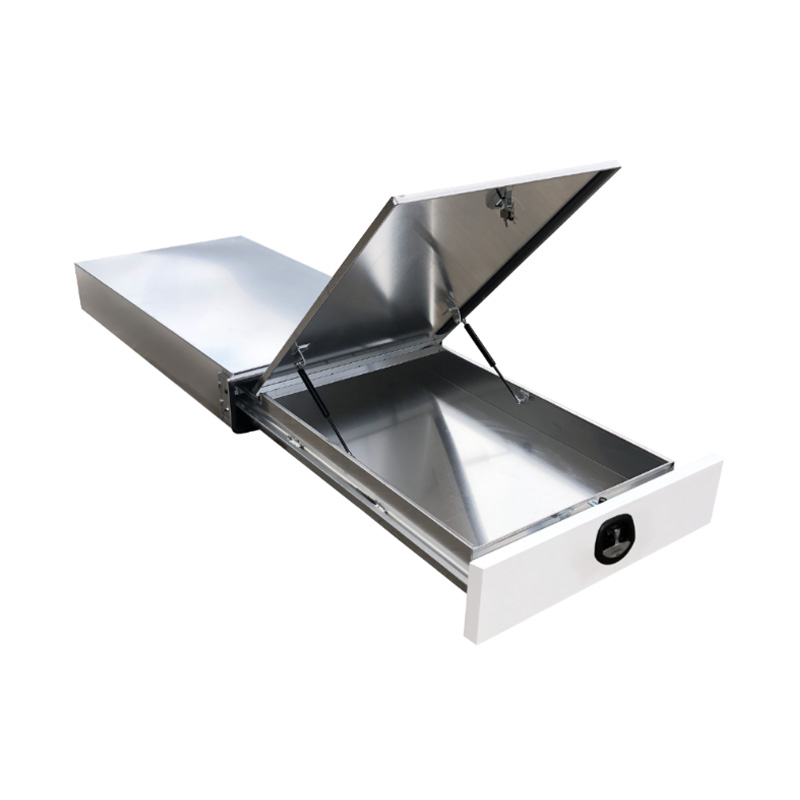 1.7m Aluminium Ute Tool box Under Tray Toolbox Trundle Roller Tray Slide Out Drawer Toolbox Benchtop LidThickness:...
1.7m Aluminium Ute Tool box Under Tray Toolbox Trundle Roller Tray Slide Out Drawer Toolbox Benchtop LidThickness:...
-
- Under Tray Water Tanks >
-
Ute Under Tray Toolboxes
>
-
Top Opening Toolboxes
>
-
Rectangle Ute Toolbox
>
-
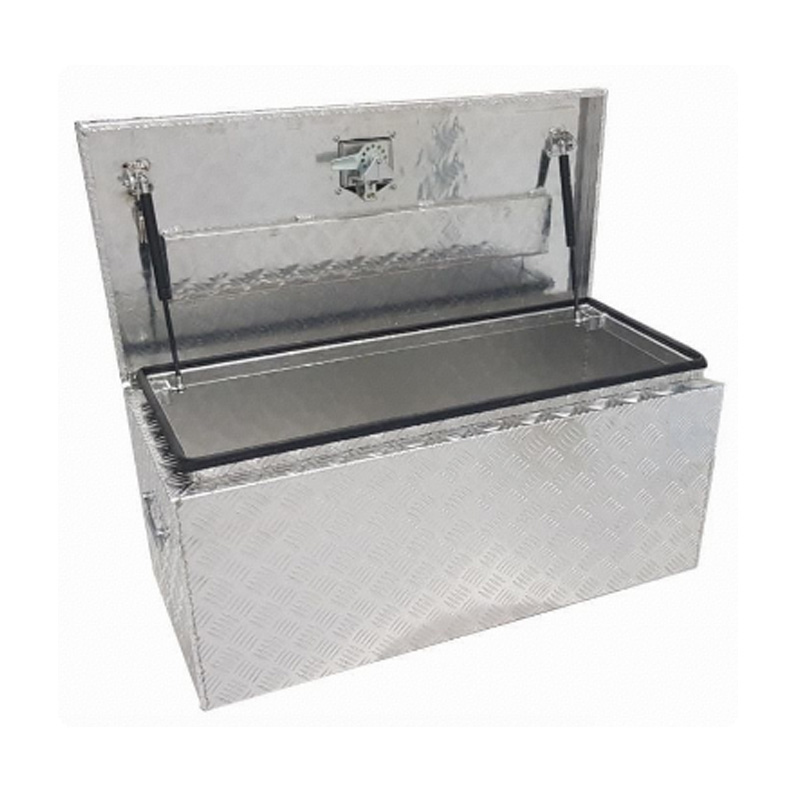 900 x 400 x 400mm Aluminium Checker Top Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:...
900 x 400 x 400mm Aluminium Checker Top Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:... -
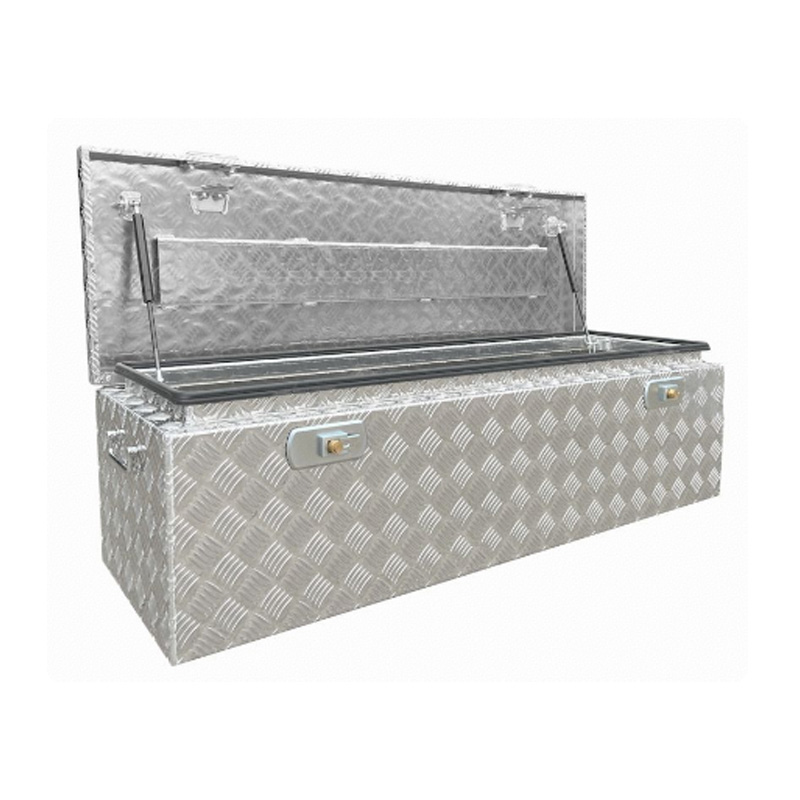 1220 x 400 x 350mm Aluminium Top Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:...
1220 x 400 x 350mm Aluminium Top Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:... -
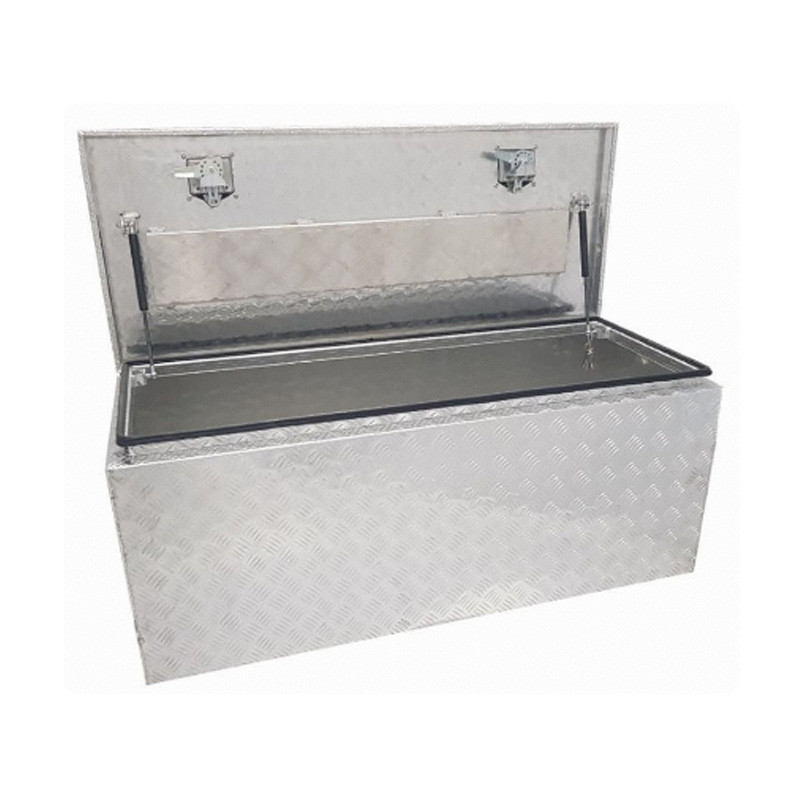 1220 x 500 x 500mm Aluminium Top Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & Canopy 1255Thickness:...
1220 x 500 x 500mm Aluminium Top Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & Canopy 1255Thickness:... -
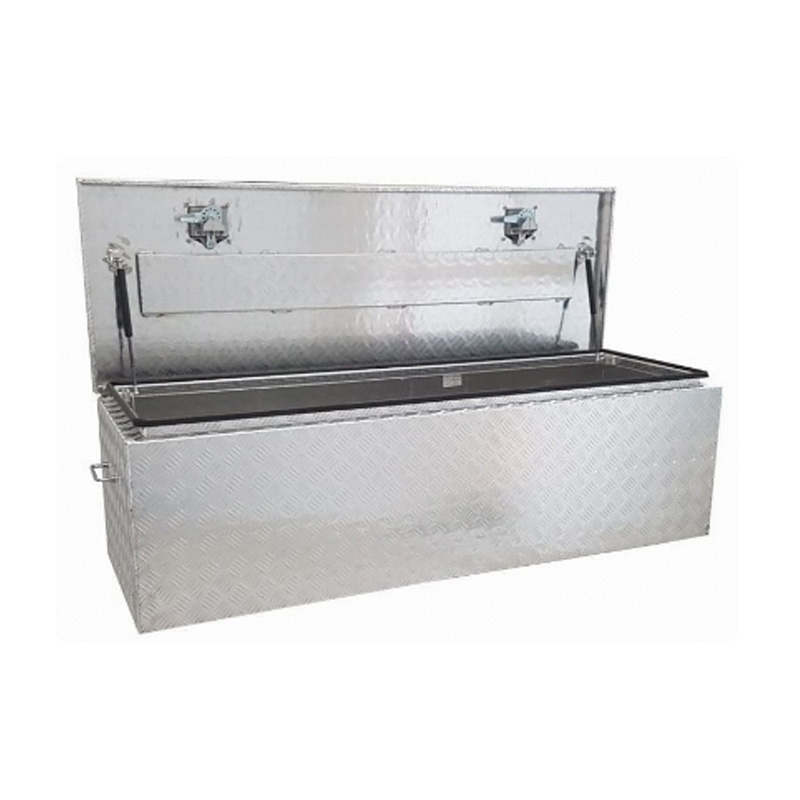 1500 x 500 x 450mm Aluminium Checker Top Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:...
1500 x 500 x 450mm Aluminium Checker Top Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:... -
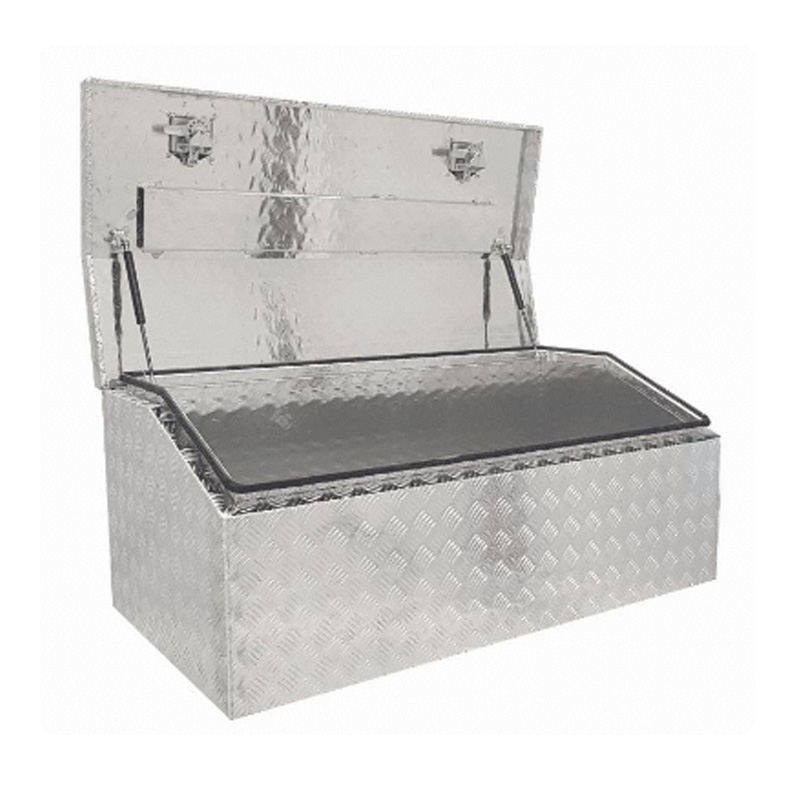 1200 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Top Chest Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & Canopy(Chest Style)Thickness:...
1200 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Top Chest Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & Canopy(Chest Style)Thickness:... -
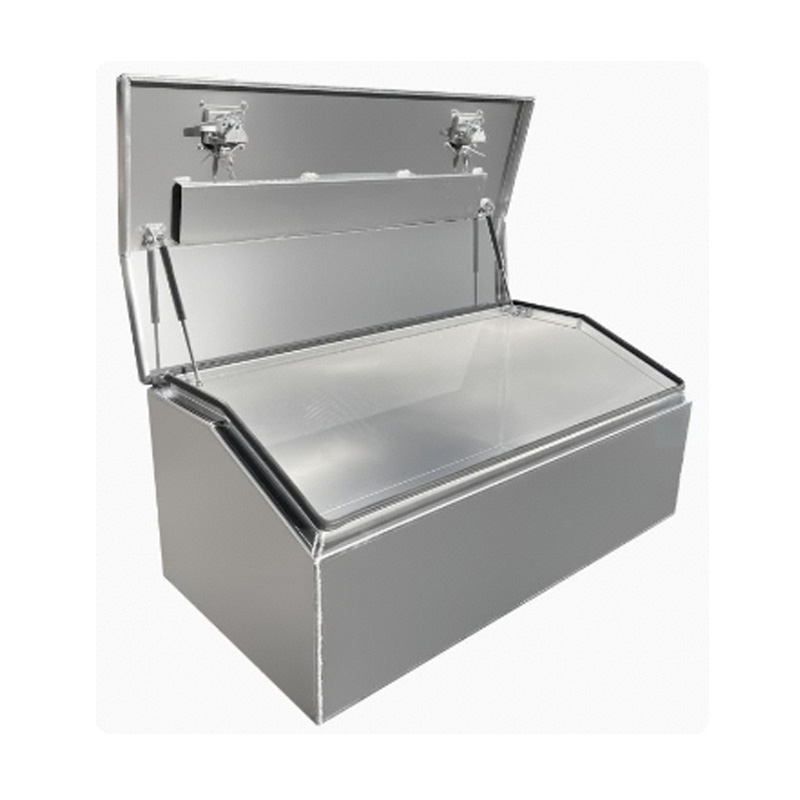 1400 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Top Chest Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:...
1400 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Top Chest Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:... -
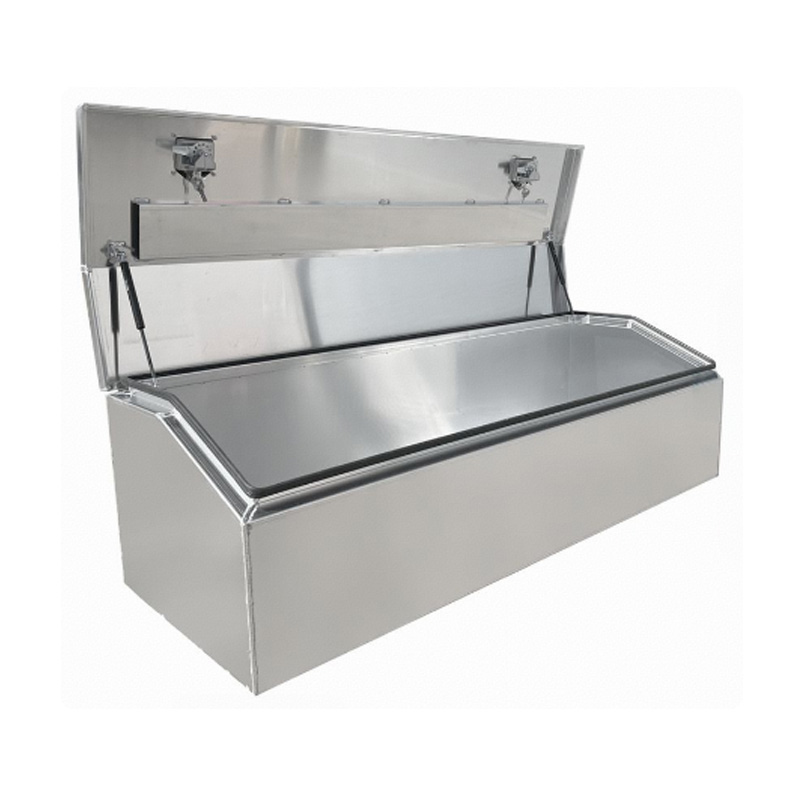 1700 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Top Chest Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:...
1700 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Top Chest Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:... -
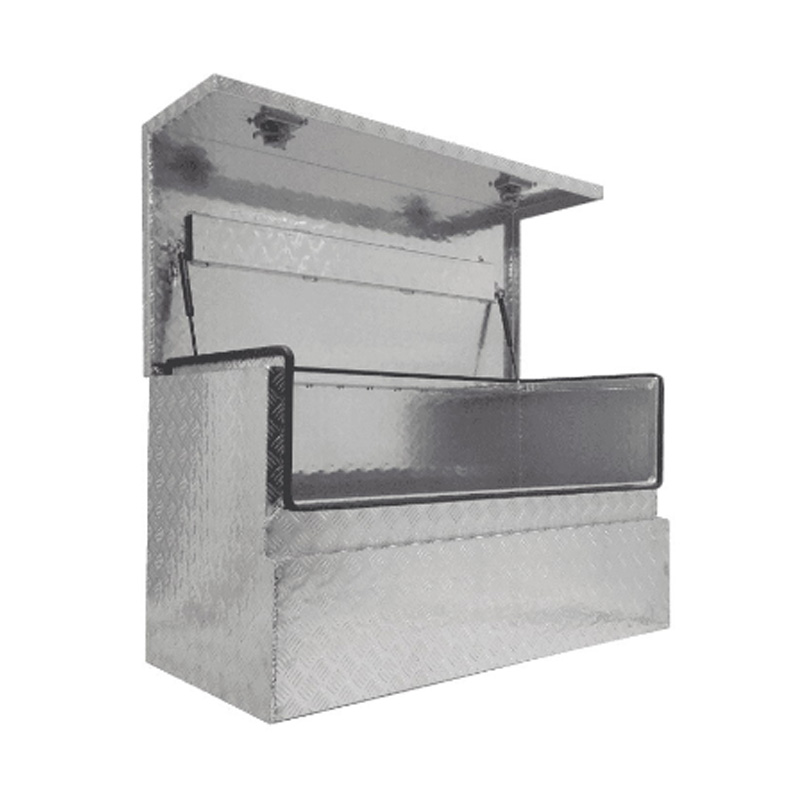 1200 x 600 x 700mm Aluminium Checker Tool Box Ute Truck Fridge Trailer 3/4 Angle Storage ToolboxThickness:...
1200 x 600 x 700mm Aluminium Checker Tool Box Ute Truck Fridge Trailer 3/4 Angle Storage ToolboxThickness:... -
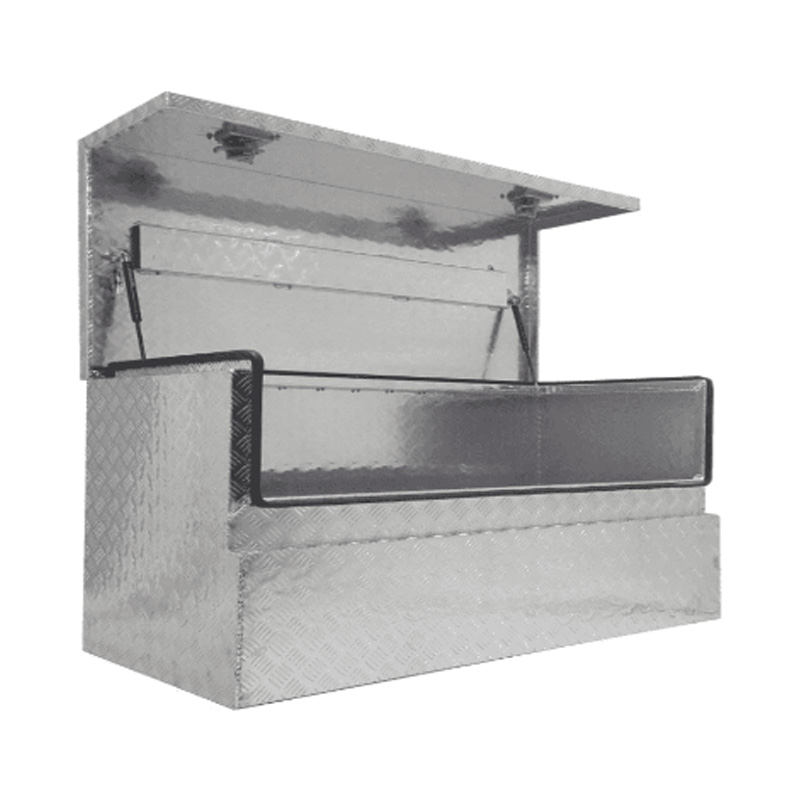 1400 x 600 x 700mm Aluminium Checker Tool Box Ute Truck Fridge Trailer 3/4 Angle Storage ToolboxThickness:...
1400 x 600 x 700mm Aluminium Checker Tool Box Ute Truck Fridge Trailer 3/4 Angle Storage ToolboxThickness:... -
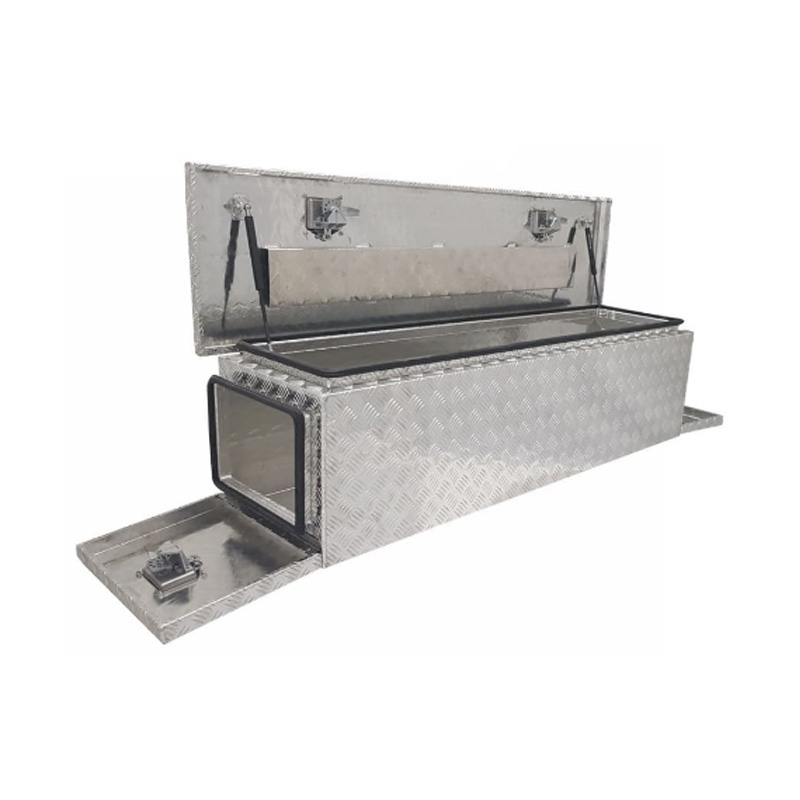 1500 x 400 x 400mm Aluminium Checker 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:...
1500 x 400 x 400mm Aluminium Checker 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:... -
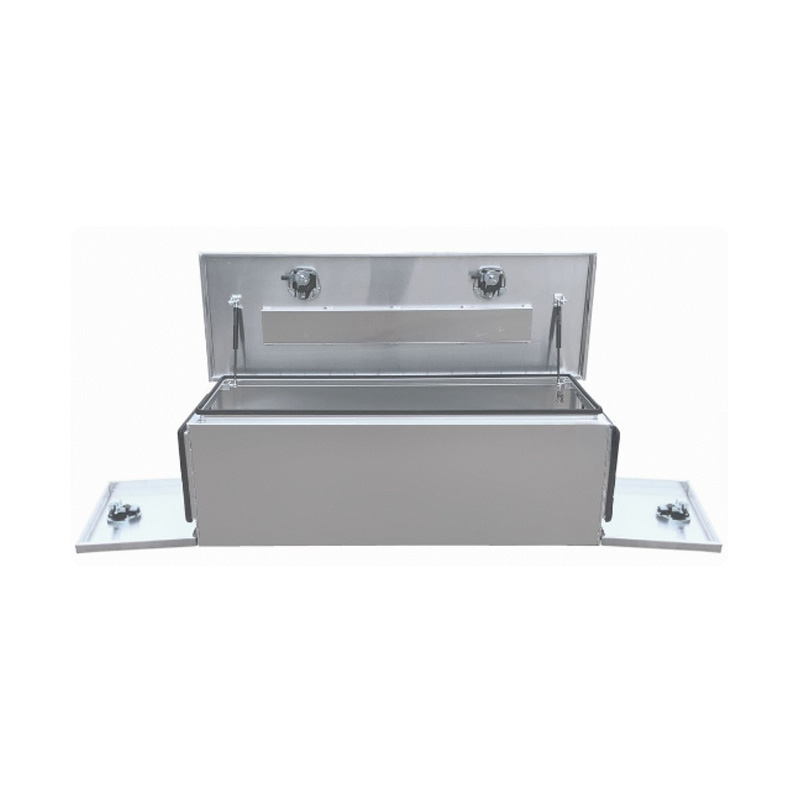 1500 x 500 x 500mm Raw Flat Aluminium 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:...
1500 x 500 x 500mm Raw Flat Aluminium 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:... -
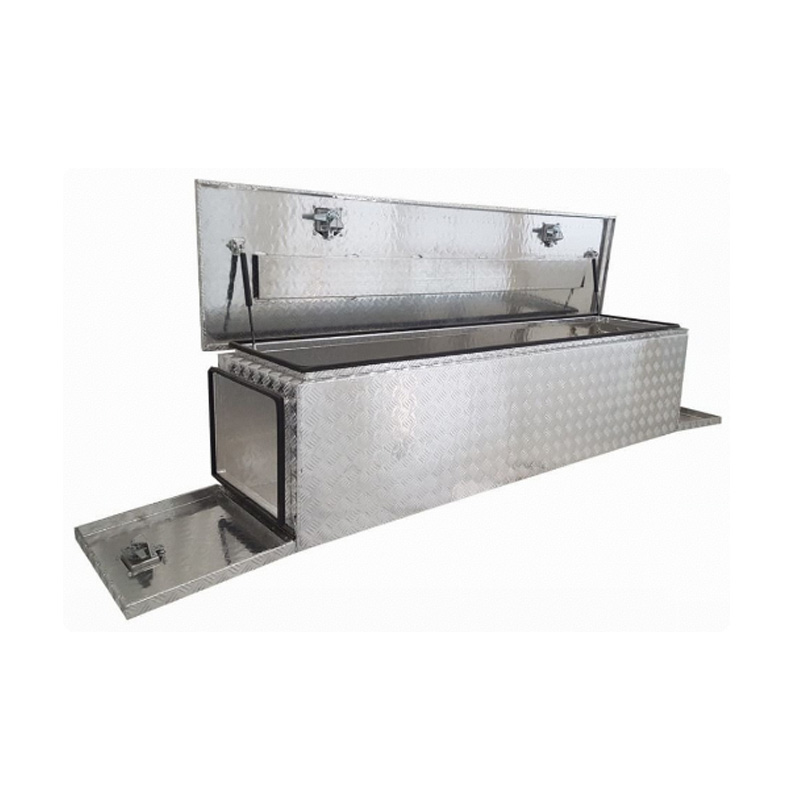 2000 x 500 x 500mm Aluminium 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:...
2000 x 500 x 500mm Aluminium 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:...
-
-
Chest Style Ute Toolbox
>
-
 1500 x 500 x 450mm Aluminium Checker Top Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:...
1500 x 500 x 450mm Aluminium Checker Top Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:... -
 1200 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Top Chest Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & Canopy(Chest Style)Thickness:...
1200 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Top Chest Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & Canopy(Chest Style)Thickness:... -
 1400 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Top Chest Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:...
1400 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Top Chest Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:...
-
- Tub Liner Ute Toolbox >
- Job Site Toolbox >
-
Camper Ute Toolbox
>
-
 1500 x 400 x 400mm Aluminium Checker 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:...
1500 x 400 x 400mm Aluminium Checker 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:... -
 1500 x 500 x 500mm Raw Flat Aluminium 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:...
1500 x 500 x 500mm Raw Flat Aluminium 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:... -
 2000 x 500 x 500mm Aluminium 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:...
2000 x 500 x 500mm Aluminium 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:... -
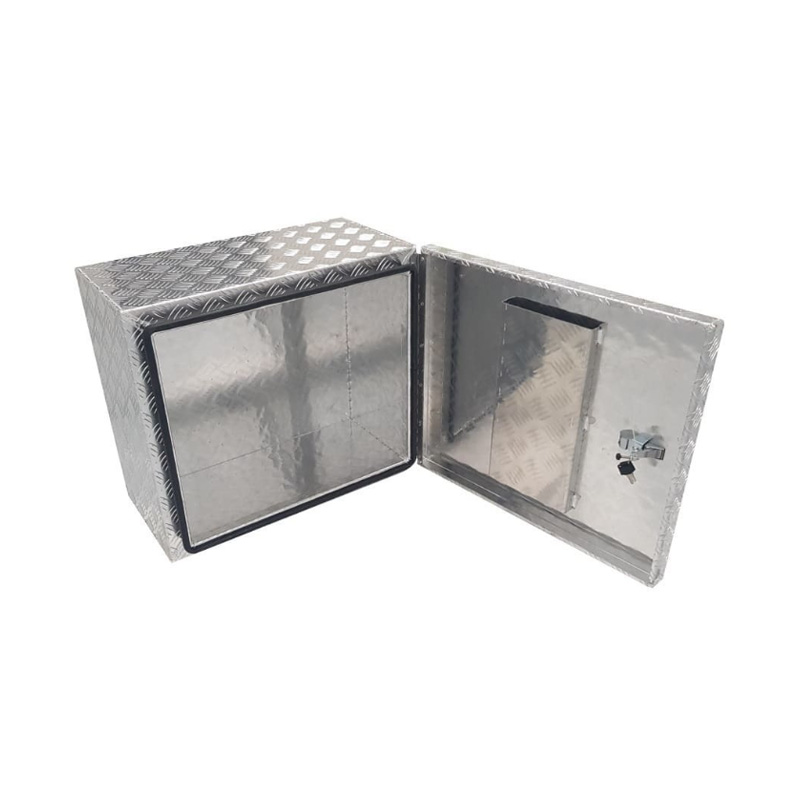 610 x 330 x 540mm Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Trailer Camper Caravan Generator Tool Box for Honda 2kvaThickness:...
610 x 330 x 540mm Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Trailer Camper Caravan Generator Tool Box for Honda 2kvaThickness:... -
 700 x 450 x 650mm Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Trailer Camper Caravan Generator Tool BoxThickness:...
700 x 450 x 650mm Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Trailer Camper Caravan Generator Tool BoxThickness:... -
 760 x 500 x 560mm Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Trailer Camper Caravan Generator Tool BoxThickness:...
760 x 500 x 560mm Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Trailer Camper Caravan Generator Tool BoxThickness:... -
 1700 x 550 x 610mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Truck Tool Box Fridge Slide & Webber BBQ Slide Camper ToolboxThickness:...
1700 x 550 x 610mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Truck Tool Box Fridge Slide & Webber BBQ Slide Camper ToolboxThickness:... -
 2200 x 550 x 550mm Aluminium 3 Lid Slides BBQ Generator Camper ToolboxThickness:...
2200 x 550 x 550mm Aluminium 3 Lid Slides BBQ Generator Camper ToolboxThickness:... -
 1400 x 550 x 800mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Webber BBQ & Fridge Slide Camper Caravan Canopy Tool BoxThickness:...
1400 x 550 x 800mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Webber BBQ & Fridge Slide Camper Caravan Canopy Tool BoxThickness:... -
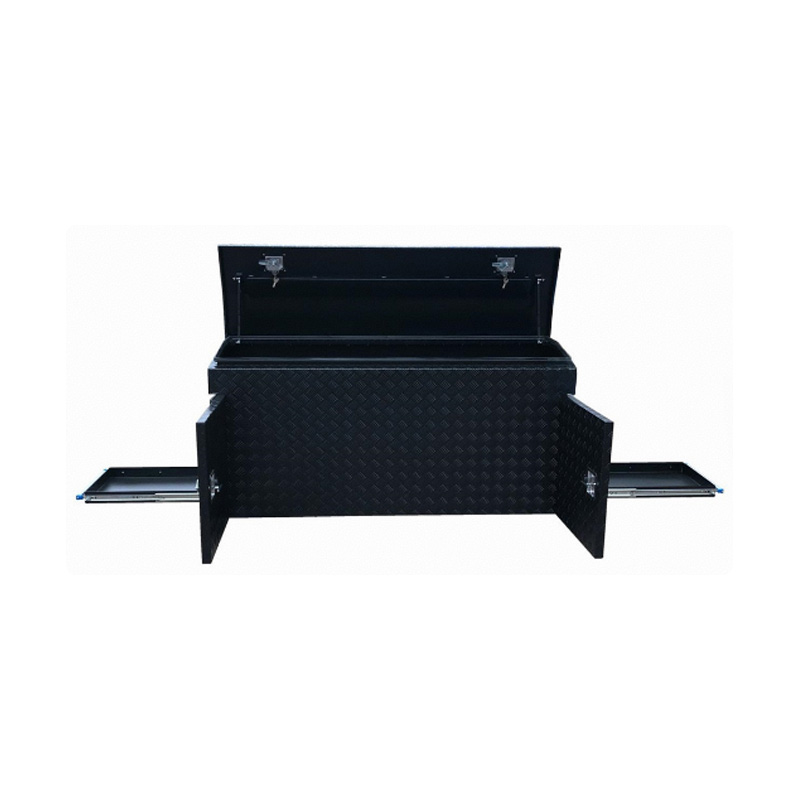 1700 x 550 x 800mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Webber BBQ & Fridge Slide Camper Caravan Canopy Tool BoxThickness:...
1700 x 550 x 800mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Webber BBQ & Fridge Slide Camper Caravan Canopy Tool BoxThickness:... -
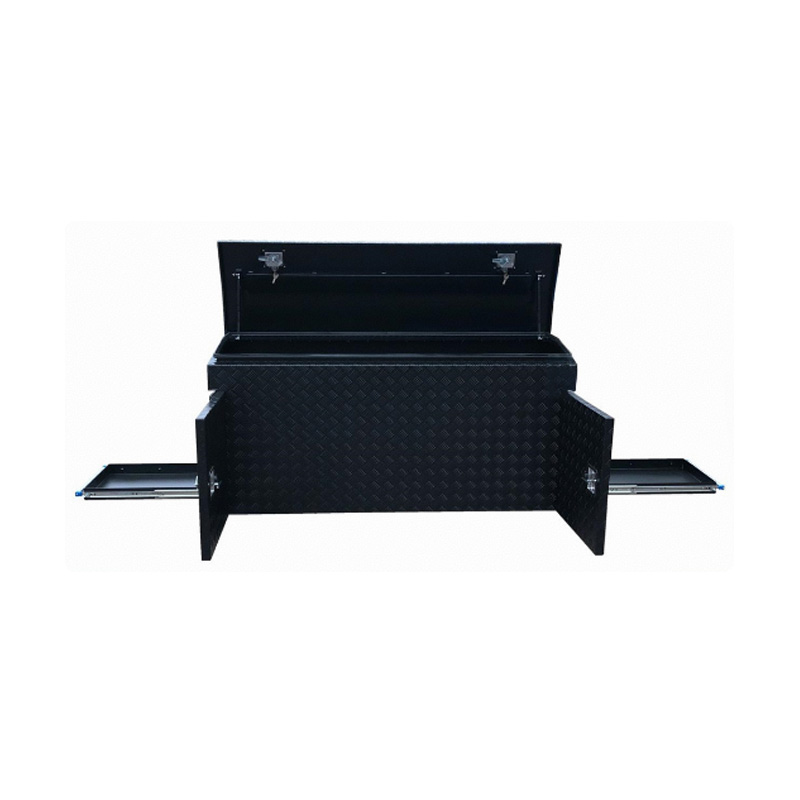 2000 x 550 x 800mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Webber BBQ & Fridge Slide Camper Caravan Canopy Tool BoxThickness:...
2000 x 550 x 800mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Webber BBQ & Fridge Slide Camper Caravan Canopy Tool BoxThickness:...
-
-
Cross Deck Gullwing
>
-
 1500 x 500 x 500mm Raw Flat Aluminium 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:...
1500 x 500 x 500mm Raw Flat Aluminium 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:... -
 2000 x 500 x 500mm Aluminium 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:...
2000 x 500 x 500mm Aluminium 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:... -
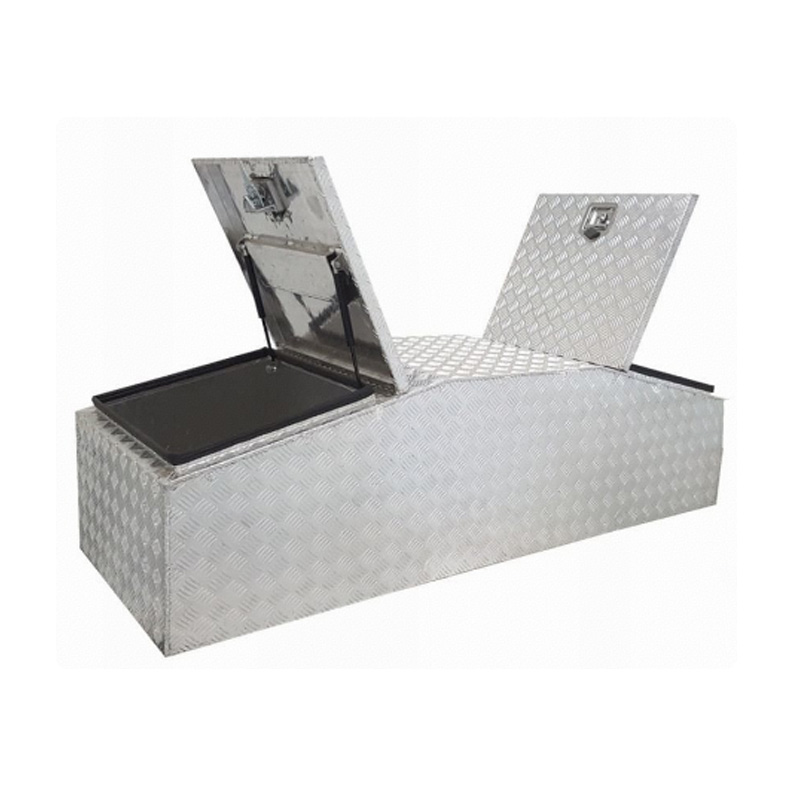 1770 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Checker Sloped Top Gullwing Cross Deck Dual 2 Lid Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:...
1770 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Checker Sloped Top Gullwing Cross Deck Dual 2 Lid Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:... -
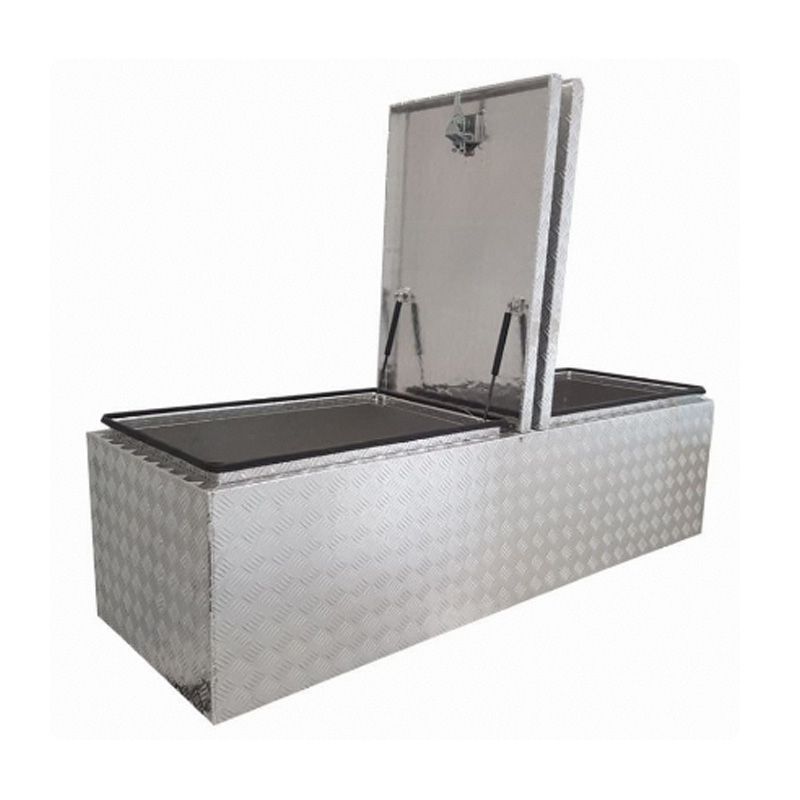 1770 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Checker Flat Top Gullwing Cross Deck Dual 2 Lid Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:...
1770 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Checker Flat Top Gullwing Cross Deck Dual 2 Lid Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:...
-
-
Rectangle Ute Toolbox
>
-
Side Opening Toolboxes
>
-
Half Lid Opening Ute Toolbox
>
-
 1200 x 600 x 700mm Aluminium Checker Tool Box Ute Truck Fridge Trailer 3/4 Angle Storage ToolboxThickness:...
1200 x 600 x 700mm Aluminium Checker Tool Box Ute Truck Fridge Trailer 3/4 Angle Storage ToolboxThickness:... -
 1400 x 600 x 700mm Aluminium Checker Tool Box Ute Truck Fridge Trailer 3/4 Angle Storage ToolboxThickness:...
1400 x 600 x 700mm Aluminium Checker Tool Box Ute Truck Fridge Trailer 3/4 Angle Storage ToolboxThickness:... -
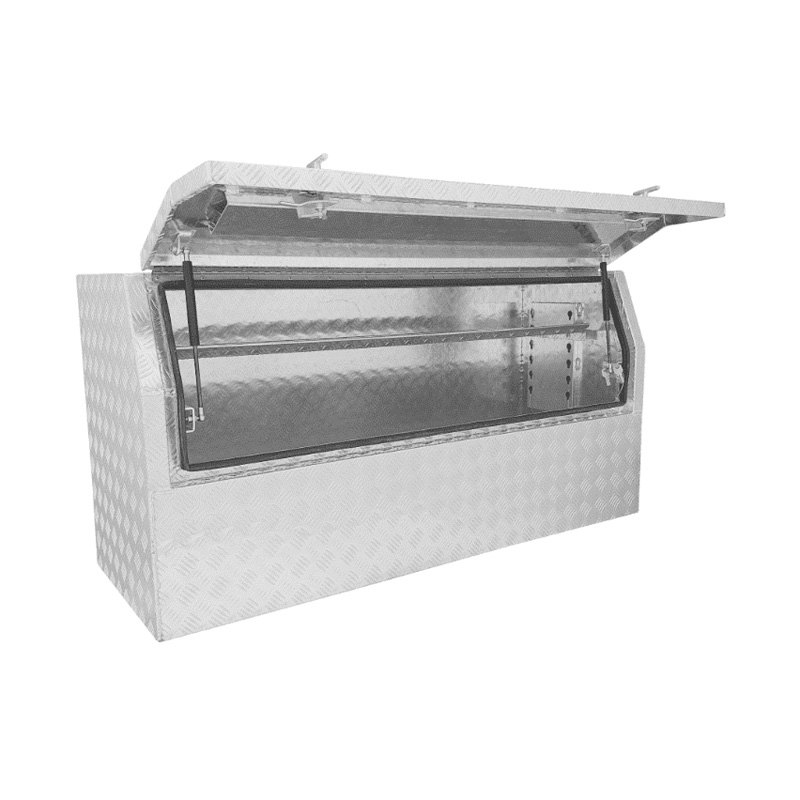 1400 x 500 x 700mm Aluminium Checker 3/4 Half Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingxThickness:...
1400 x 500 x 700mm Aluminium Checker 3/4 Half Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingxThickness:... -
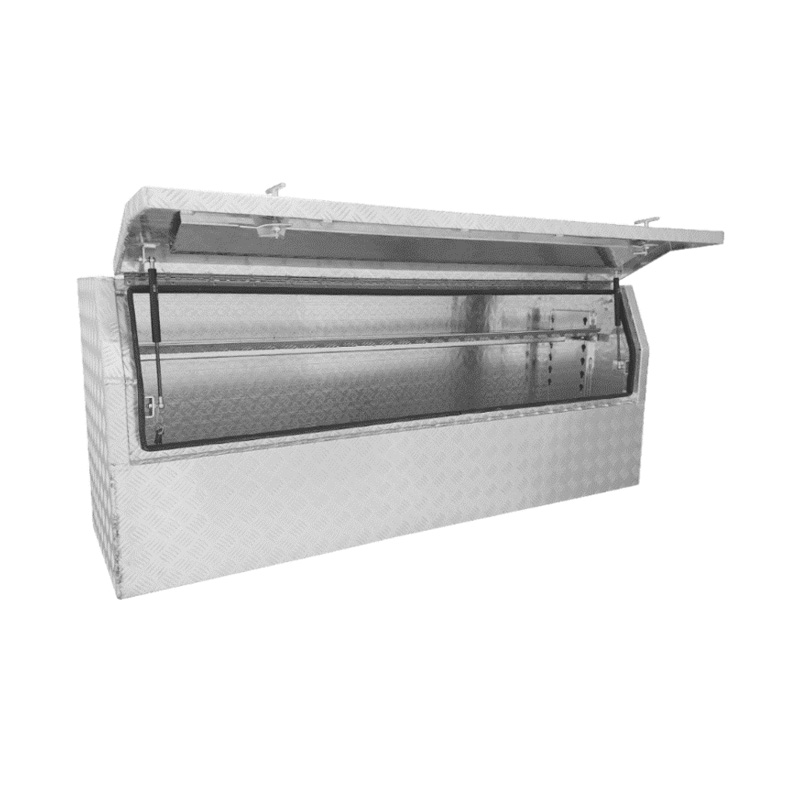 1700 x 500 x 700mm Aluminium Checker 3/4 Half Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1700 x 500 x 700mm Aluminium Checker 3/4 Half Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
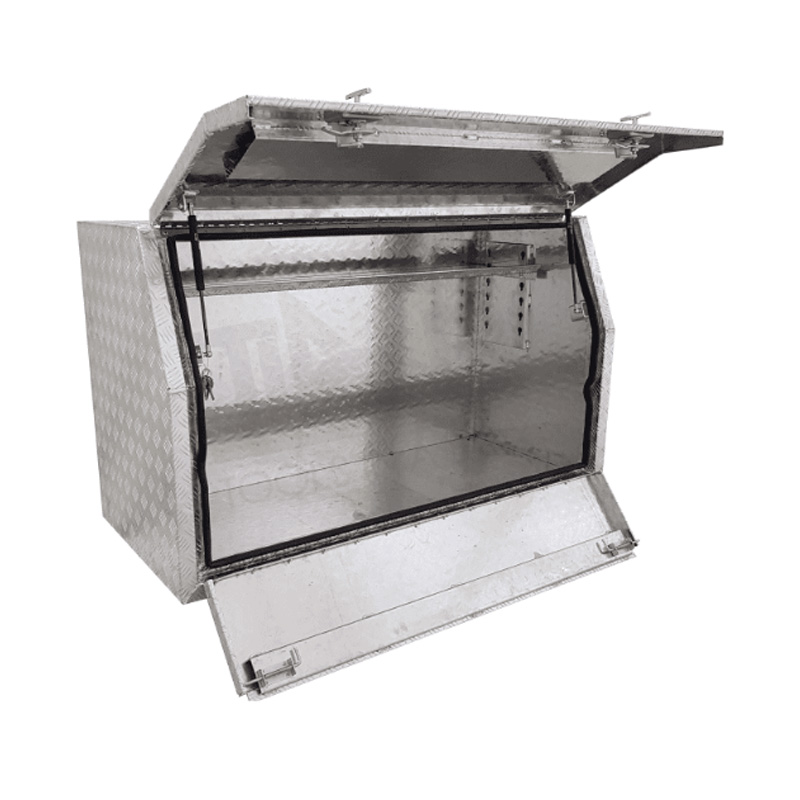 1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full or Half Side Multi Lid Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full or Half Side Multi Lid Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
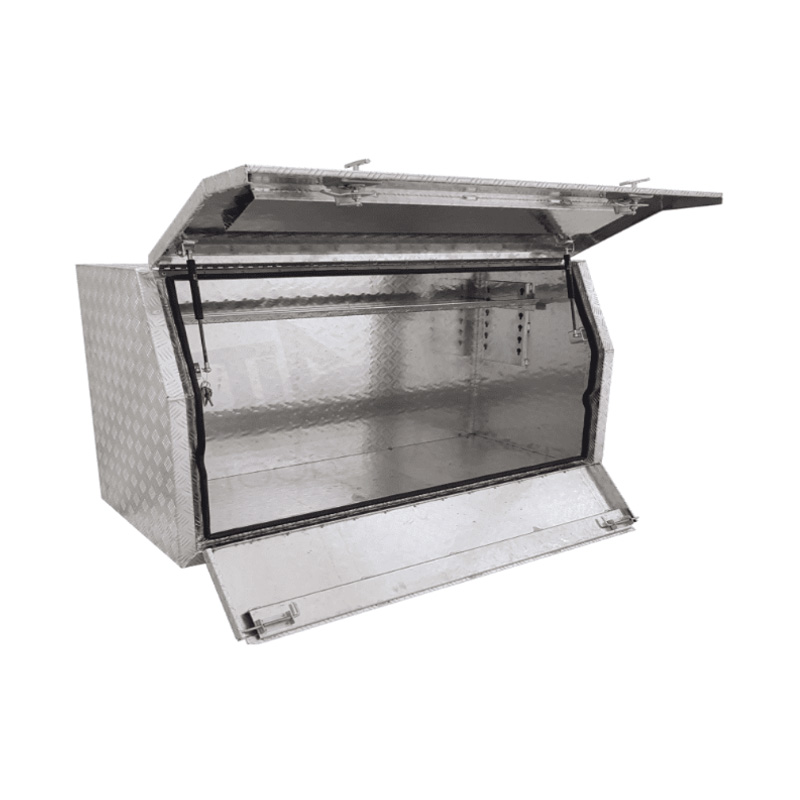 1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full or Half Side Multi Lid Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full or Half Side Multi Lid Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
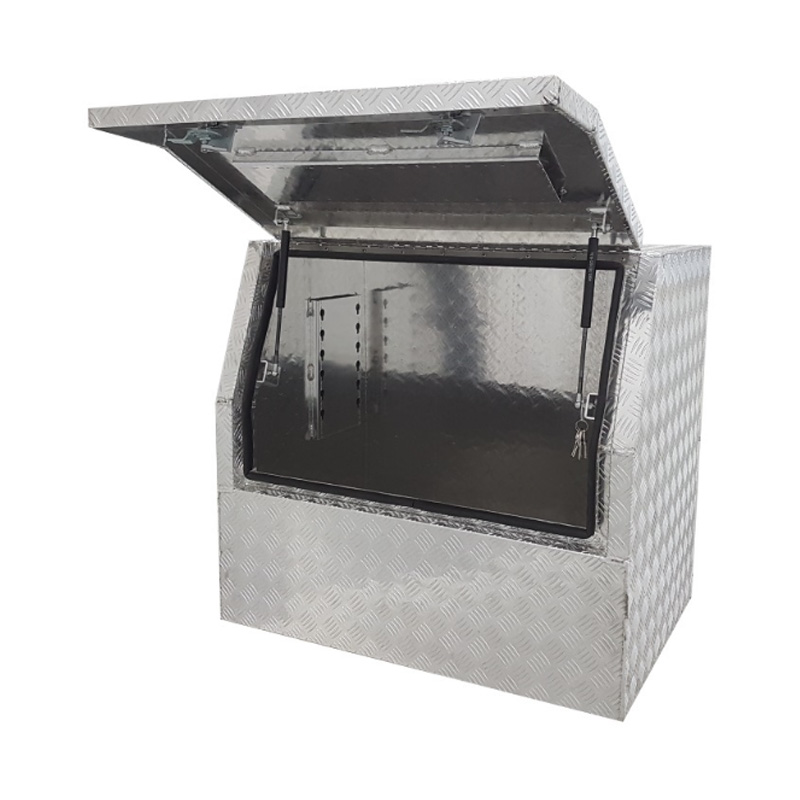 900 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker 3/4 Half Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
900 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker 3/4 Half Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
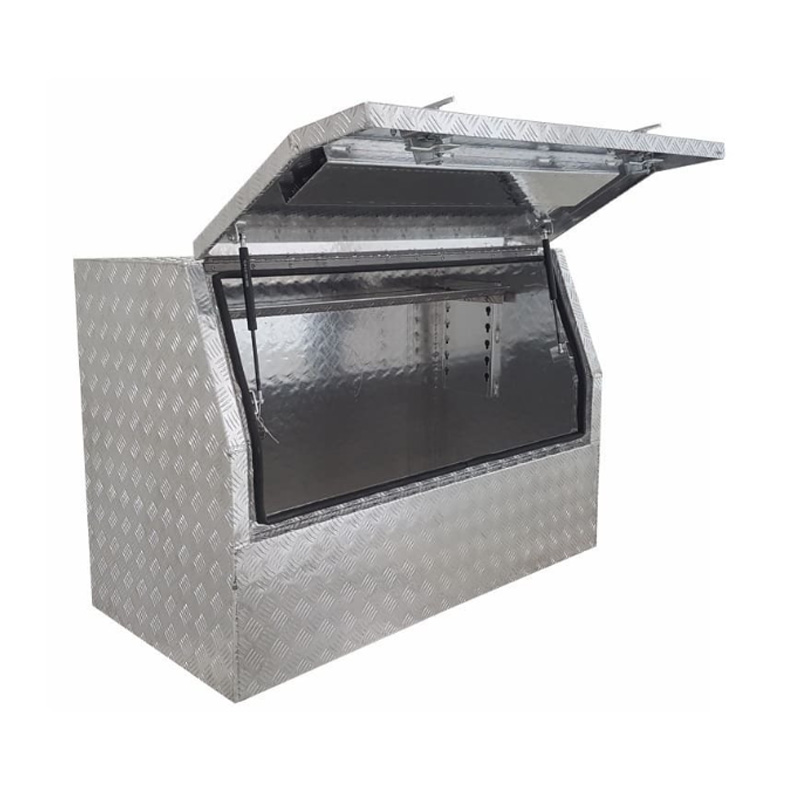 1200 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker 3/4 Half Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1200 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker 3/4 Half Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
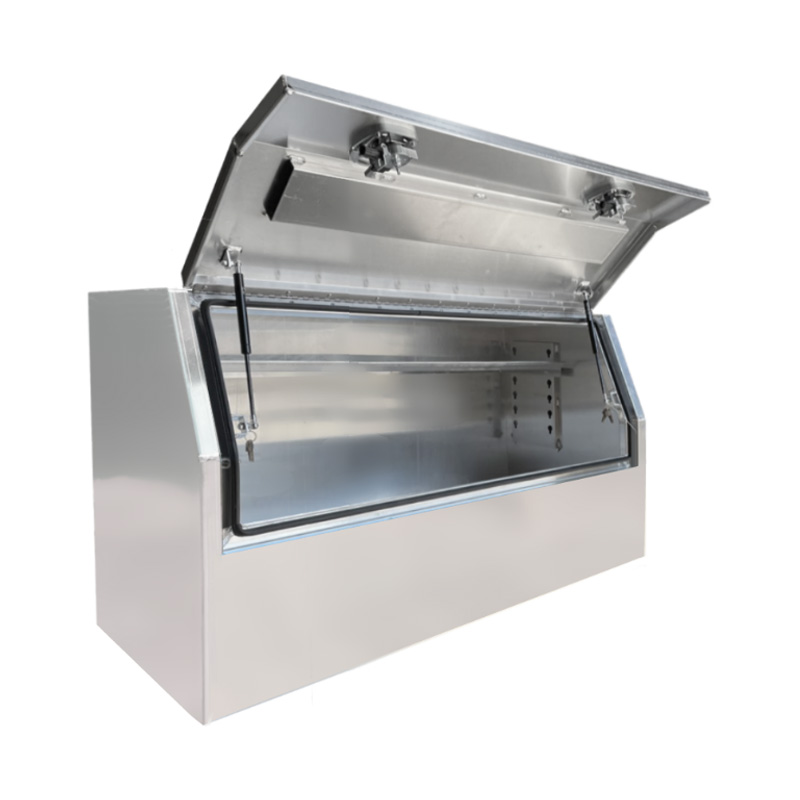 1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium 3/4 Half Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium 3/4 Half Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
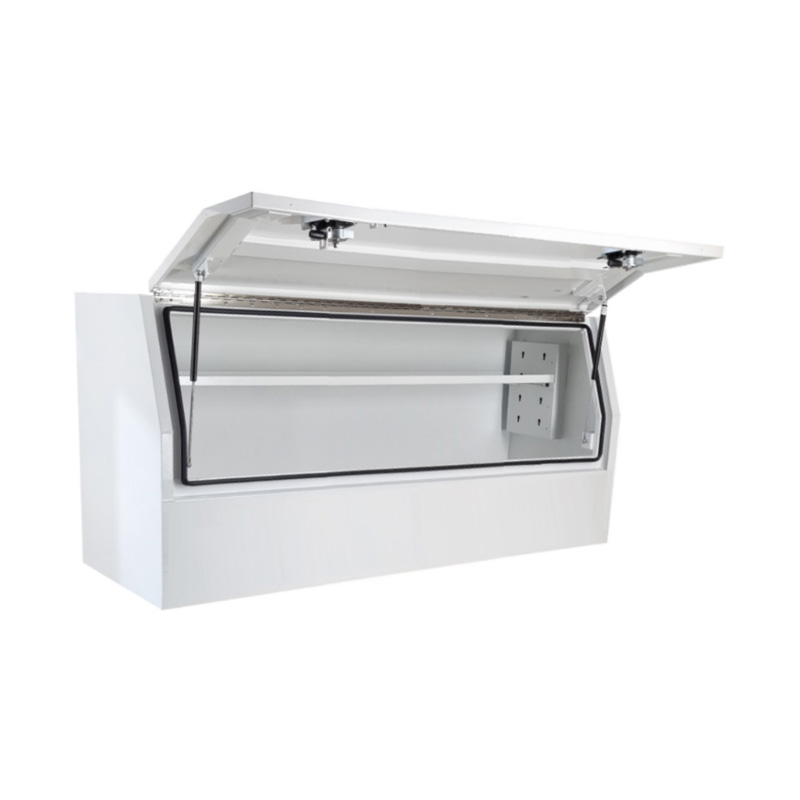 1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium 3/4 Half Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium 3/4 Half Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
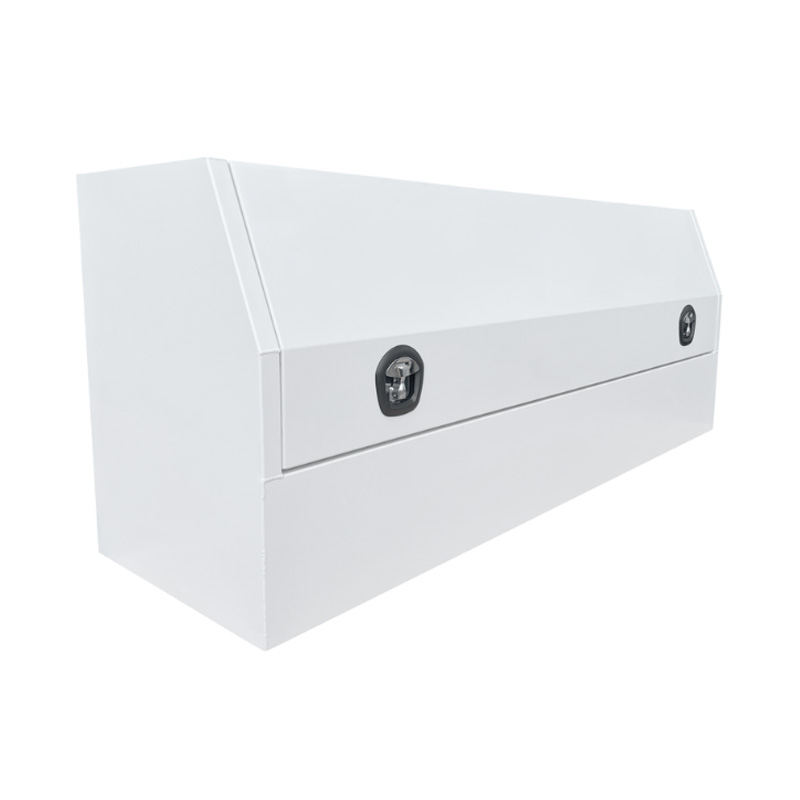 2100 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium 3/4 Half Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
2100 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium 3/4 Half Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
-
-
Half Lid Ute Toolbox With Drawers
>
-
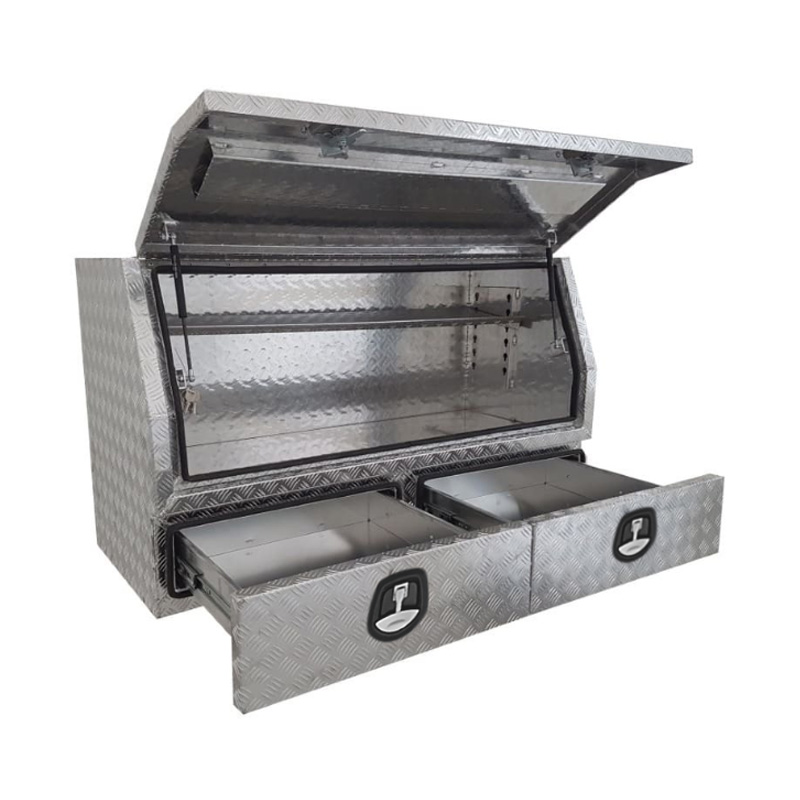 1500 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker 3/4 Half Side Opening 2 Drawer Slide Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1500 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker 3/4 Half Side Opening 2 Drawer Slide Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
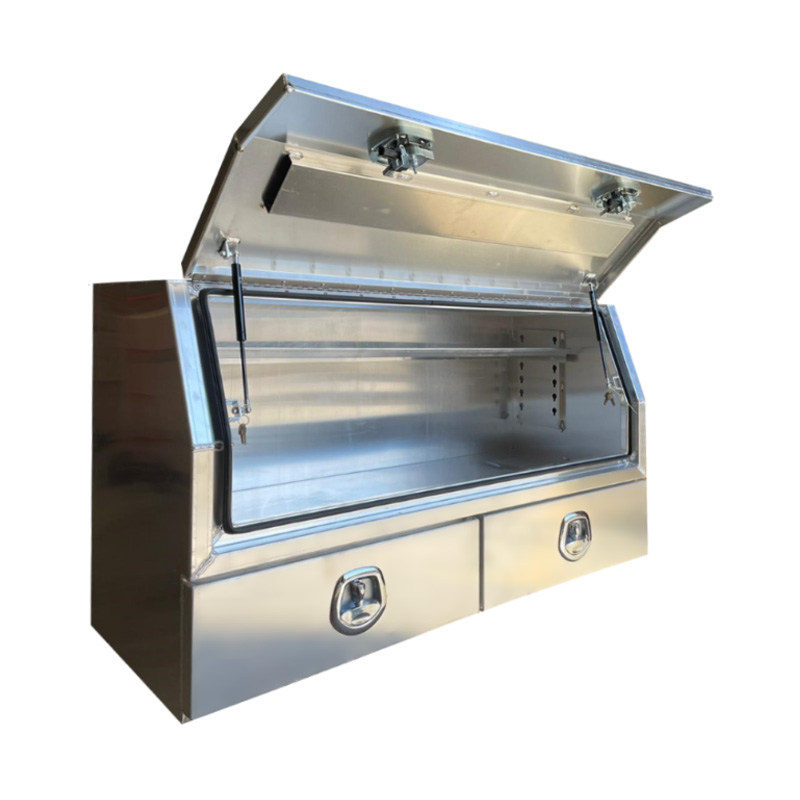 1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium 3/4 Half Side Opening 2 Drawer Slide Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium 3/4 Half Side Opening 2 Drawer Slide Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
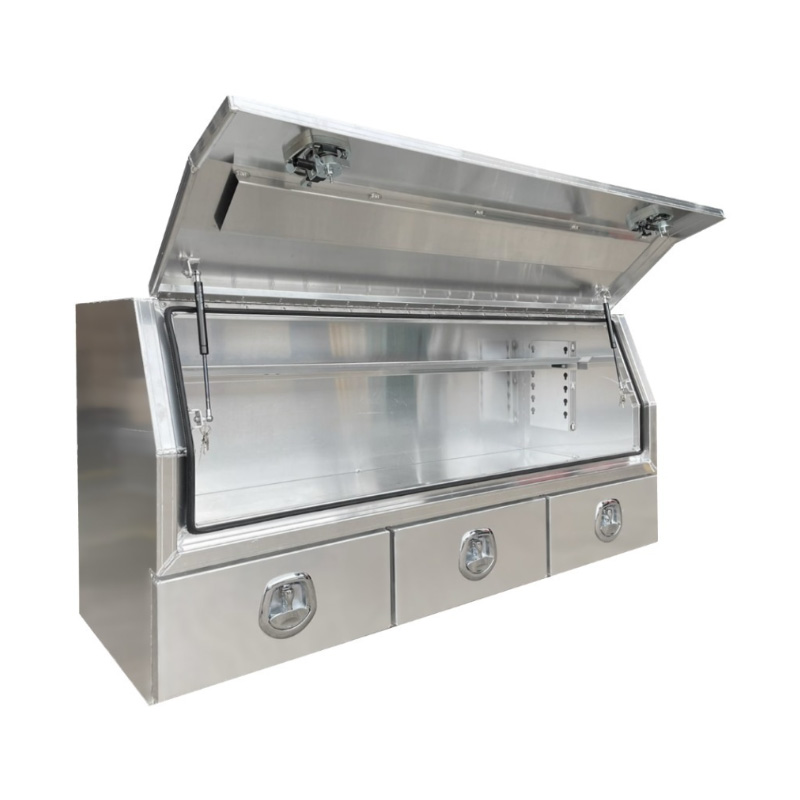 1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium 3/4 Half Side Opening 3 Drawer Slide Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium 3/4 Half Side Opening 3 Drawer Slide Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
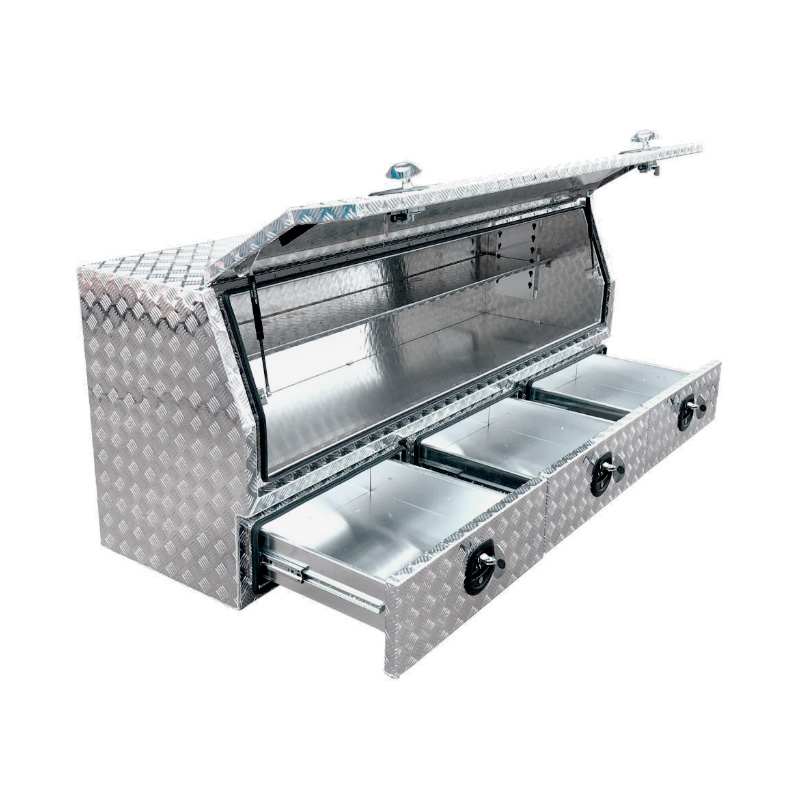 2100 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium 3/4 Half Side Opening 3 Drawer Slide Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
2100 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium 3/4 Half Side Opening 3 Drawer Slide Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
-
-
Full Lid Opening Ute Toolbox
>
-
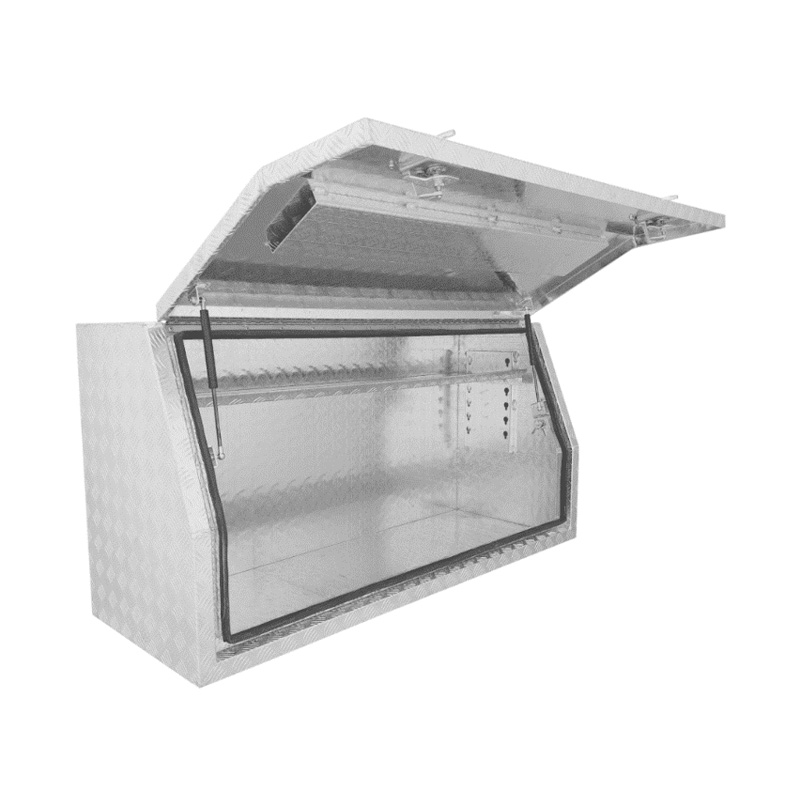 1400 x 500 x 700mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1400 x 500 x 700mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
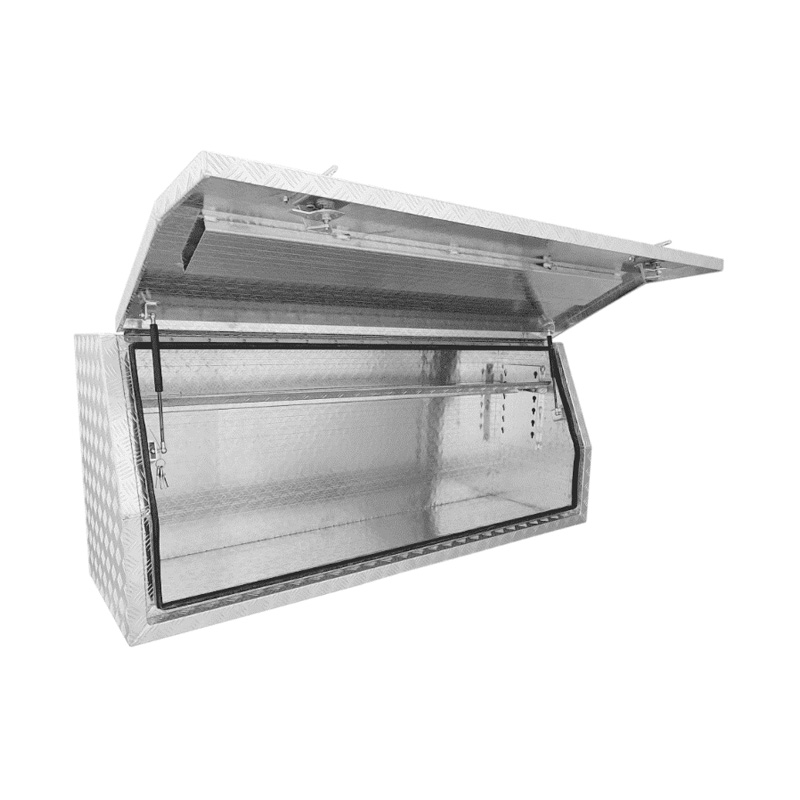 1700 x 500 x 700mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1700 x 500 x 700mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
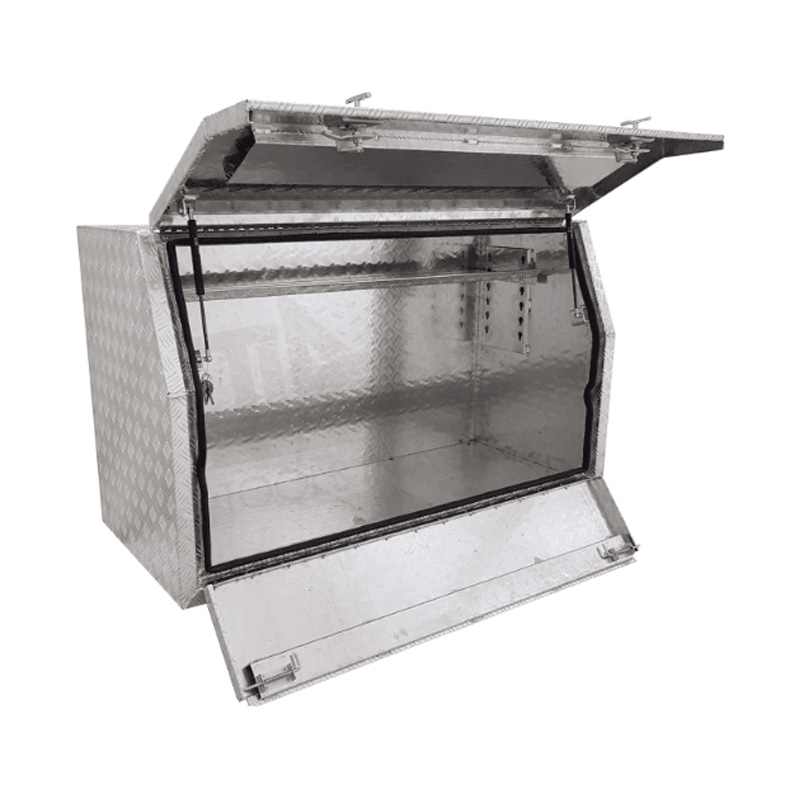 1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full or Half Side Multi Lid Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full or Half Side Multi Lid Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
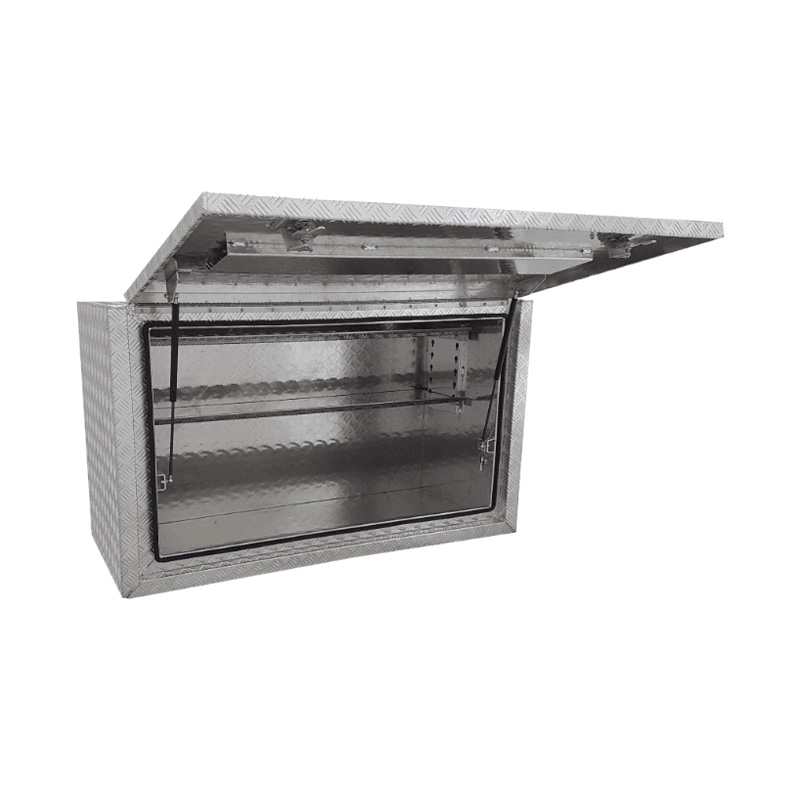 1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Square Edge Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Square Edge Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
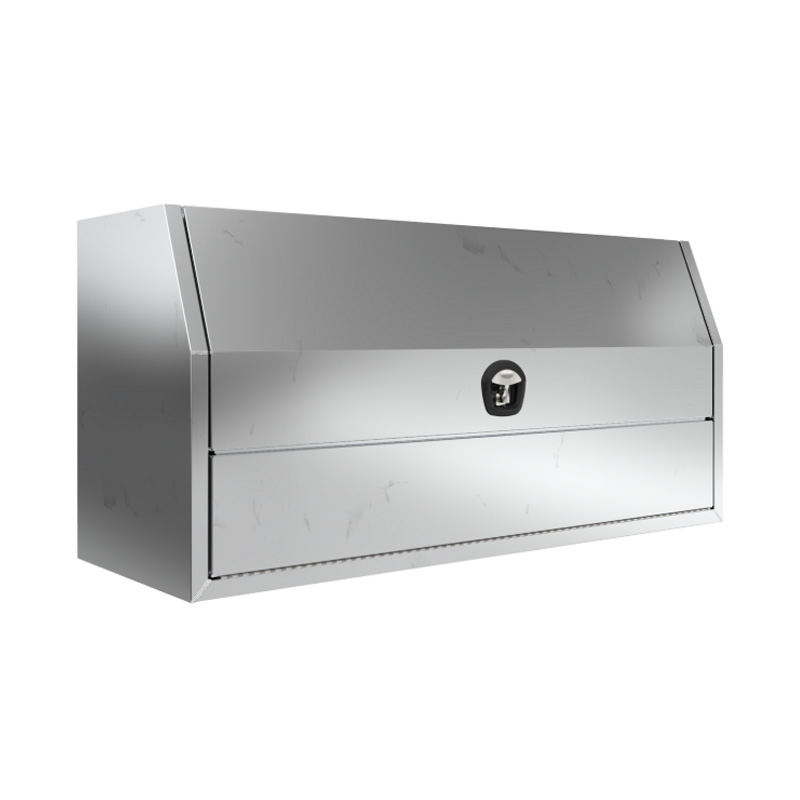 1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full or Half Side Multi Lid Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full or Half Side Multi Lid Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
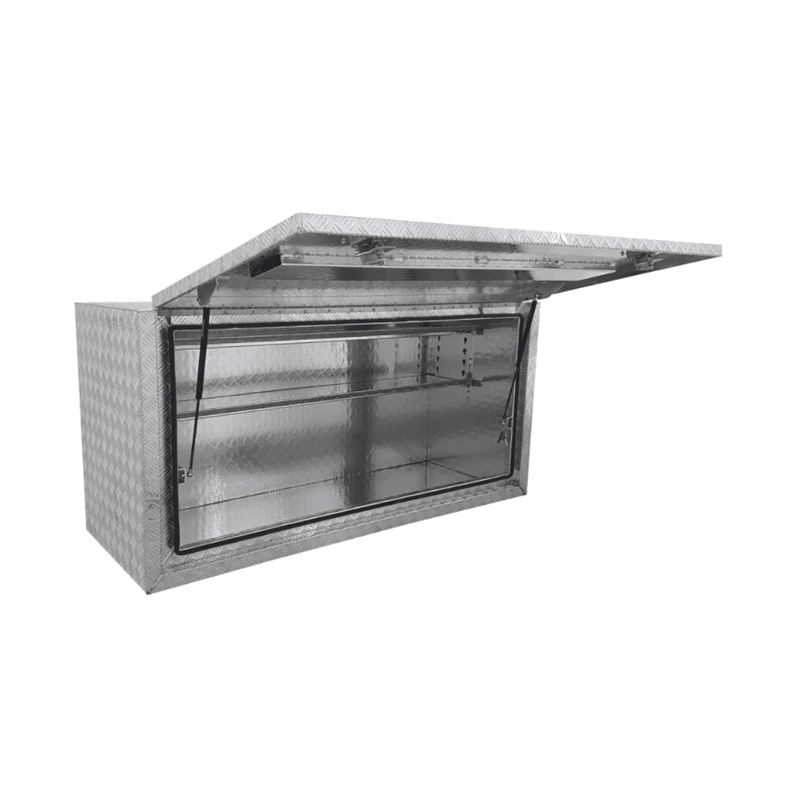 1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Square Edge Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Square Edge Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
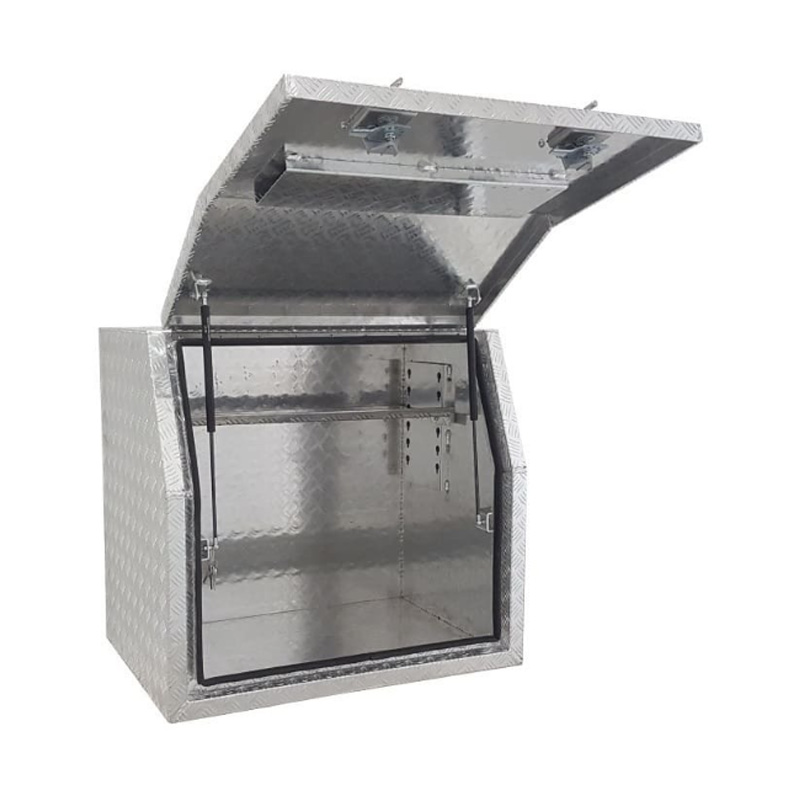 900 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
900 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
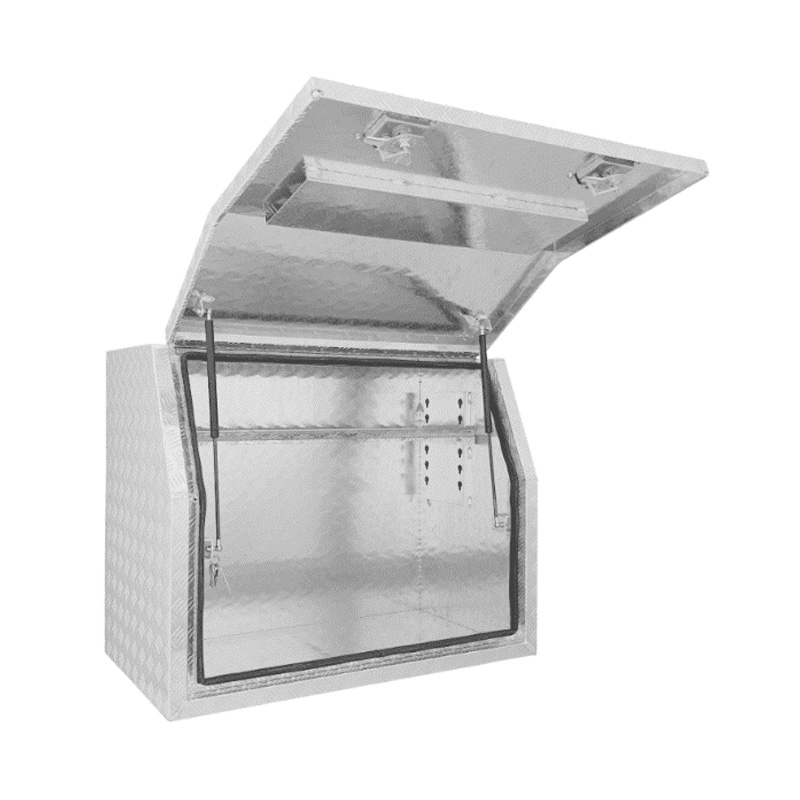 1000 x 530 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Side Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:...
1000 x 530 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Side Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:... -
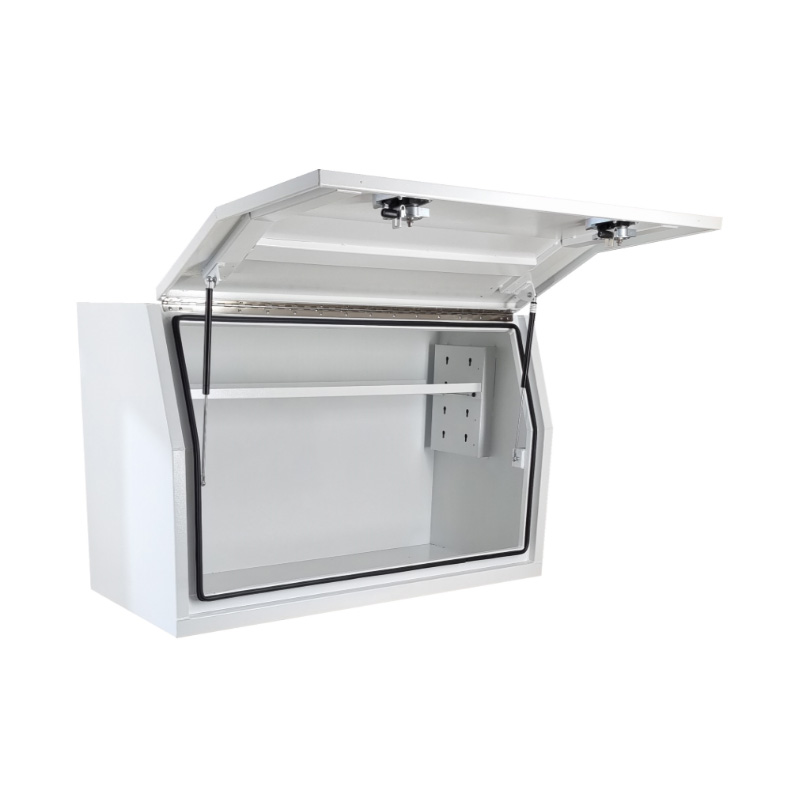 1200 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1200 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
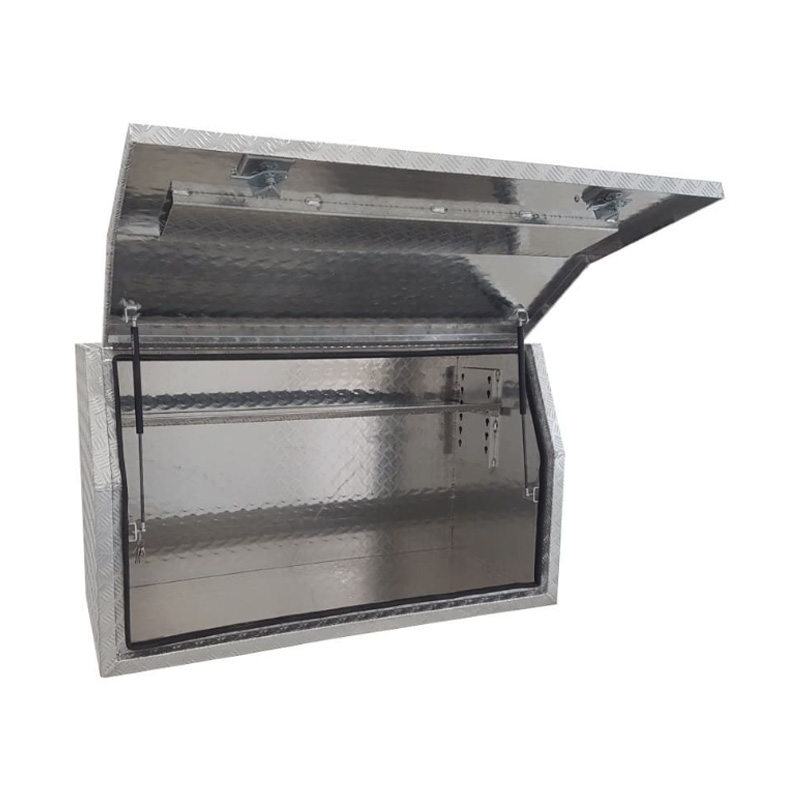 1400 x 530 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1400 x 530 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
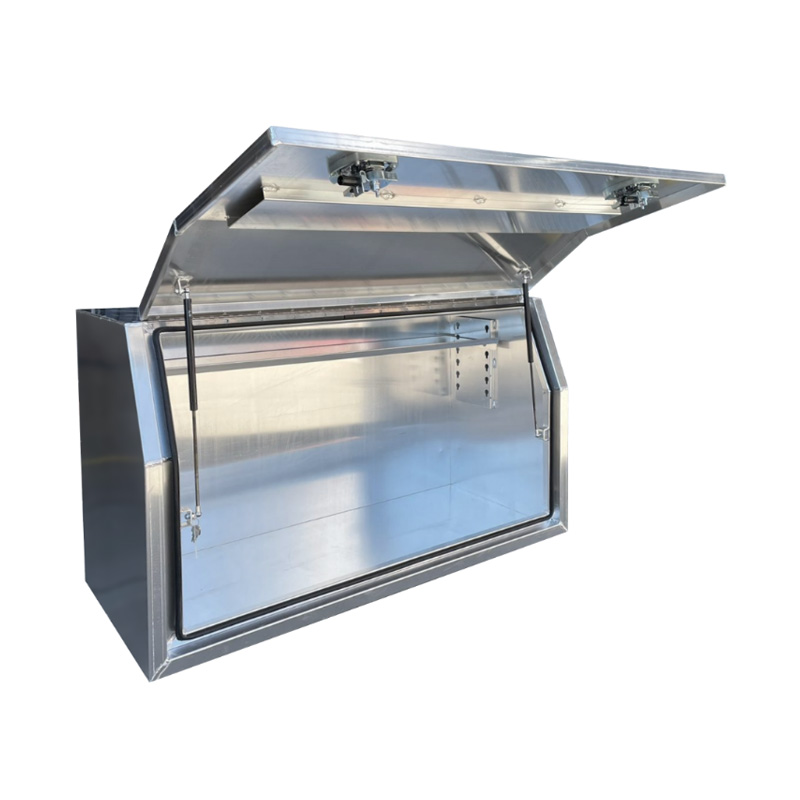 1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
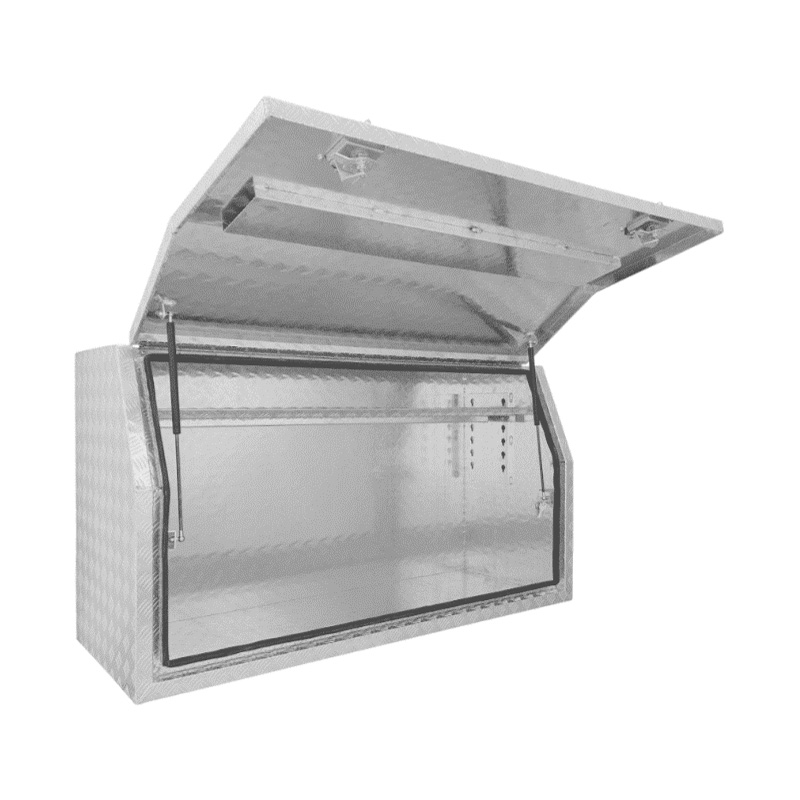 1500 x 530 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1500 x 530 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
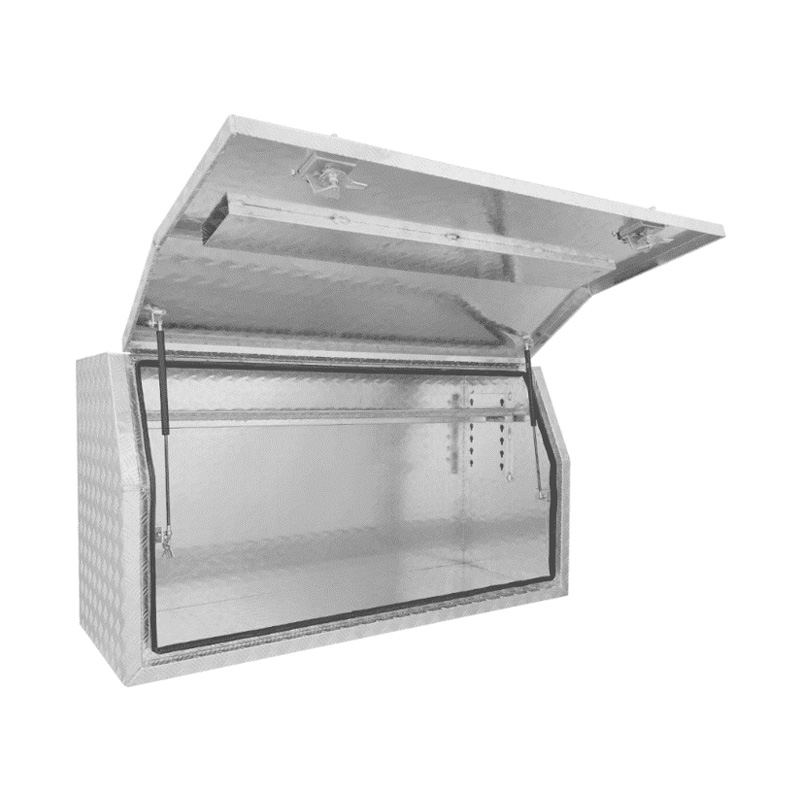 1600 x 530 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1600 x 530 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
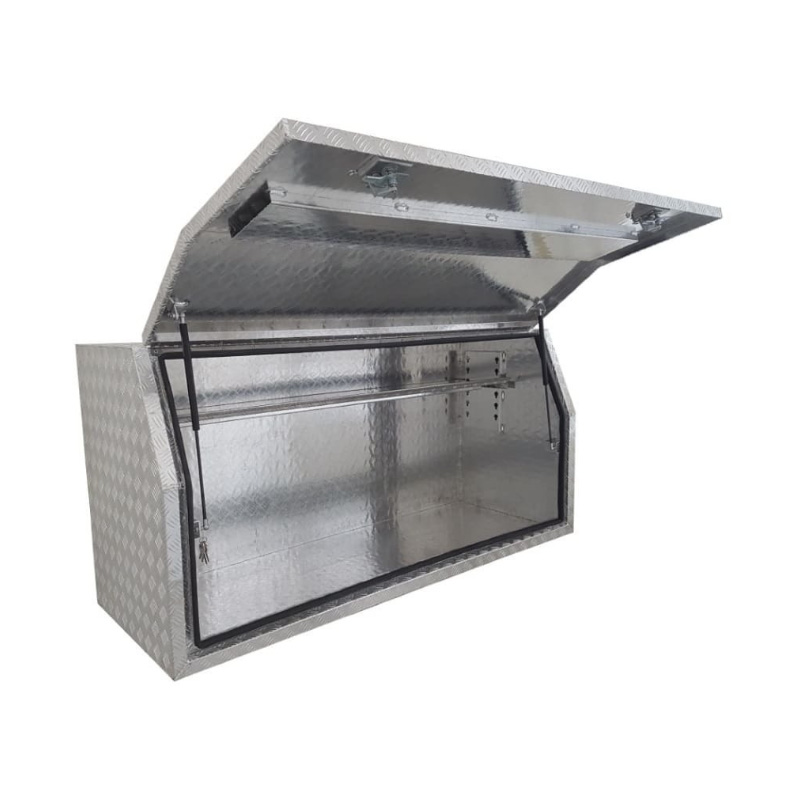 1600 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1600 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
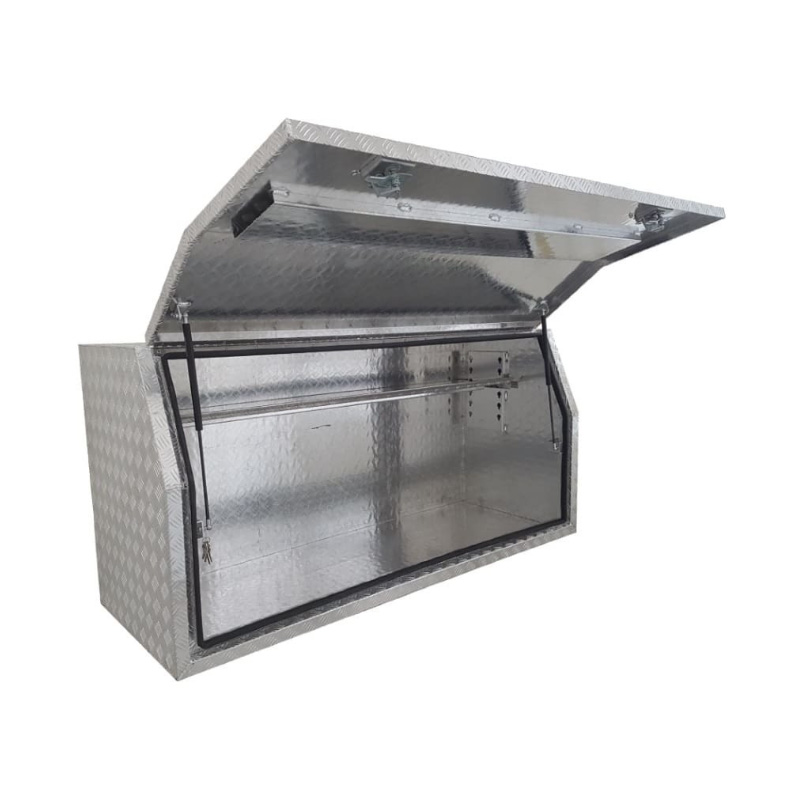 1700 x 530 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1700 x 530 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
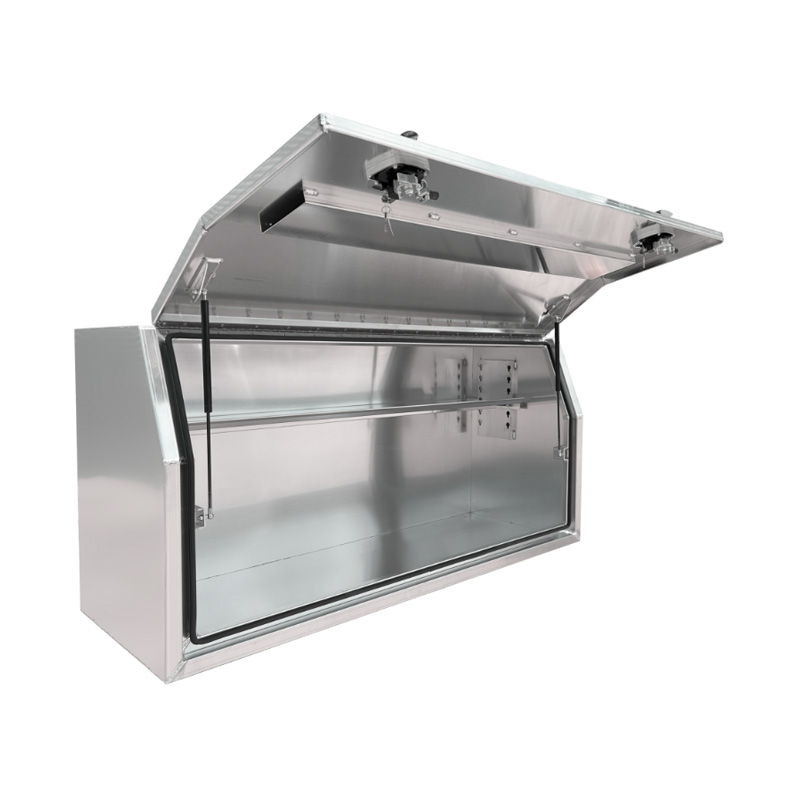 1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
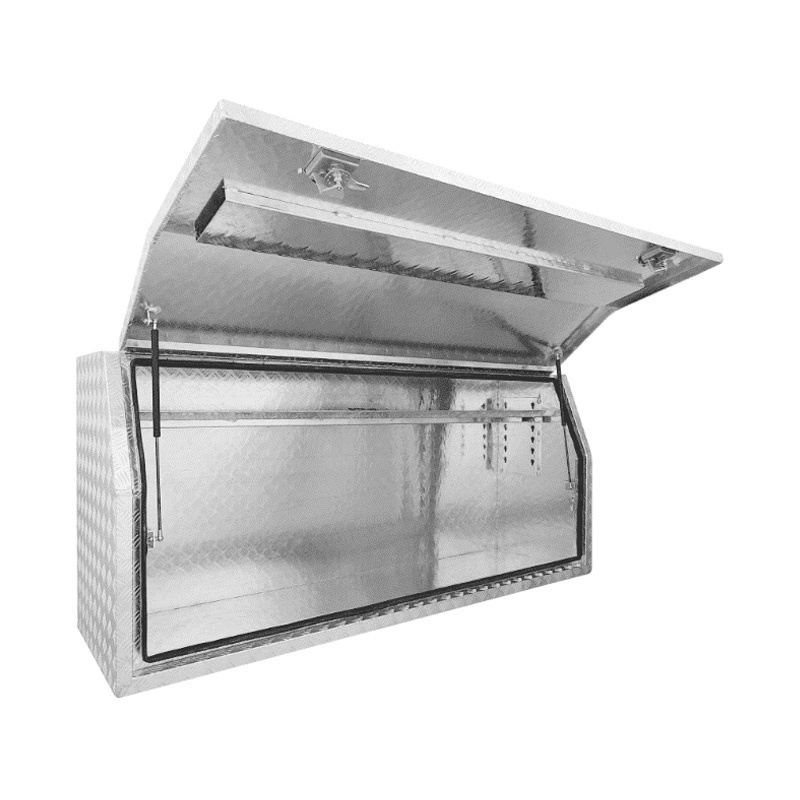 1800 x 530 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1800 x 530 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
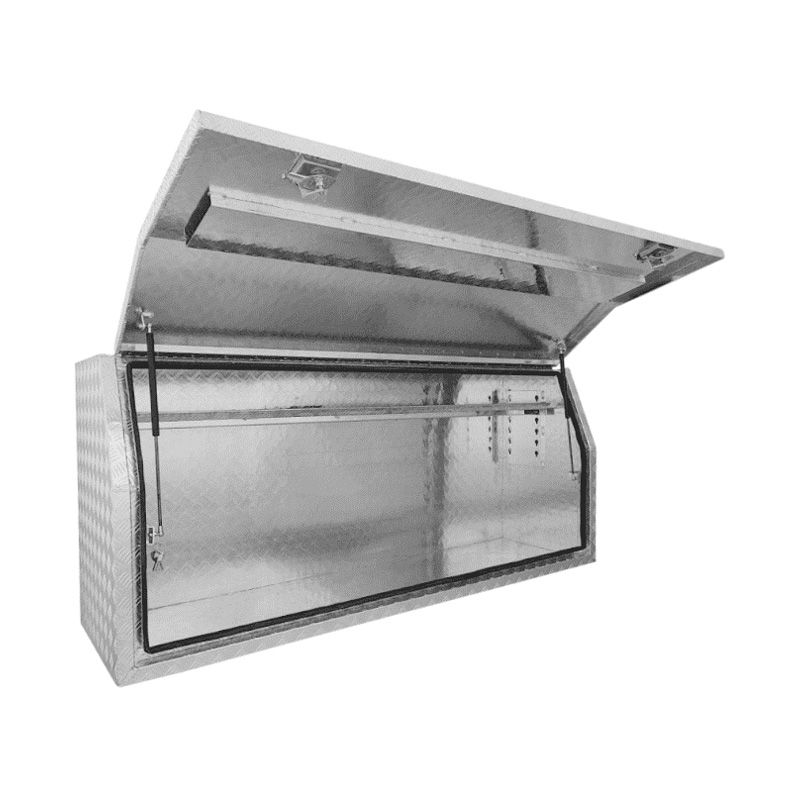 1900 x 530 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1900 x 530 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
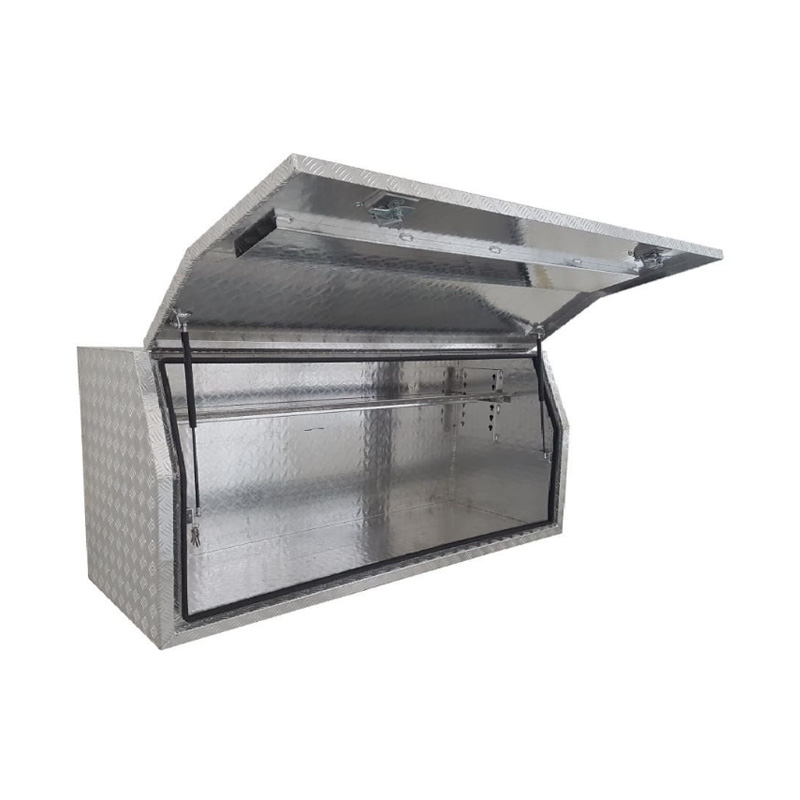 2100 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
2100 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
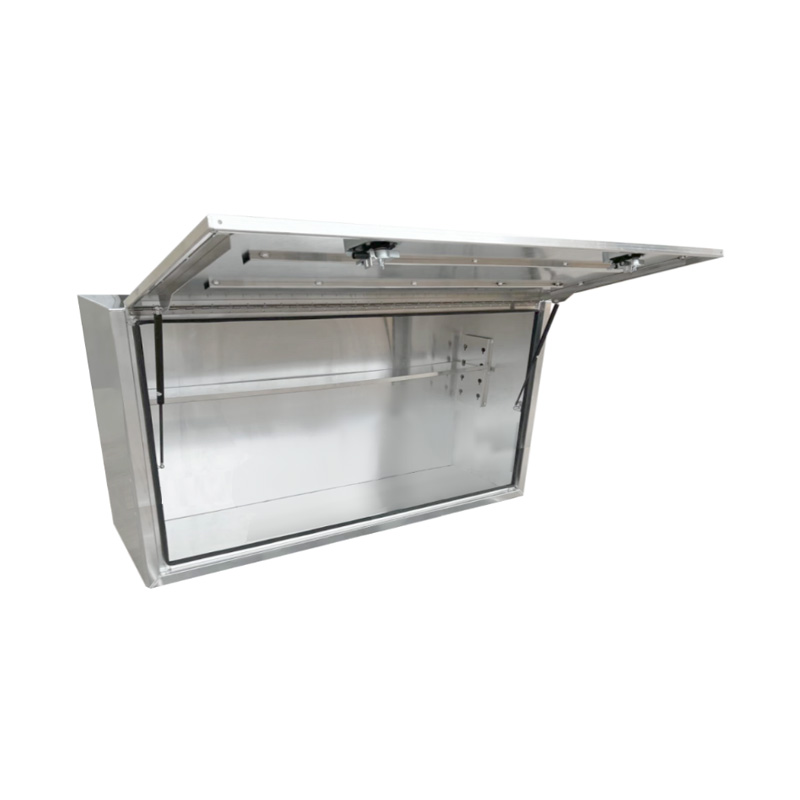 1900 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening Truck Tool Box HIGH Side Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1900 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening Truck Tool Box HIGH Side Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
-
-
Full Lid Ute Toolbox With Drawers
>
-
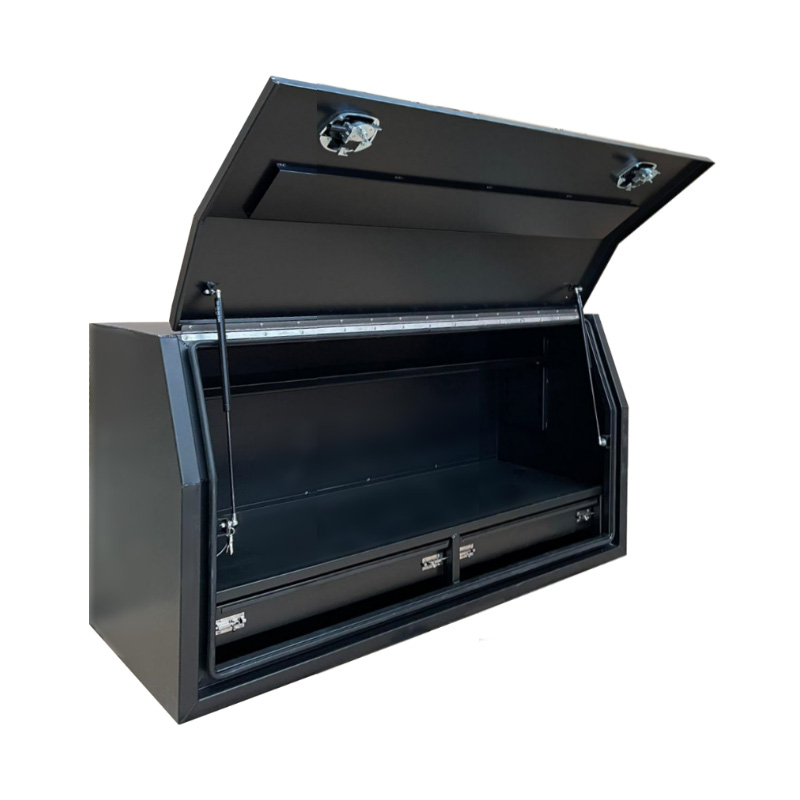 1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening 2 Drawer Slide Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening 2 Drawer Slide Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
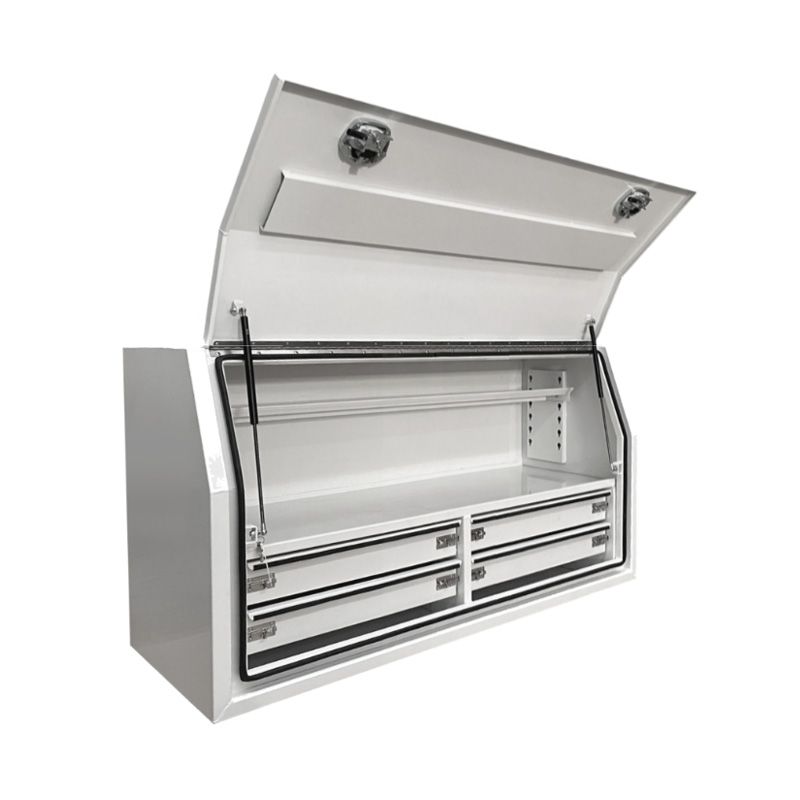 1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening 4 Drawer Slide Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening 4 Drawer Slide Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
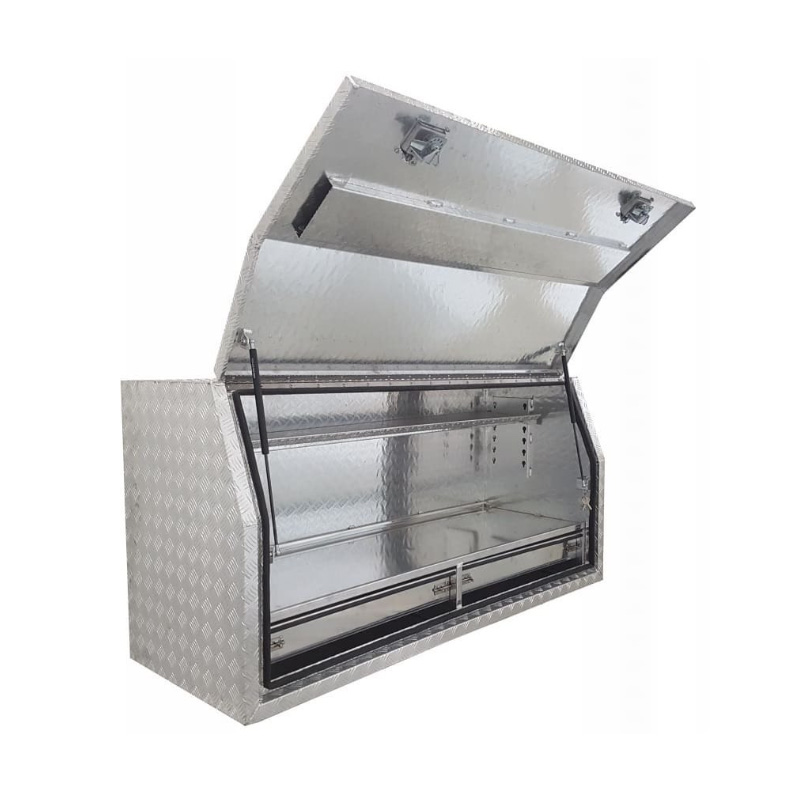 1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening 2 Drawer Slide Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening 2 Drawer Slide Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
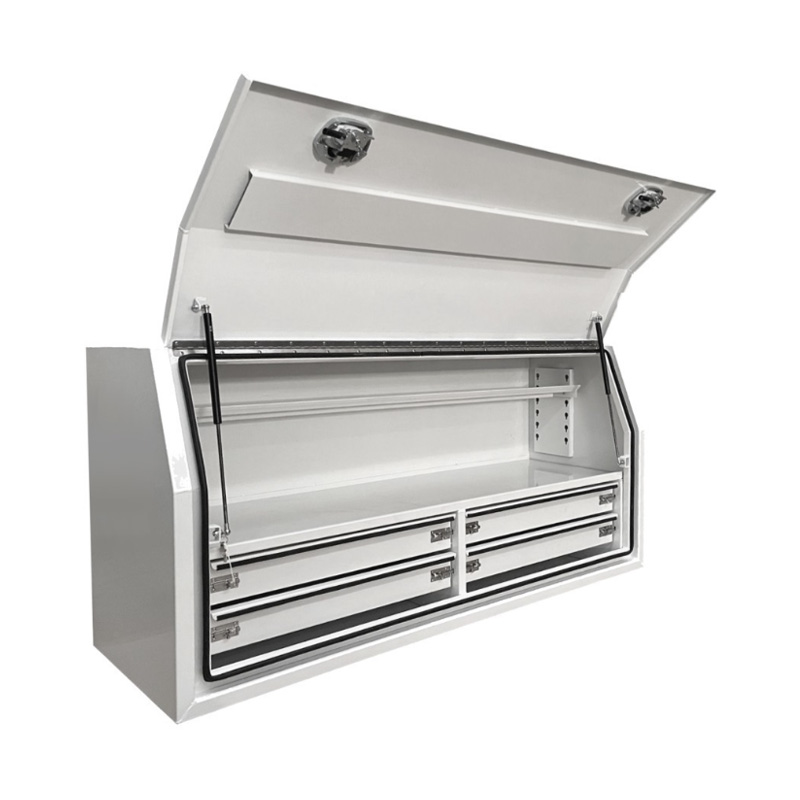 1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening 4 Drawer Slide Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening 4 Drawer Slide Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
-
-
Multi-Lid Ute Toolbox
>
-
 1770 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Checker Sloped Top Gullwing Cross Deck Dual 2 Lid Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:...
1770 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Checker Sloped Top Gullwing Cross Deck Dual 2 Lid Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:... -
 1770 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Checker Flat Top Gullwing Cross Deck Dual 2 Lid Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:...
1770 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Checker Flat Top Gullwing Cross Deck Dual 2 Lid Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:... -
 1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full or Half Side Multi Lid Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full or Half Side Multi Lid Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
 1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full or Half Side Multi Lid Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full or Half Side Multi Lid Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
 1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full or Half Side Multi Lid Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full or Half Side Multi Lid Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
 1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full or Half Side Multi Lid Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full or Half Side Multi Lid Opening Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
-
-
Half Lid Opening Ute Toolbox
>
-
Truck Toolboxes
>
-
Under Truck Tool Boxes
>
-
 600 x 450 x 450mm Aluminium Checker Under Tray Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:...
600 x 450 x 450mm Aluminium Checker Under Tray Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:... -
 600 x 450 x 450mm Flat Aluminium Under Tray Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:...
600 x 450 x 450mm Flat Aluminium Under Tray Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:... -
 900 x 450 x 450mm Flat Aluminium Under Tray Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:...
900 x 450 x 450mm Flat Aluminium Under Tray Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:... -
 1000 x 450 x 450mm Flat Aluminium Under Tray Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:...
1000 x 450 x 450mm Flat Aluminium Under Tray Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:... -
 1200 x 450 x 450mm Flat Aluminium Under Tray Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:...
1200 x 450 x 450mm Flat Aluminium Under Tray Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:... -
 600 x 500 x 500mm Black Aluminium Under Tray Slide Drawer Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:...
600 x 500 x 500mm Black Aluminium Under Tray Slide Drawer Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:... -
 900 x 500 x 500mm Raw Flat Aluminium Under Tray Slide Drawer Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:...
900 x 500 x 500mm Raw Flat Aluminium Under Tray Slide Drawer Body Tool box Truck Storage ToolboxThickness:...
-
- Half Lid Truck Toolbox With Drawers >
-
Full Lid Opening Truck Toolbox
>
-
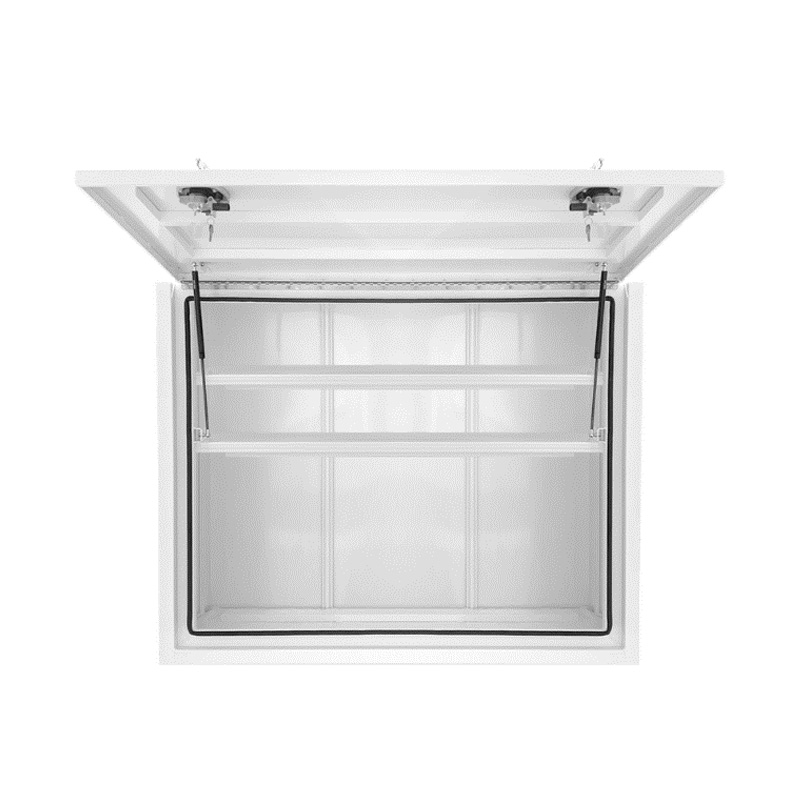 1400 x 600 x 1200mm Aluminium Full Side Opening Truck Tool Box HIGH Side Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1400 x 600 x 1200mm Aluminium Full Side Opening Truck Tool Box HIGH Side Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
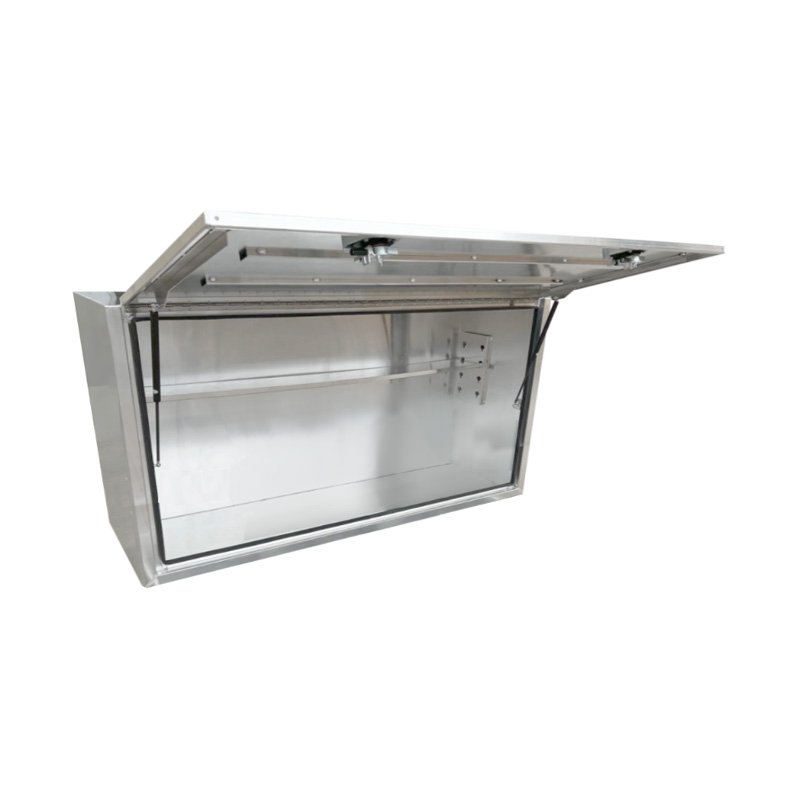 1900 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening Truck Tool Box HIGH Side Trailer Toolbox Shelving 1968SFD-CPThickness:...
1900 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Full Side Opening Truck Tool Box HIGH Side Trailer Toolbox Shelving 1968SFD-CPThickness:... -
 1900 x 600 x 1200mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Truck Tool Box HIGH Side Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1900 x 600 x 1200mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Truck Tool Box HIGH Side Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
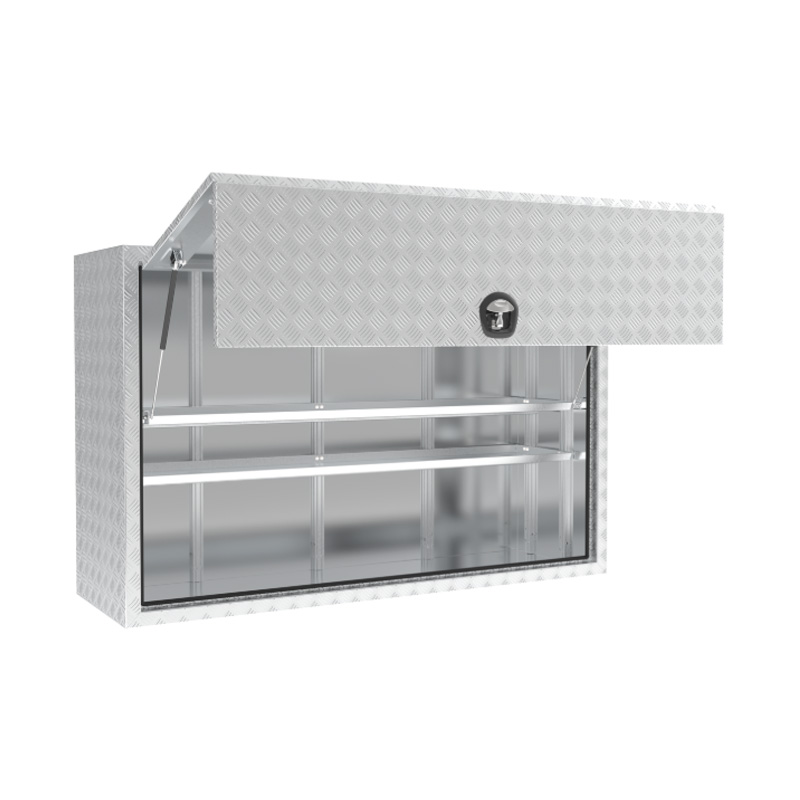 1900 x 600 x 1200mm Checker PRO Full Side Truck Tool Box HIGH Side Toolbox Shelving ReinforcedThickness:...
1900 x 600 x 1200mm Checker PRO Full Side Truck Tool Box HIGH Side Toolbox Shelving ReinforcedThickness:... -
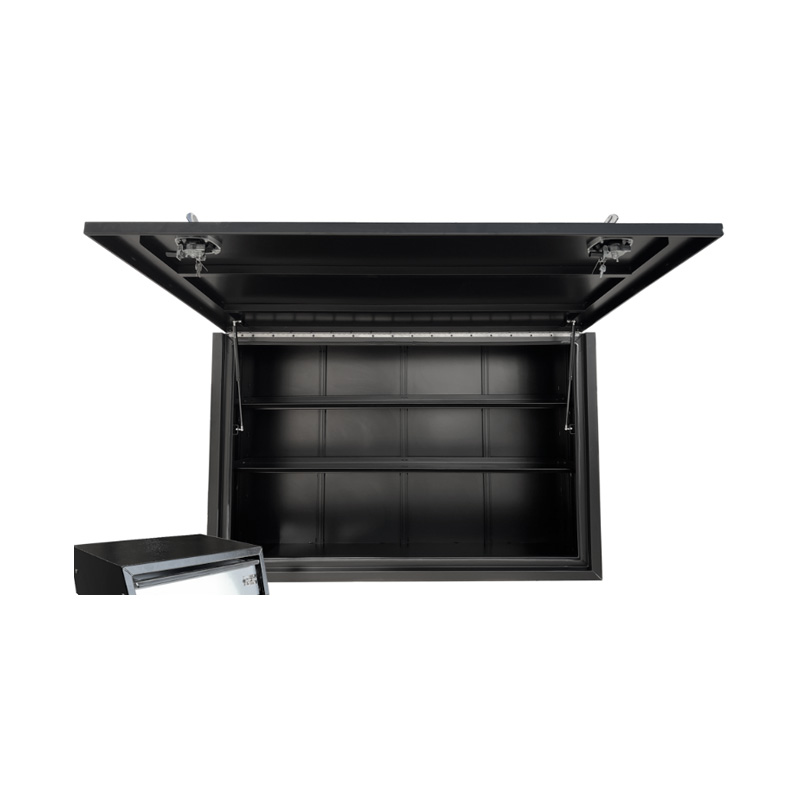 1900 x 600 x 1200mm Aluminium Flat PRO Full Side Truck Tool Box HIGH Side Toolbox Shelving ReinforcedThickness:...
1900 x 600 x 1200mm Aluminium Flat PRO Full Side Truck Tool Box HIGH Side Toolbox Shelving ReinforcedThickness:... -
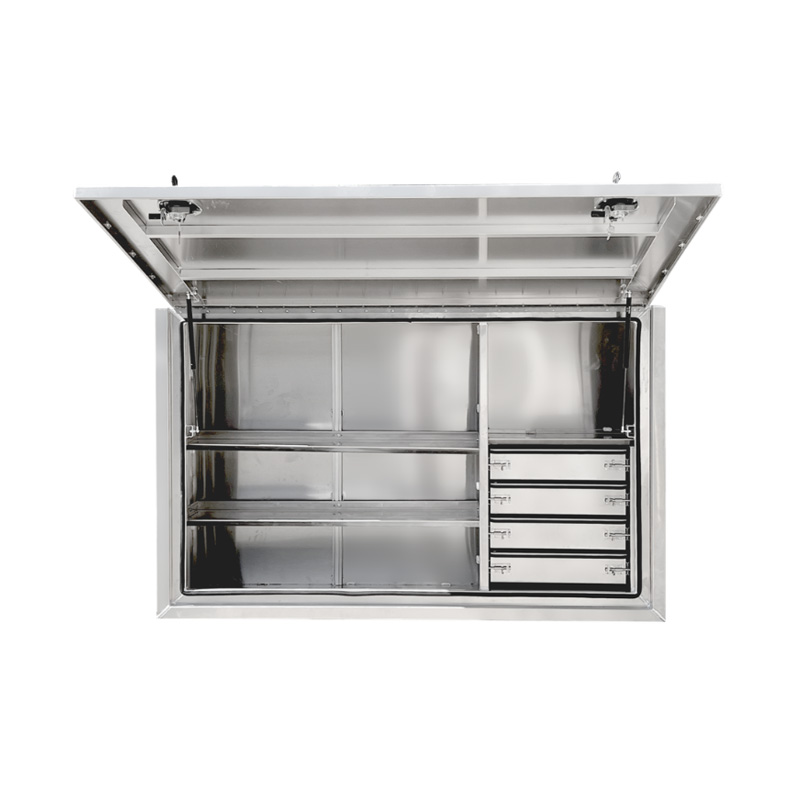 1900 x 600 x 1200mm Aluminium 4 Drawer Full Side Truck Tool Box HIGH Side Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1900 x 600 x 1200mm Aluminium 4 Drawer Full Side Truck Tool Box HIGH Side Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
 1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Square Edge Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1400 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Square Edge Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:... -
 1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Square Edge Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
1700 x 600 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Opening Square Edge Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Toolbox ShelvingThickness:...
-
- Full Lid Truck Toolbox With Drawers >
-
Under Truck Tool Boxes
>
- Dog Boxes >
-
Toolbox Canopies
>
-
 1770 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Checker Sloped Top Gullwing Cross Deck Dual 2 Lid Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:...
1770 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Checker Sloped Top Gullwing Cross Deck Dual 2 Lid Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:... -
 1770 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Checker Flat Top Gullwing Cross Deck Dual 2 Lid Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:...
1770 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Checker Flat Top Gullwing Cross Deck Dual 2 Lid Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:... -
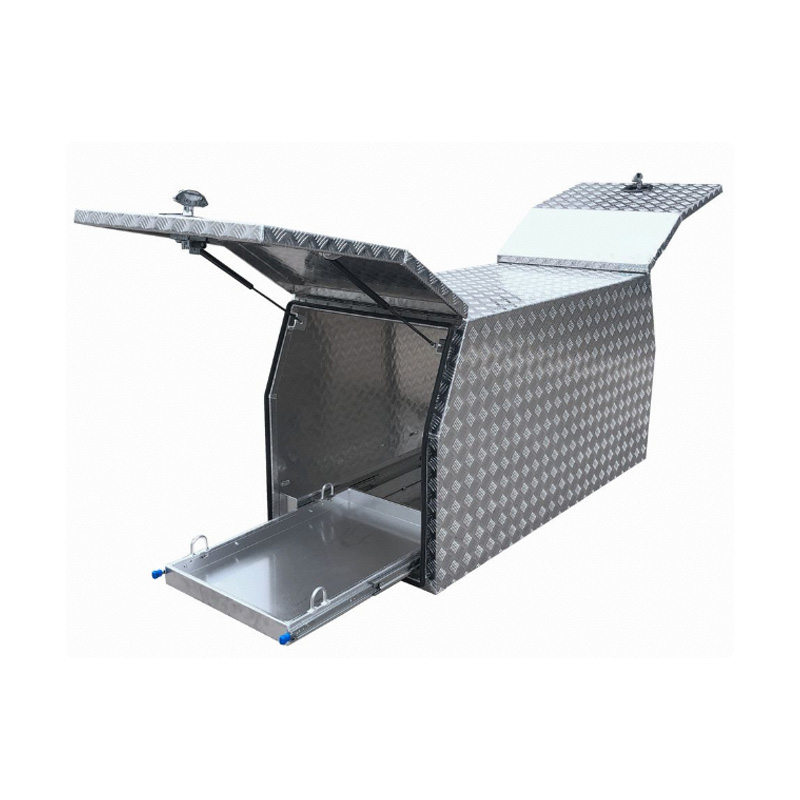 1600 x 700 x 820mm Aluminium Ute Truck Trailer Toolbox Canopy Gullwing 1678-CP-SLDThickness:...
1600 x 700 x 820mm Aluminium Ute Truck Trailer Toolbox Canopy Gullwing 1678-CP-SLDThickness:... -
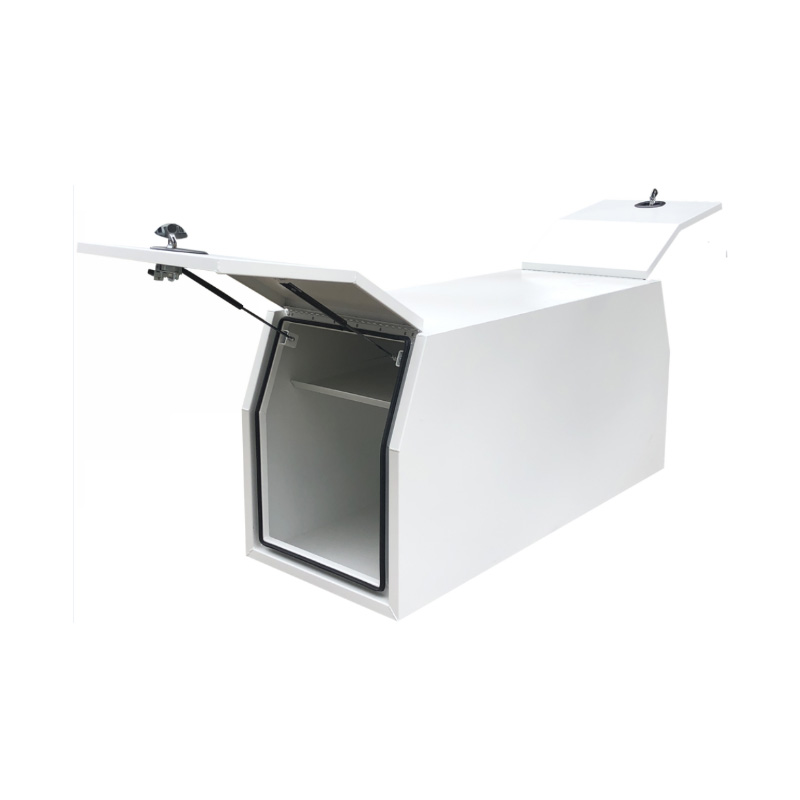 1770 x 700 x 820mm Aluminium Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Full Lid Part Canopy ToolboxThickness:...
1770 x 700 x 820mm Aluminium Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Full Lid Part Canopy ToolboxThickness:... -
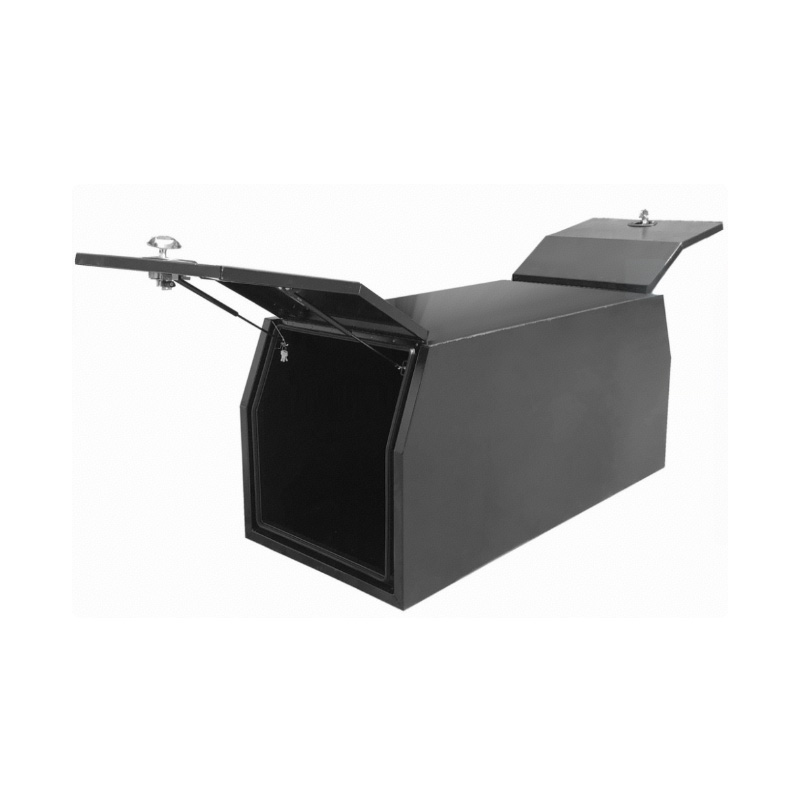 1770 x 800 x 820mm Flat Aluminium Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Full Lid Part Canopy ToolboxThickness:...
1770 x 800 x 820mm Flat Aluminium Ute Tool Box Truck Trailer Full Lid Part Canopy ToolboxThickness:... -
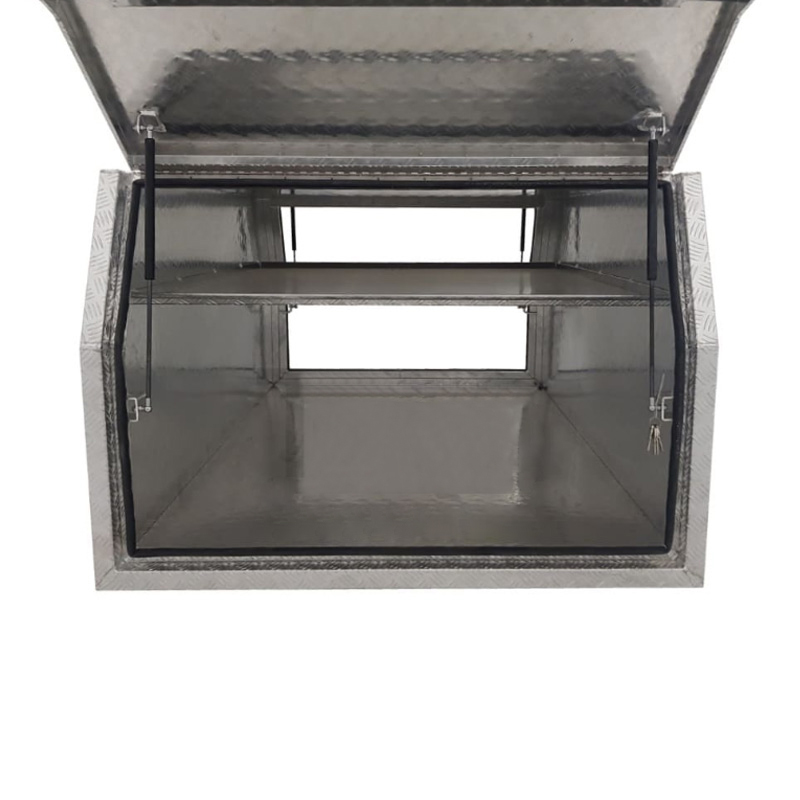 1770 x 1200 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Part Canopy Tool Box Ute Truck Trailer Toolbox Storage Gullwing ShelvingThickness:...
1770 x 1200 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Part Canopy Tool Box Ute Truck Trailer Toolbox Storage Gullwing ShelvingThickness:...
-
-
Camper & Trailer Boxes
>
-
Trailer Boxes/Draw bar Boxes
>
-
 900 x 400 x 400mm Aluminium Checker Top Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:...
900 x 400 x 400mm Aluminium Checker Top Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:... -
 1220 x 400 x 350mm Aluminium Top Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:...
1220 x 400 x 350mm Aluminium Top Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:... -
 1220 x 500 x 500mm Aluminium Top Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & Canopy 1255Thickness:...
1220 x 500 x 500mm Aluminium Top Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & Canopy 1255Thickness:... -
 1500 x 500 x 450mm Aluminium Checker Top Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:...
1500 x 500 x 450mm Aluminium Checker Top Opening Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:... -
 1200 x 600 x 700mm Aluminium Checker Tool Box Ute Truck Fridge Trailer 3/4 Angle Storage ToolboxThickness:...
1200 x 600 x 700mm Aluminium Checker Tool Box Ute Truck Fridge Trailer 3/4 Angle Storage ToolboxThickness:... -
 1400 x 600 x 700mm Aluminium Checker Tool Box Ute Truck Fridge Trailer 3/4 Angle Storage ToolboxThickness:...
1400 x 600 x 700mm Aluminium Checker Tool Box Ute Truck Fridge Trailer 3/4 Angle Storage ToolboxThickness:... -
 1500 x 400 x 400mm Aluminium Checker 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:...
1500 x 400 x 400mm Aluminium Checker 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:... -
 1500 x 500 x 500mm Raw Flat Aluminium 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:...
1500 x 500 x 500mm Raw Flat Aluminium 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:... -
 2000 x 500 x 500mm Aluminium 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:...
2000 x 500 x 500mm Aluminium 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:... -
 1700 x 550 x 610mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Truck Tool Box Fridge Slide & Webber BBQ Slide Camper ToolboxThickness:...
1700 x 550 x 610mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Truck Tool Box Fridge Slide & Webber BBQ Slide Camper ToolboxThickness:... -
 2200 x 550 x 550mm Aluminium 3 Lid Slides BBQ Generator Camper ToolboxThickness:...
2200 x 550 x 550mm Aluminium 3 Lid Slides BBQ Generator Camper ToolboxThickness:... -
 1400 x 550 x 800mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Webber BBQ & Fridge Slide Camper Caravan Canopy Tool BoxThickness:...
1400 x 550 x 800mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Webber BBQ & Fridge Slide Camper Caravan Canopy Tool BoxThickness:... -
 1700 x 550 x 800mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Webber BBQ & Fridge Slide Camper Caravan Canopy Tool BoxThickness:...
1700 x 550 x 800mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Webber BBQ & Fridge Slide Camper Caravan Canopy Tool BoxThickness:... -
 2000 x 550 x 800mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Webber BBQ & Fridge Slide Camper Caravan Canopy Tool BoxThickness:...
2000 x 550 x 800mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Webber BBQ & Fridge Slide Camper Caravan Canopy Tool BoxThickness:... -
 1770 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Checker Sloped Top Gullwing Cross Deck Dual 2 Lid Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:...
1770 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Checker Sloped Top Gullwing Cross Deck Dual 2 Lid Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:... -
 1770 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Checker Flat Top Gullwing Cross Deck Dual 2 Lid Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:...
1770 x 600 x 500mm Aluminium Checker Flat Top Gullwing Cross Deck Dual 2 Lid Ute Tool box 4 Your Truck Ute Trailer Toolbox & CanopyThickness:... -
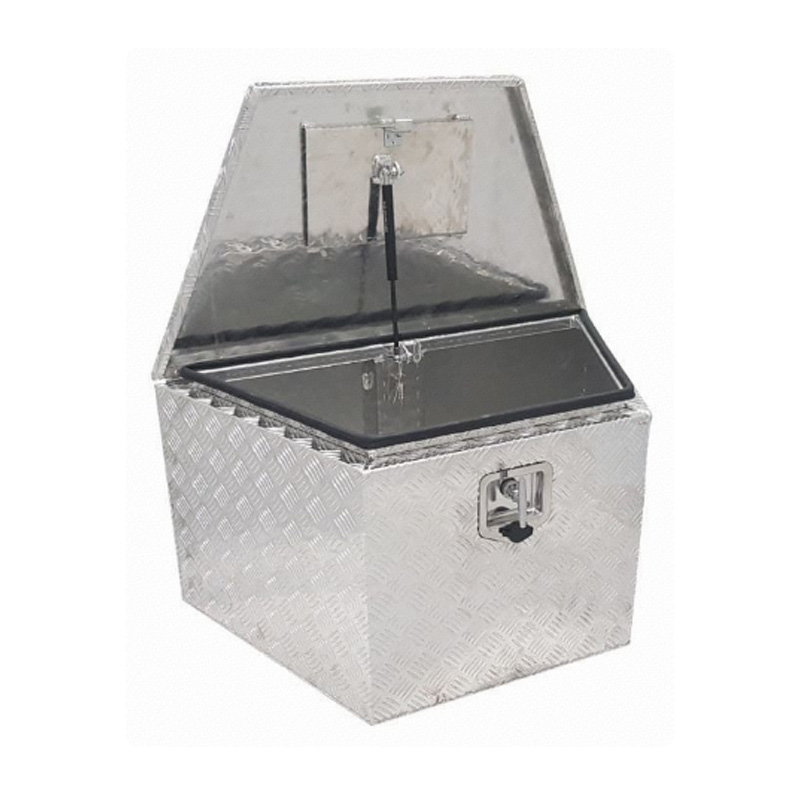 860 x 460 x 460mm Aluminium Checker Toolbox Trailer Draw Bar Storage DrawBar Tool BoxThickness:...
860 x 460 x 460mm Aluminium Checker Toolbox Trailer Draw Bar Storage DrawBar Tool BoxThickness:... -
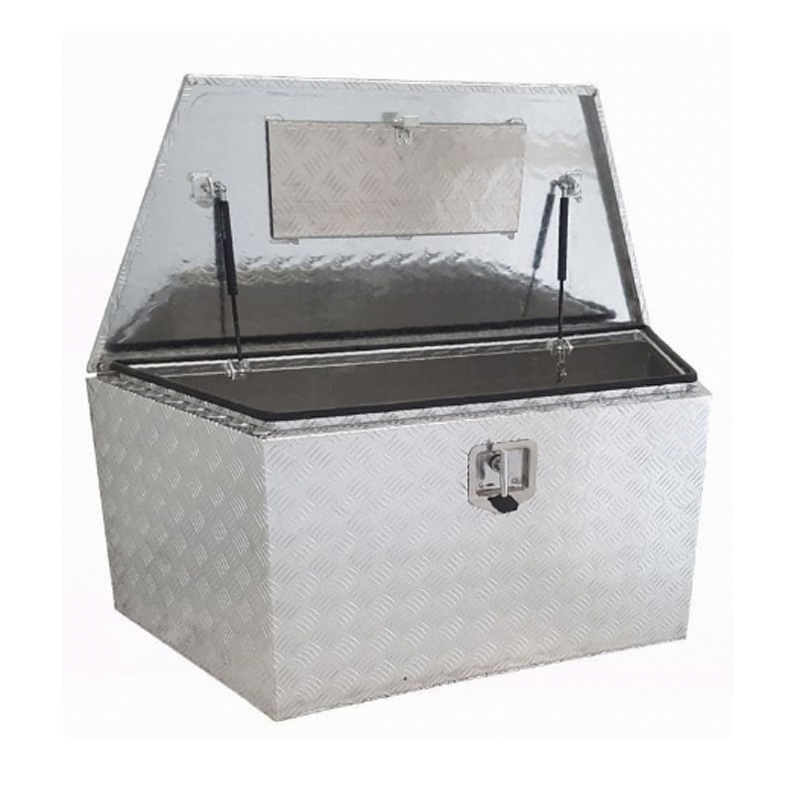 1200 x 500 x 500mm Aluminium Toolbox Trailer Draw Bar Storage DrawBar Tool BoxThickness:...
1200 x 500 x 500mm Aluminium Toolbox Trailer Draw Bar Storage DrawBar Tool BoxThickness:... -
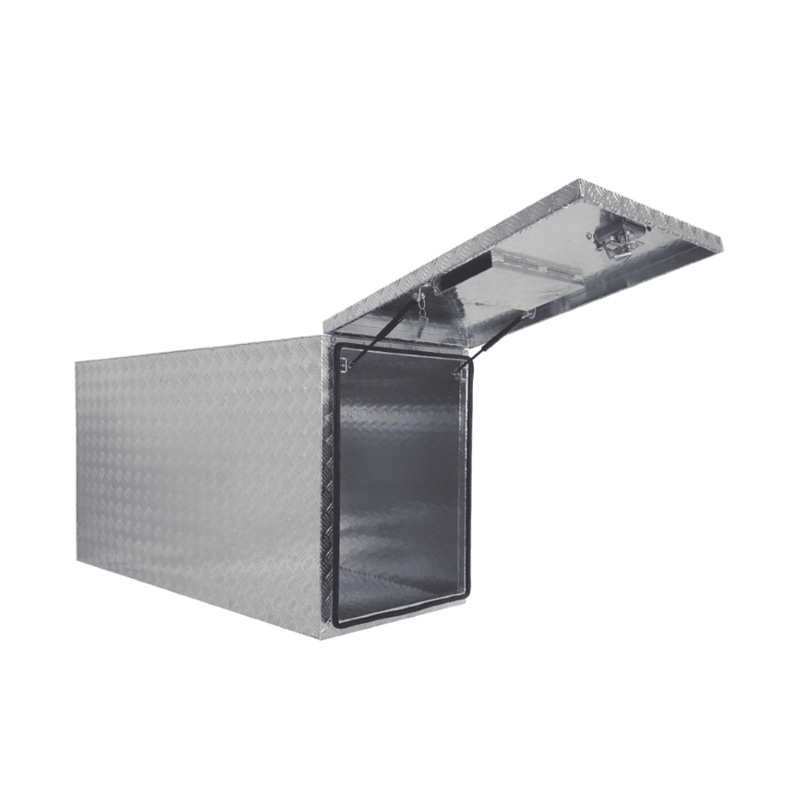 1400 x 580 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Center Box Caravan Ute Tool Box Truck Cab Trailer ToolboxThickness:...
1400 x 580 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Center Box Caravan Ute Tool Box Truck Cab Trailer ToolboxThickness:... -
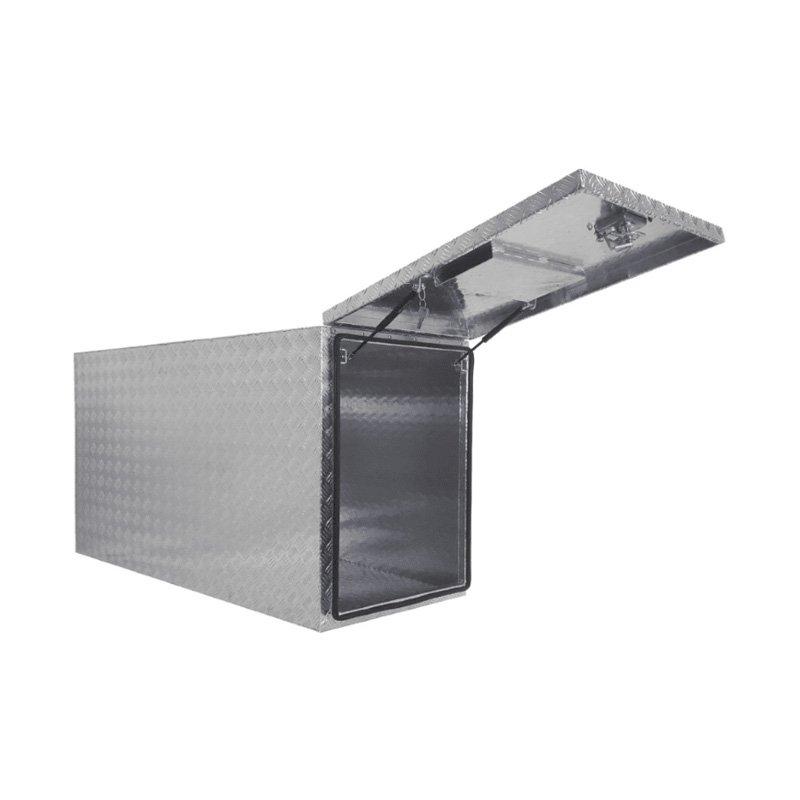 1700 x 580 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Center Box Caravan Ute Tool Box Truck Cab Trailer ToolboxThickness:...
1700 x 580 x 820mm Aluminium Checker Full Side Center Box Caravan Ute Tool Box Truck Cab Trailer ToolboxThickness:...
-
-
Caravan Boxes
>
-
 1500 x 400 x 400mm Aluminium Checker 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:...
1500 x 400 x 400mm Aluminium Checker 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:... -
 1500 x 500 x 500mm Raw Flat Aluminium 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:...
1500 x 500 x 500mm Raw Flat Aluminium 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:... -
 2000 x 500 x 500mm Aluminium 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:...
2000 x 500 x 500mm Aluminium 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Camping Camper Caravan Truck Tool BoxThickness:... -
 1700 x 550 x 610mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Truck Tool Box Fridge Slide & Webber BBQ Slide Camper ToolboxThickness:...
1700 x 550 x 610mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Truck Tool Box Fridge Slide & Webber BBQ Slide Camper ToolboxThickness:... -
 2200 x 550 x 550mm Aluminium 3 Lid Slides BBQ Generator Camper ToolboxThickness:...
2200 x 550 x 550mm Aluminium 3 Lid Slides BBQ Generator Camper ToolboxThickness:... -
 1400 x 550 x 800mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Webber BBQ & Fridge Slide Camper Caravan Canopy Tool BoxThickness:...
1400 x 550 x 800mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Webber BBQ & Fridge Slide Camper Caravan Canopy Tool BoxThickness:... -
 1700 x 550 x 800mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Webber BBQ & Fridge Slide Camper Caravan Canopy Tool BoxThickness:...
1700 x 550 x 800mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Webber BBQ & Fridge Slide Camper Caravan Canopy Tool BoxThickness:... -
 2000 x 550 x 800mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Webber BBQ & Fridge Slide Camper Caravan Canopy Tool BoxThickness:...
2000 x 550 x 800mm Black Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Webber BBQ & Fridge Slide Camper Caravan Canopy Tool BoxThickness:... -
 1600 x 700 x 820mm Aluminium Ute Truck Trailer Toolbox Canopy Gullwing 1678-CP-SLDThickness:...
1600 x 700 x 820mm Aluminium Ute Truck Trailer Toolbox Canopy Gullwing 1678-CP-SLDThickness:...
-
-
Generator Boxes
>
-
 610 x 330 x 540mm Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Trailer Camper Caravan Generator Tool Box for Honda 2kvaThickness:...
610 x 330 x 540mm Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Trailer Camper Caravan Generator Tool Box for Honda 2kvaThickness:... -
 700 x 450 x 650mm Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Trailer Camper Caravan Generator Tool BoxThickness:...
700 x 450 x 650mm Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Trailer Camper Caravan Generator Tool BoxThickness:... -
 760 x 500 x 560mm Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Trailer Camper Caravan Generator Tool BoxThickness:...
760 x 500 x 560mm Aluminium Checker Ute Toolbox Trailer Camper Caravan Generator Tool BoxThickness:...
-
-
Trailer Boxes/Draw bar Boxes
>
-
Under Tray Toolboxes
>
- Accessories
-
Trailers Accessories
>
- Trailer Jockey Wheel >
-
Trailer Coupler
>
-
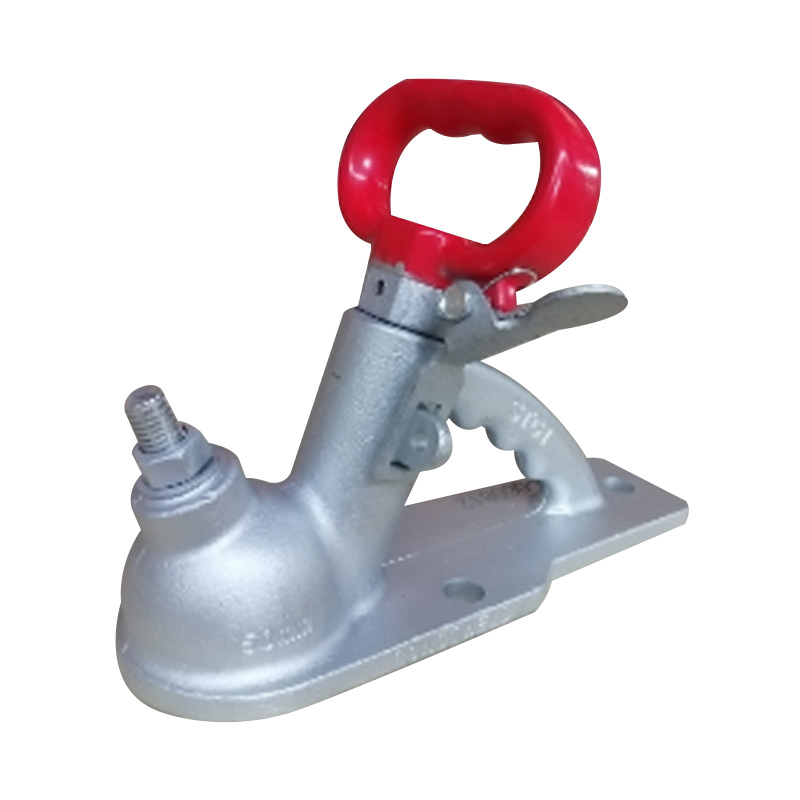 AU 2/3 Hole Quick Release 50 mm Non Braked CouplerSuits 50mm...
AU 2/3 Hole Quick Release 50 mm Non Braked CouplerSuits 50mm... -
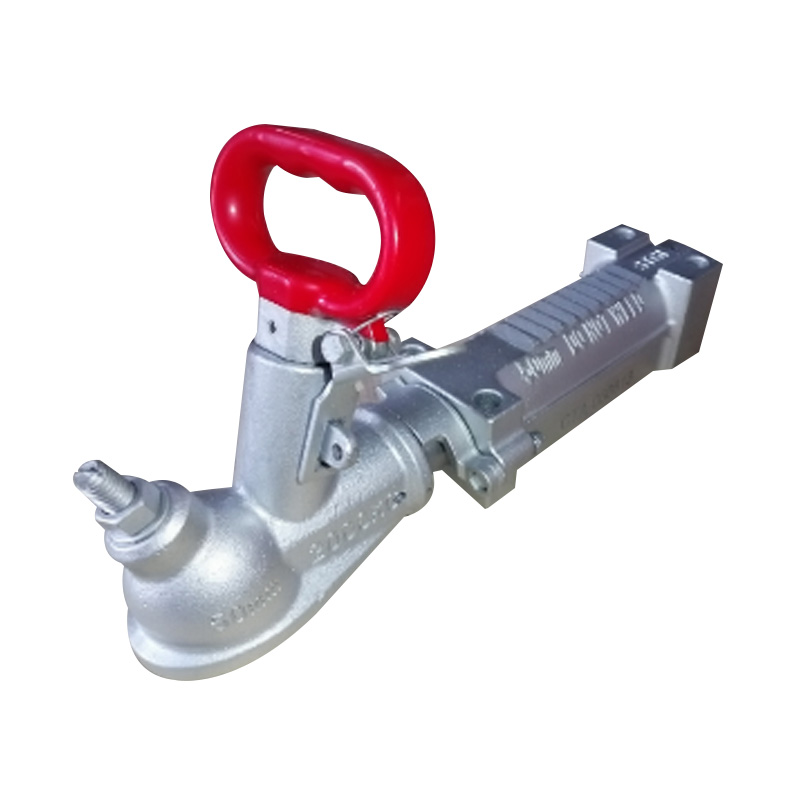 AU 50 mm Mechanical Brake CouplerSuits 50mm...
AU 50 mm Mechanical Brake CouplerSuits 50mm... -
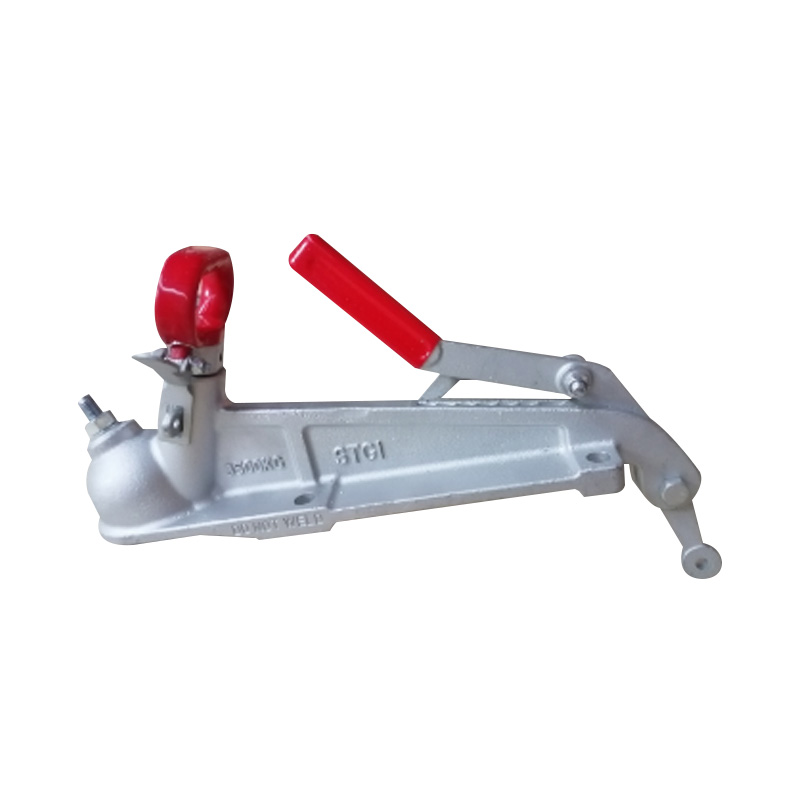 AU Electric Coupling 50 mm Towball 3.5T RatedSuits 50mm...
AU Electric Coupling 50 mm Towball 3.5T RatedSuits 50mm... -
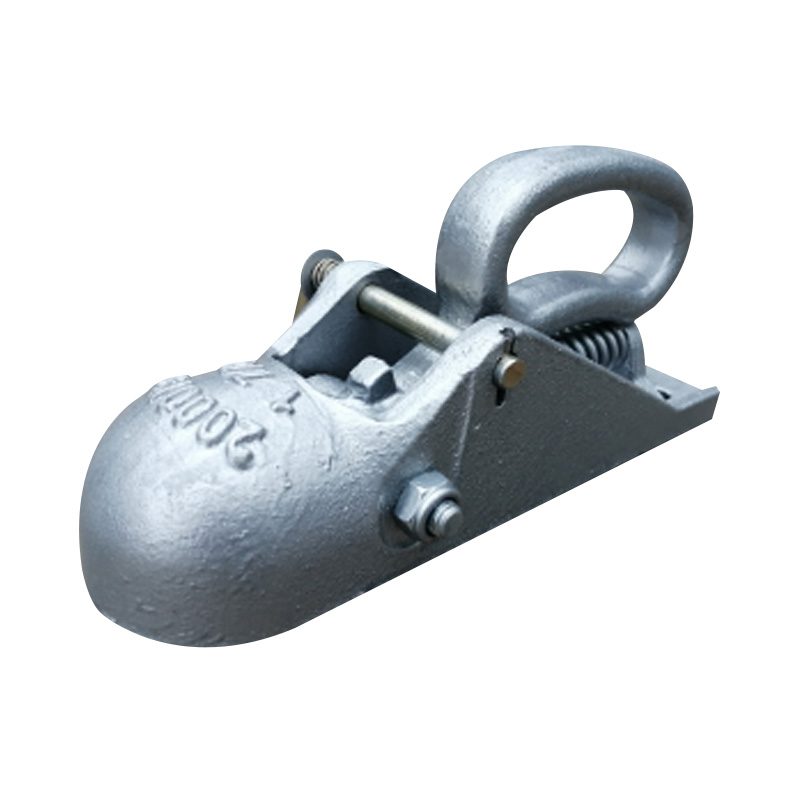 NZ 1-7/8 Non Braked CouplerSuits 45mm...
NZ 1-7/8 Non Braked CouplerSuits 45mm... -
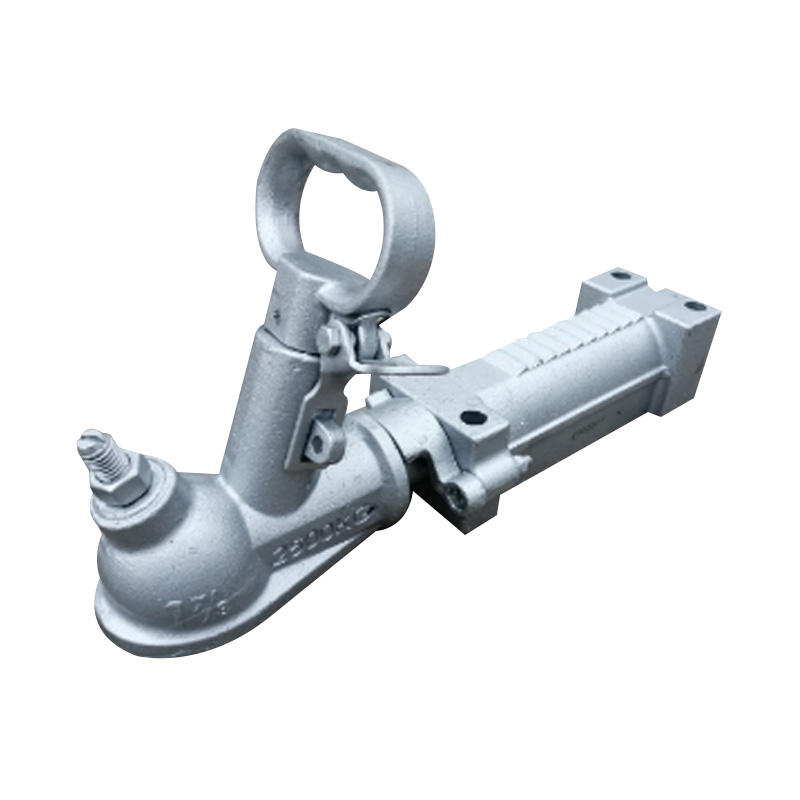 NZ 1-7/8 Mechanical Brake CouplerSuits 45mm...
NZ 1-7/8 Mechanical Brake CouplerSuits 45mm... -
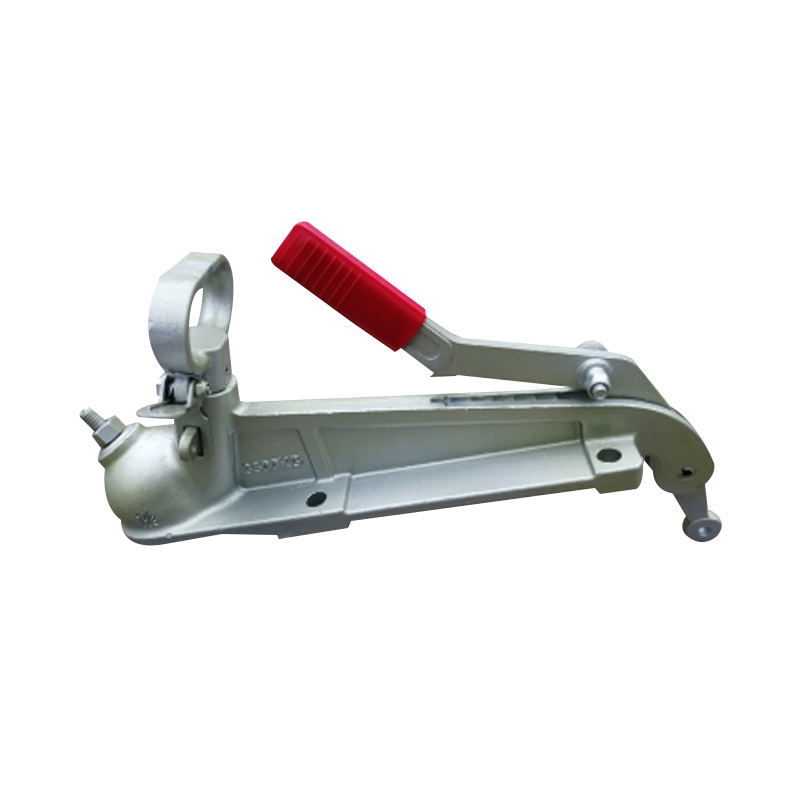 NZ Electric Coupling 50 mm Towball 3.5T RatedSuits 50mm...
NZ Electric Coupling 50 mm Towball 3.5T RatedSuits 50mm...
-
-
Trailer Spring
>
-
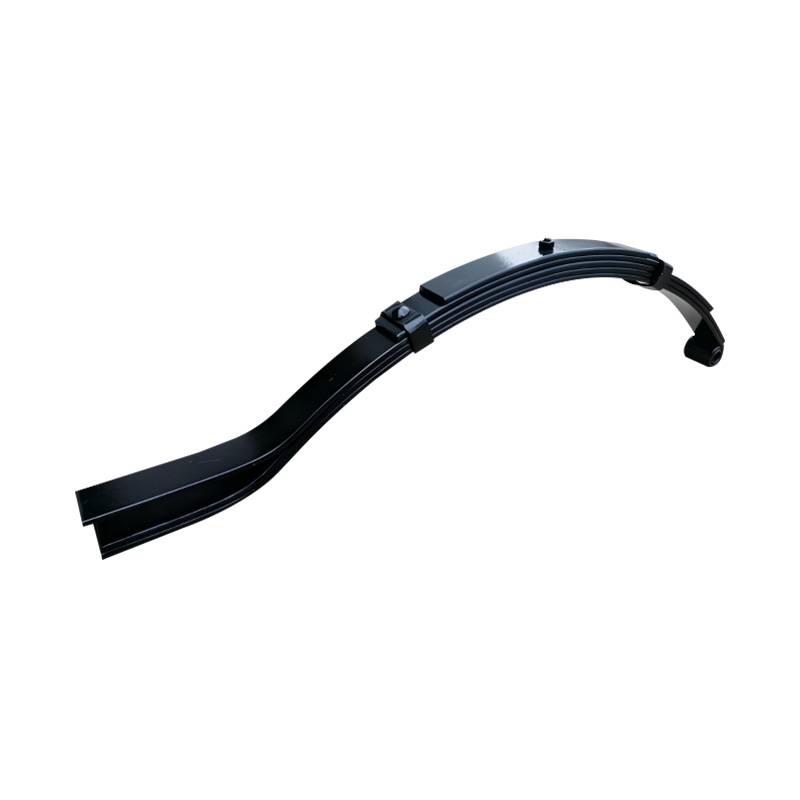 Slipper to Eye Spring, 6×45×5
Slipper to Eye Spring, 6×45×5 -
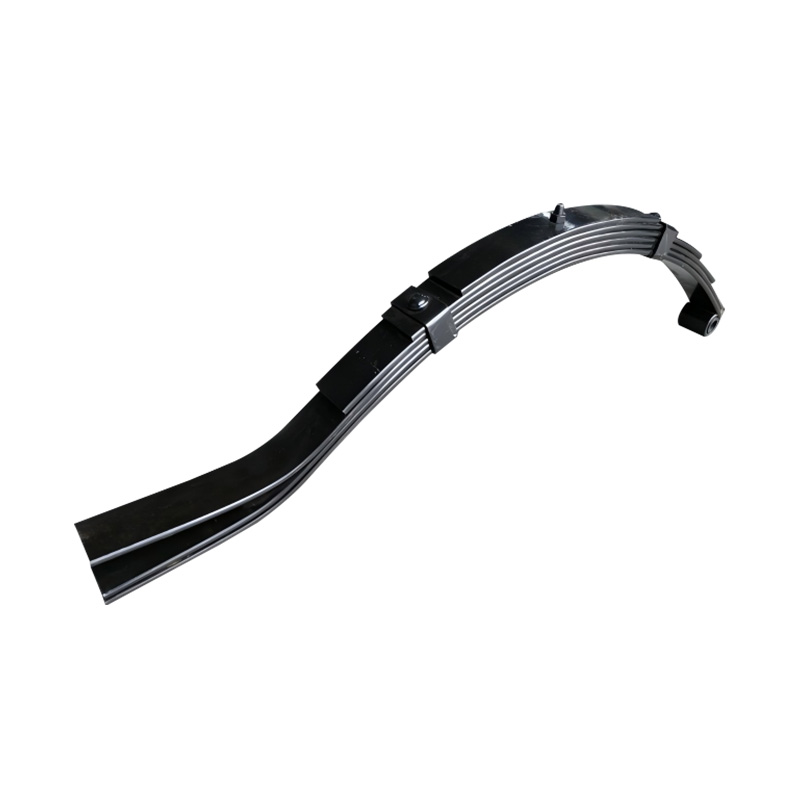 Slipper to Eye Spring, 6×45×6
Slipper to Eye Spring, 6×45×6 -
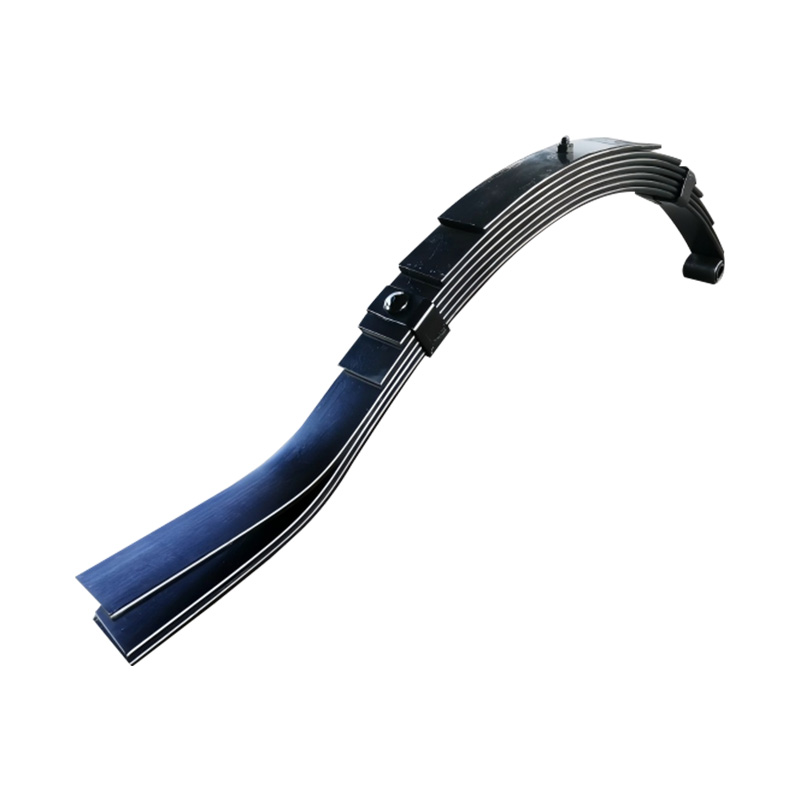 Slipper to Eye Spring, 6×45×7
Slipper to Eye Spring, 6×45×7 -
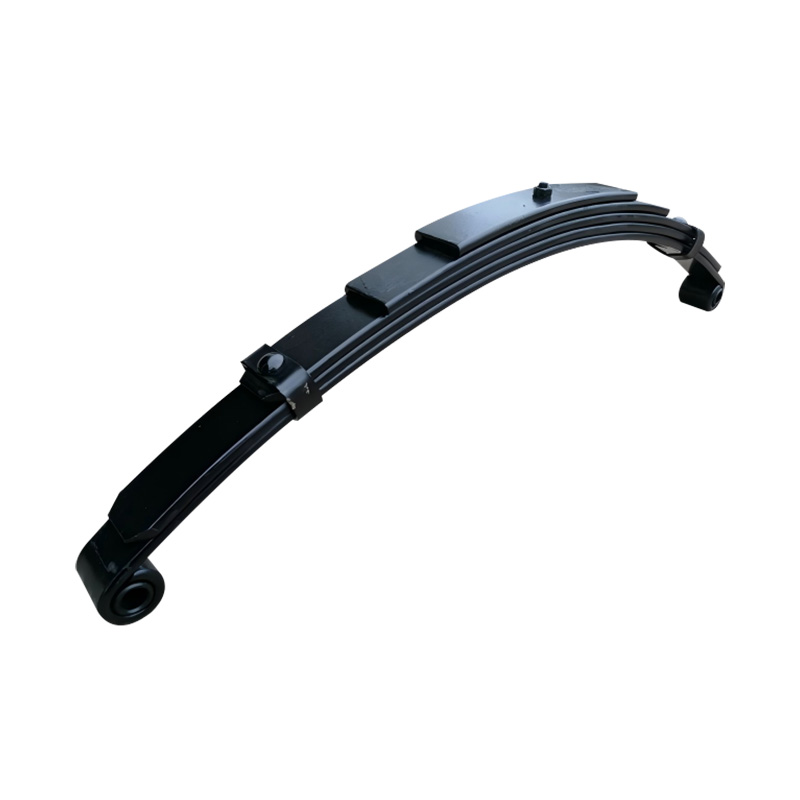 Eye to Eye Spring, 8×45×5
Eye to Eye Spring, 8×45×5 -
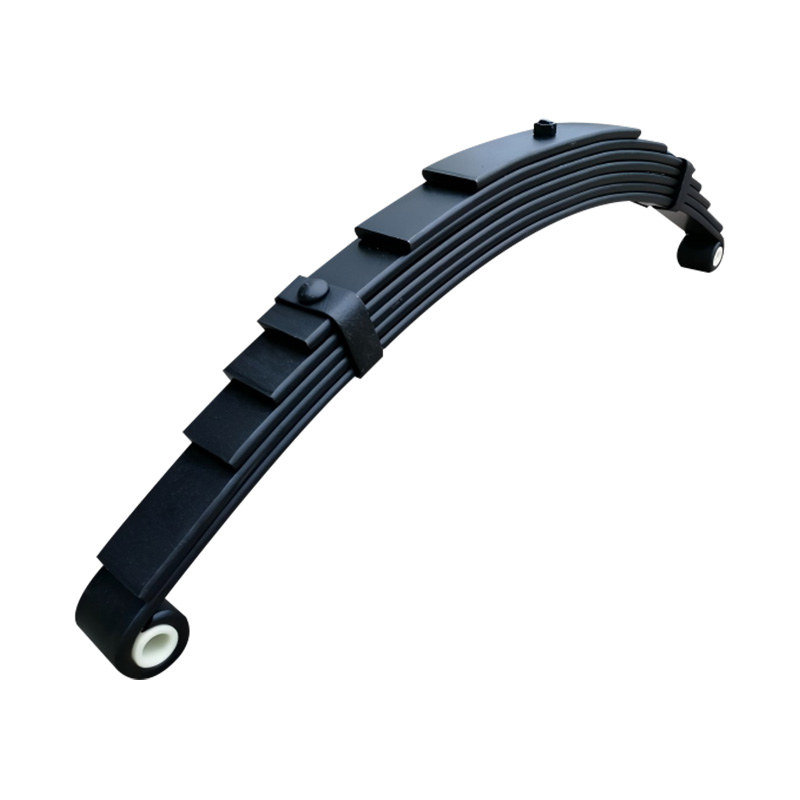 Eye to Eye Spring, 8×45×7
Eye to Eye Spring, 8×45×7 -
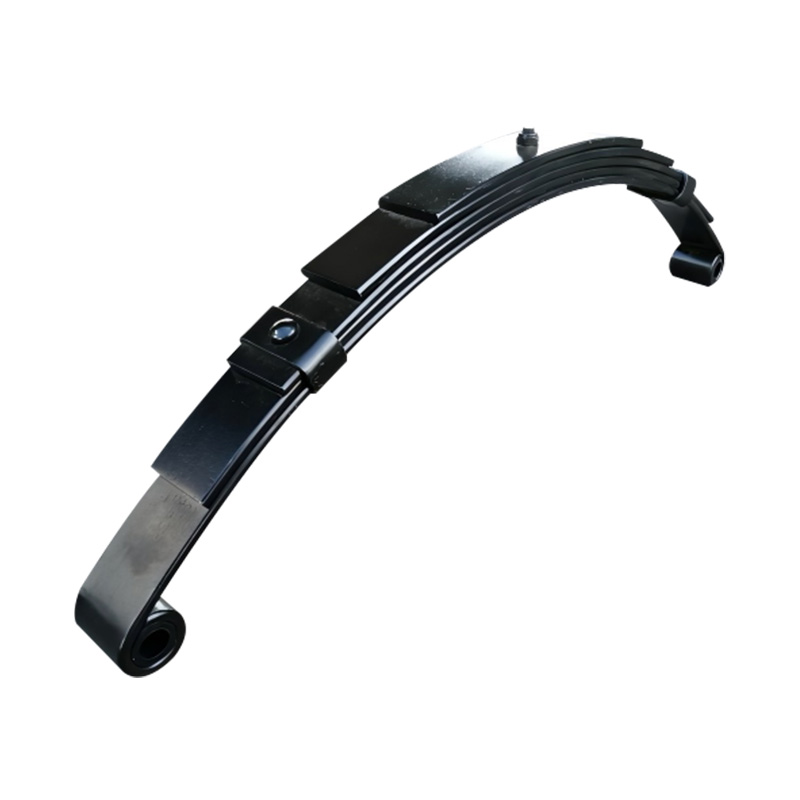 Eye to Eye Spring 6×45×5
Eye to Eye Spring 6×45×5 -
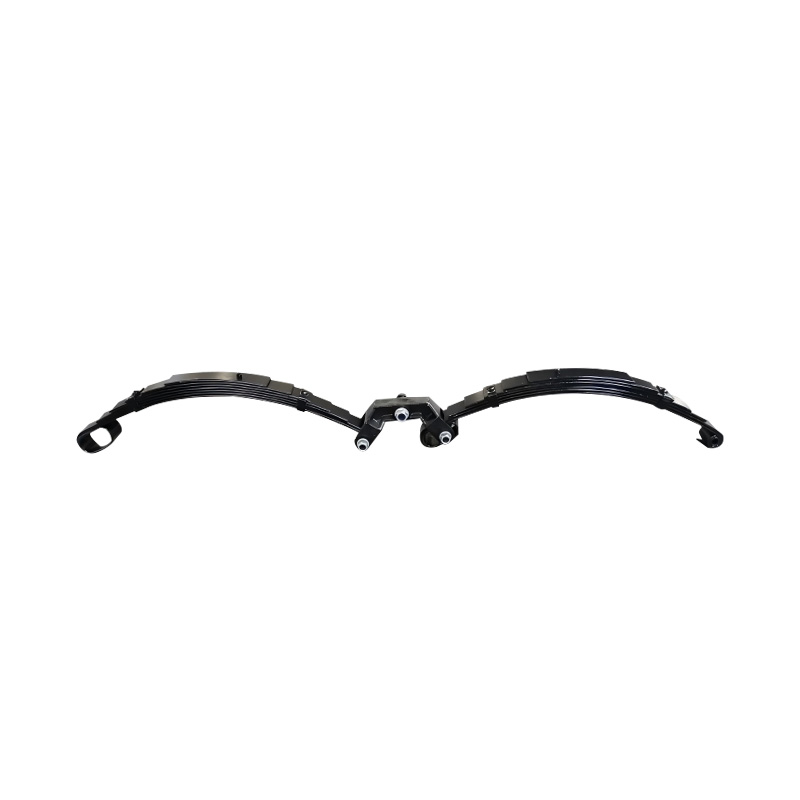 Leaf Rocker Roller Spring, 6×60×7
Leaf Rocker Roller Spring, 6×60×7 -
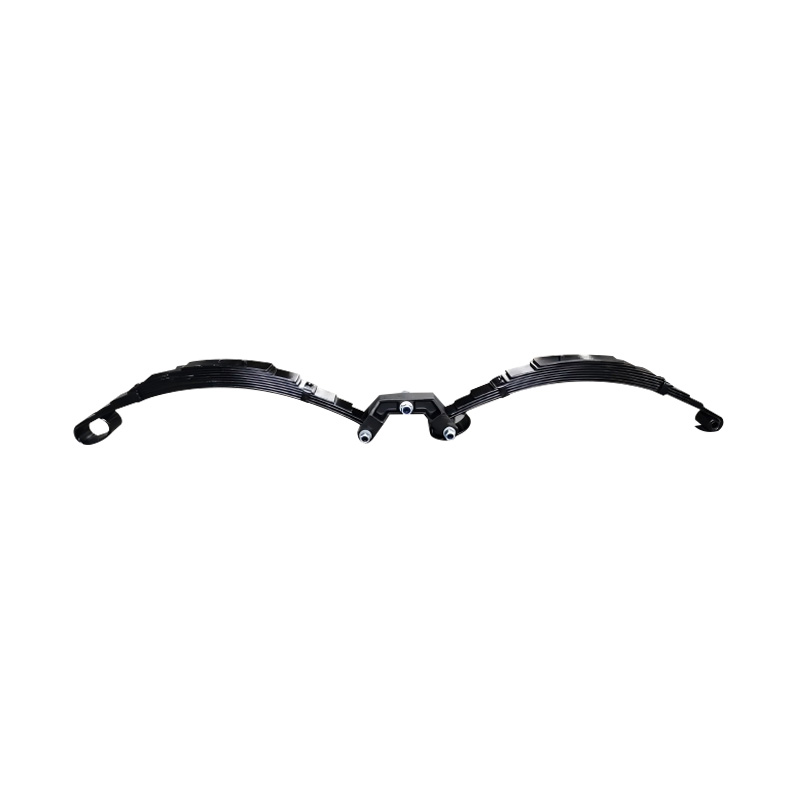 Leaf Rocker Roller Spring, 6×60×9
Leaf Rocker Roller Spring, 6×60×9 -
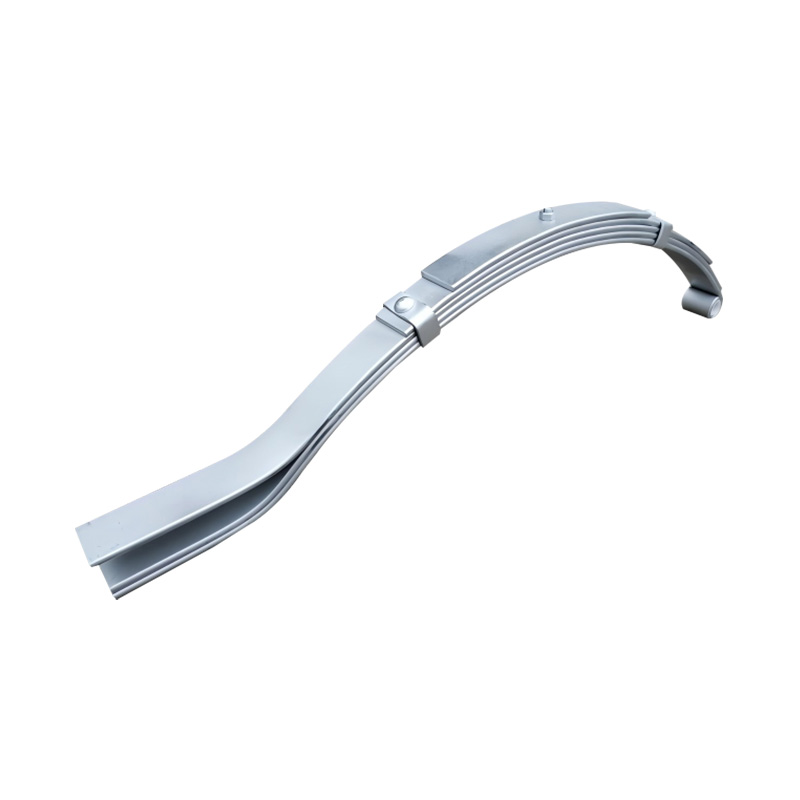 Boat trailer Slipper to Eye Spring 6×45×5
Boat trailer Slipper to Eye Spring 6×45×5 -
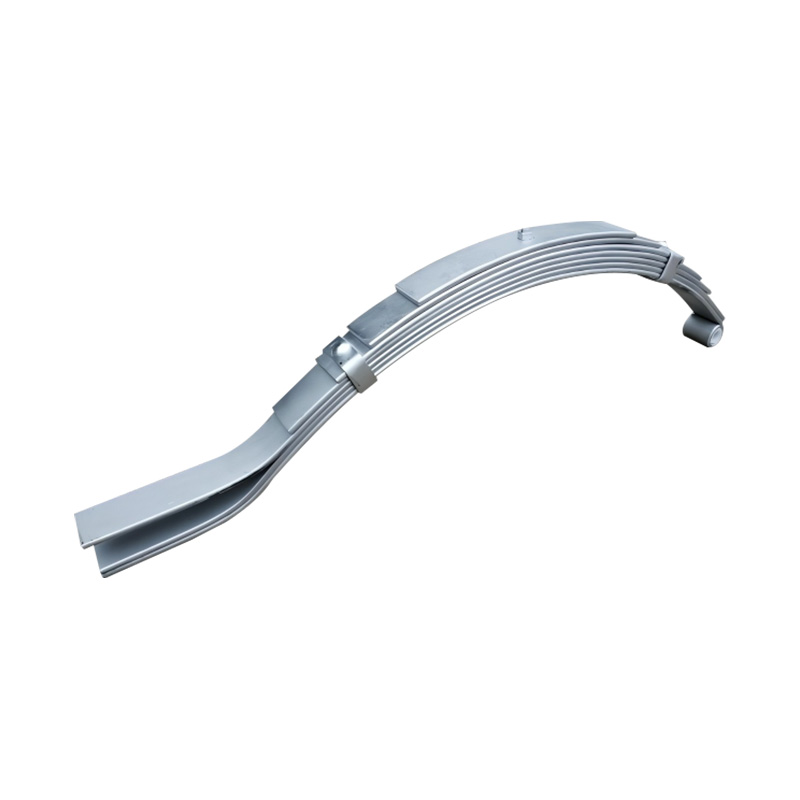 Boat trailer Slipper to Eye Spring 6×45×7
Boat trailer Slipper to Eye Spring 6×45×7
-
- Trailer Axle >
- Trailer Brake >
- Trailer U Bolt >
- Trailer Wheel >
-
Trailer Mudguard
>
-
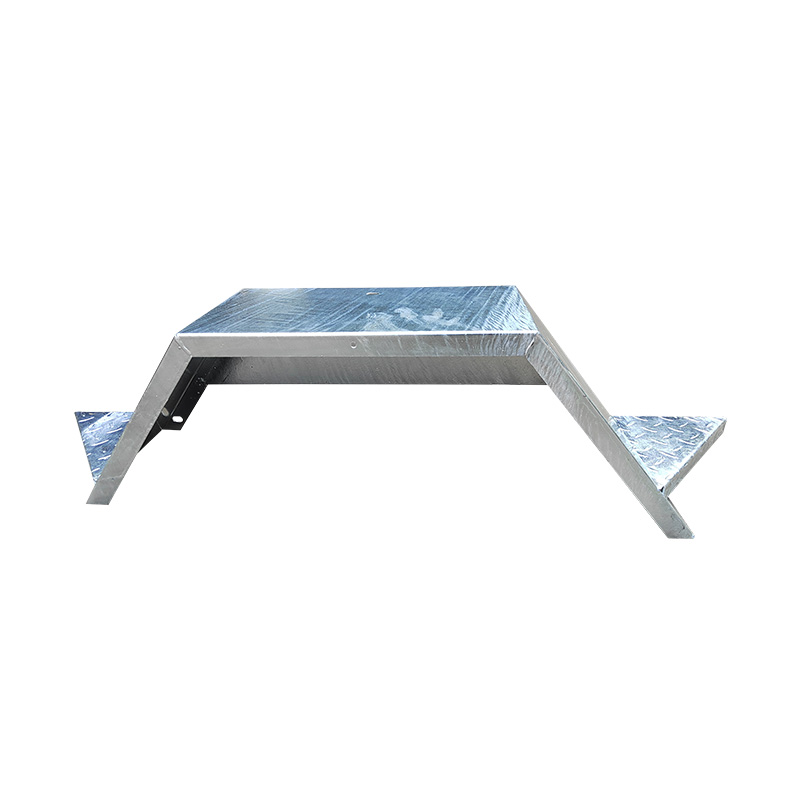 13" Single Axle Galvanized Trailer MudguardThis 13-in...
13" Single Axle Galvanized Trailer MudguardThis 13-in... -
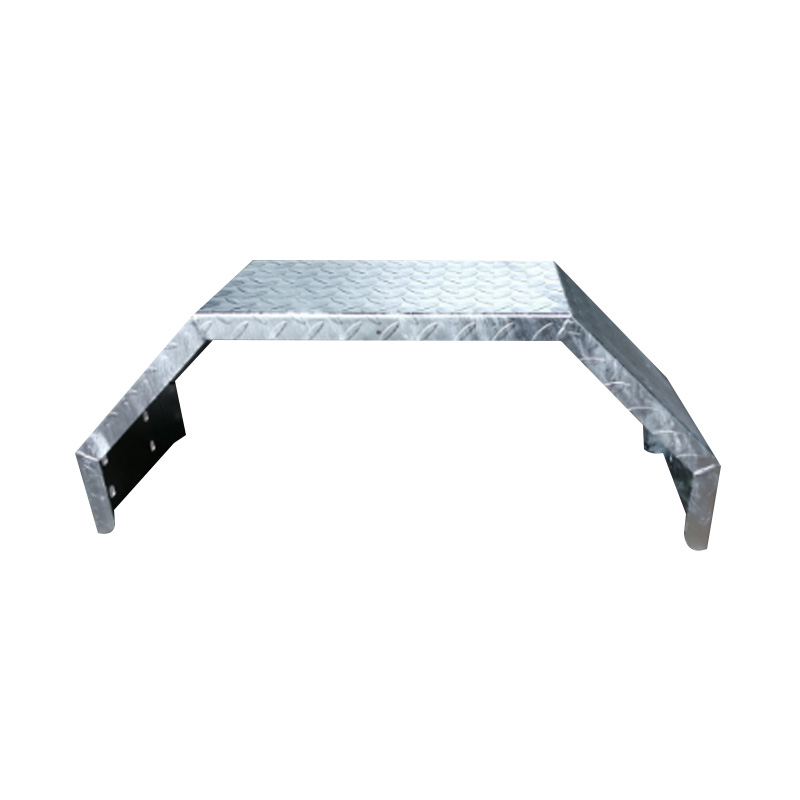 14" Single Axle Galvanized Trailer MudguardBuilt for ...
14" Single Axle Galvanized Trailer MudguardBuilt for ... -
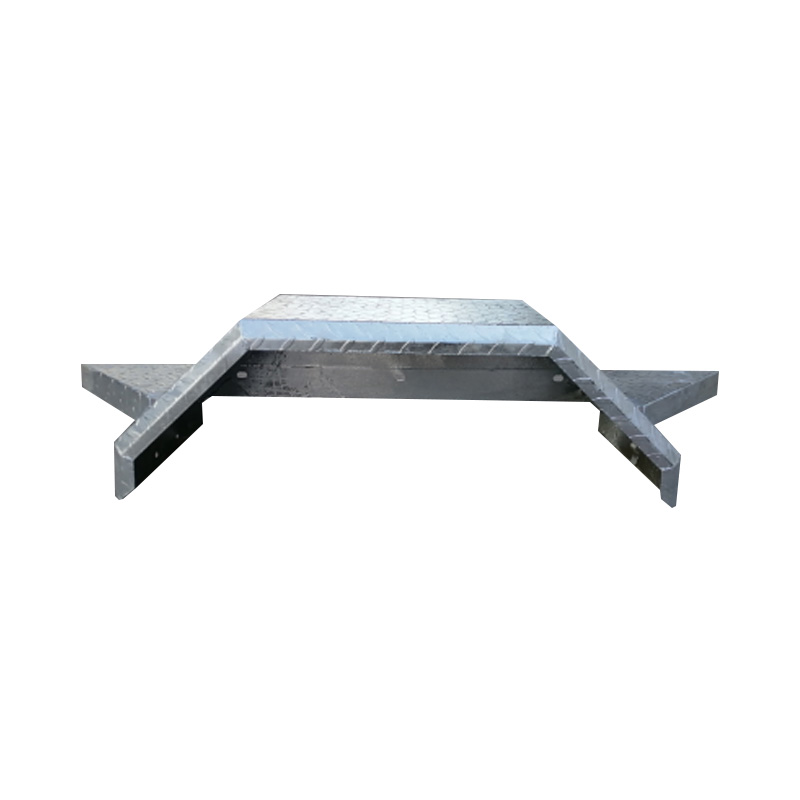 14" Single Axle Galvanized Trailer Mudguard with Side StepThis 14-in...
14" Single Axle Galvanized Trailer Mudguard with Side StepThis 14-in... -
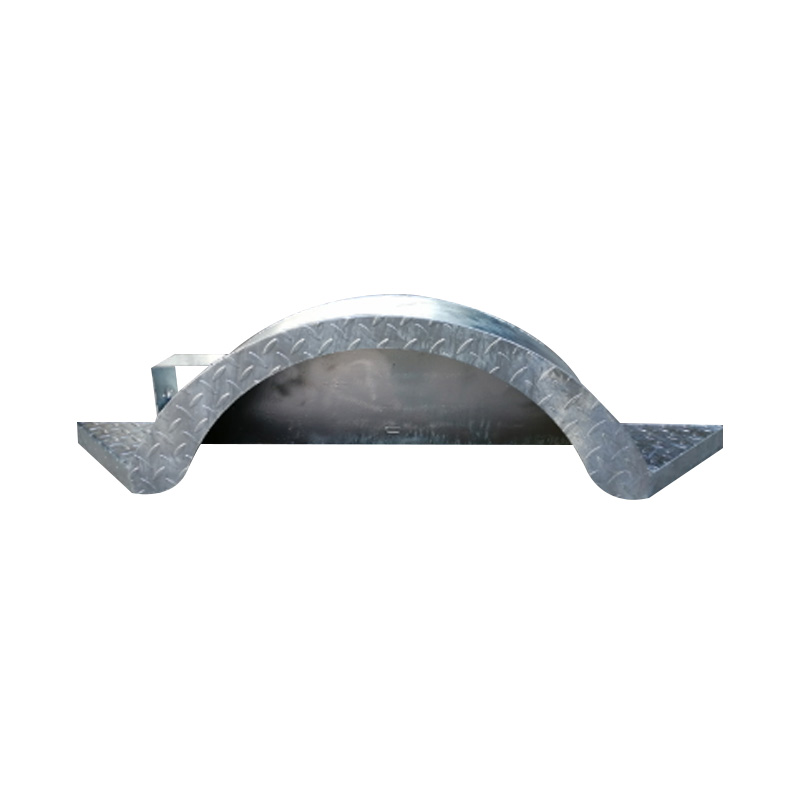 14" Single Axle Round Galvanized Trailer MudguardCrafted wi...
14" Single Axle Round Galvanized Trailer MudguardCrafted wi... -
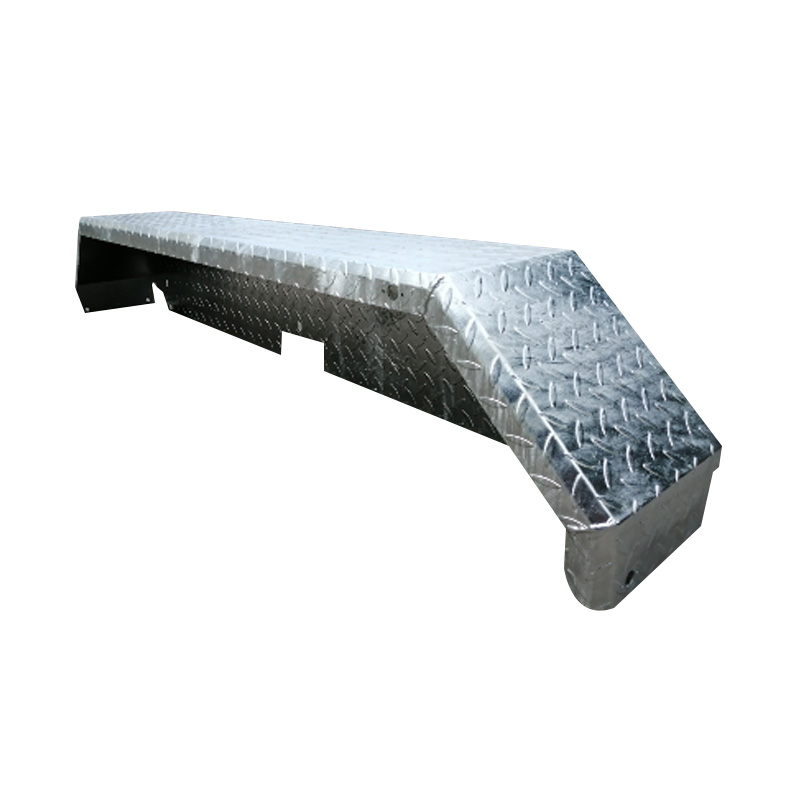 14" Tandem Galvanized Trailer MudguardEngineered...
14" Tandem Galvanized Trailer MudguardEngineered... -
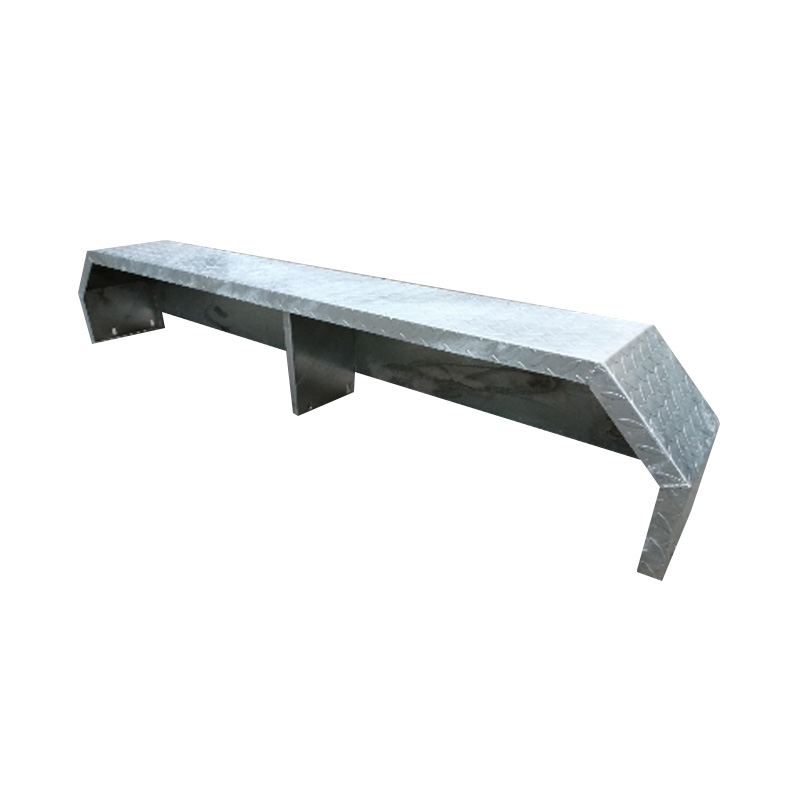 14" Tandem Aluminum Trailer MudguardThis 14-in...
14" Tandem Aluminum Trailer MudguardThis 14-in...
-
-
Trailer Light
>
-
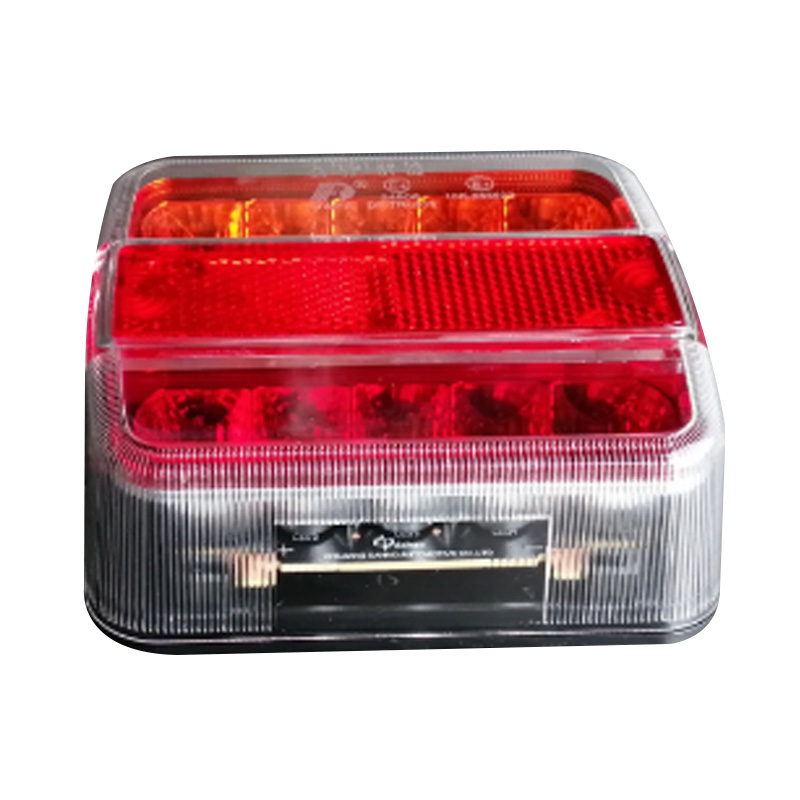 LED Tail light M/Volt 107 x 99 mm 12/24V without Number Plate LightTrailer li...
LED Tail light M/Volt 107 x 99 mm 12/24V without Number Plate LightTrailer li... -
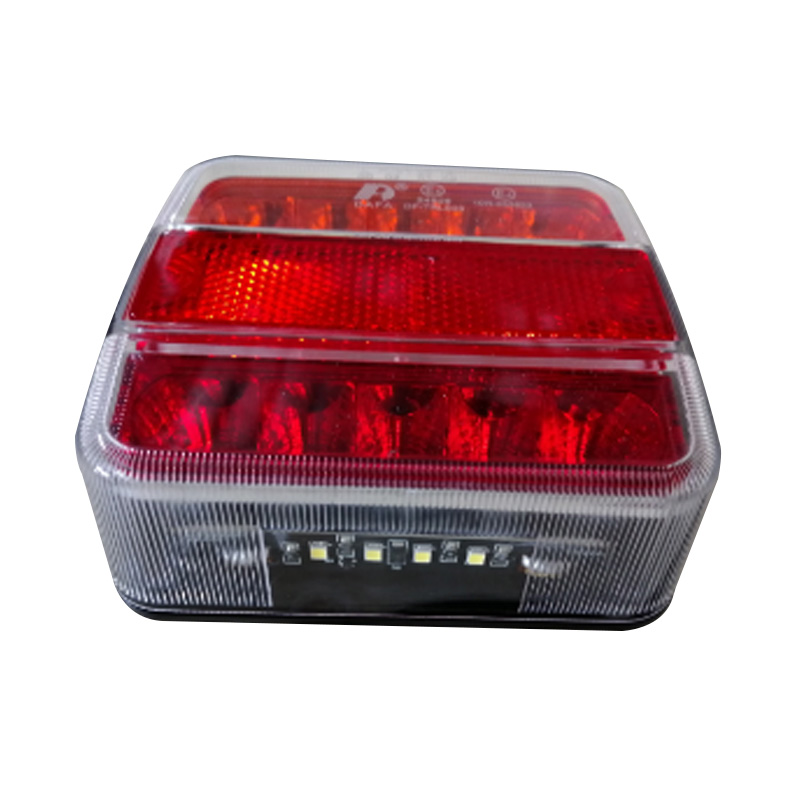 LED Tail light M/Volt 107 x 99 mm 12/24V with Number Plate LightTrailer li...
LED Tail light M/Volt 107 x 99 mm 12/24V with Number Plate LightTrailer li... -
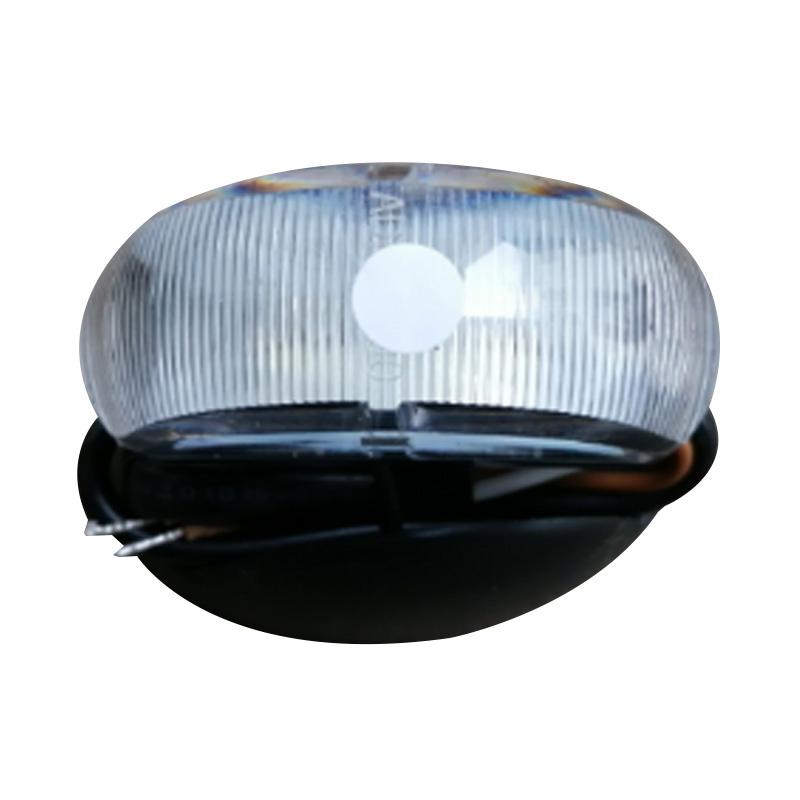 White- LED SIDE Marker 60×38 mm M/Volt ClearTrailer si...
White- LED SIDE Marker 60×38 mm M/Volt ClearTrailer si... -
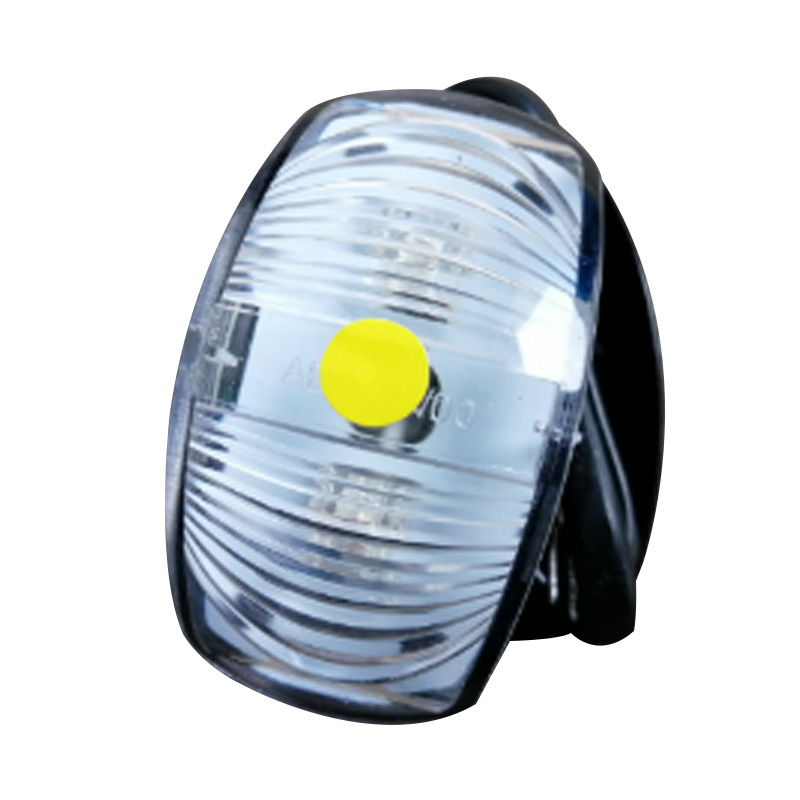 Yellow-LED SIDE Marker 59×35 mm M/Volt ClearTrailer si...
Yellow-LED SIDE Marker 59×35 mm M/Volt ClearTrailer si... -
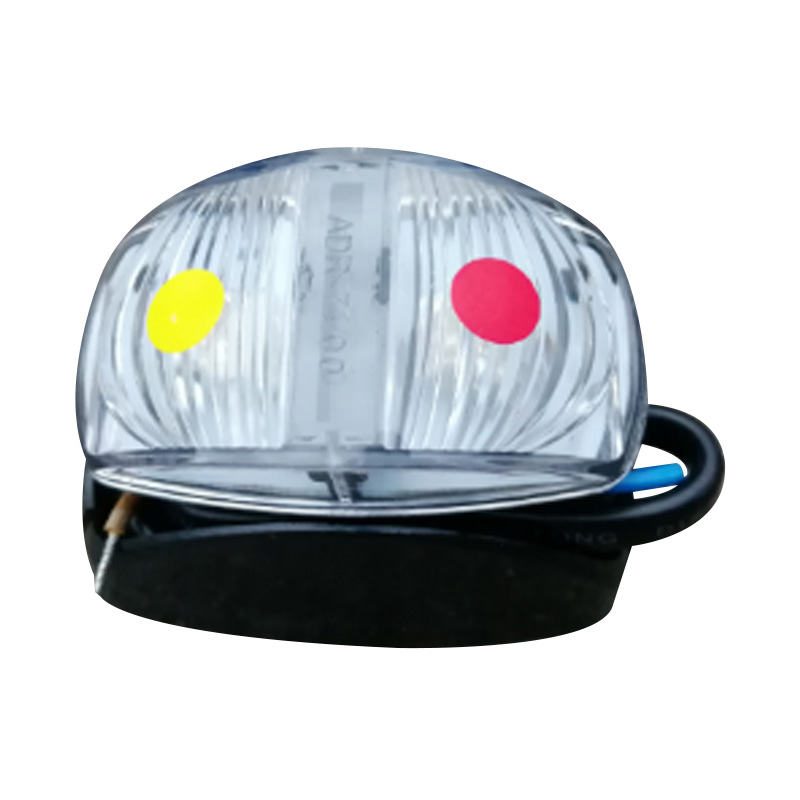 Yellow & Red-LED SIDE 59×35 mm Marker M/Volt ClearTrailer si...
Yellow & Red-LED SIDE 59×35 mm Marker M/Volt ClearTrailer si... -
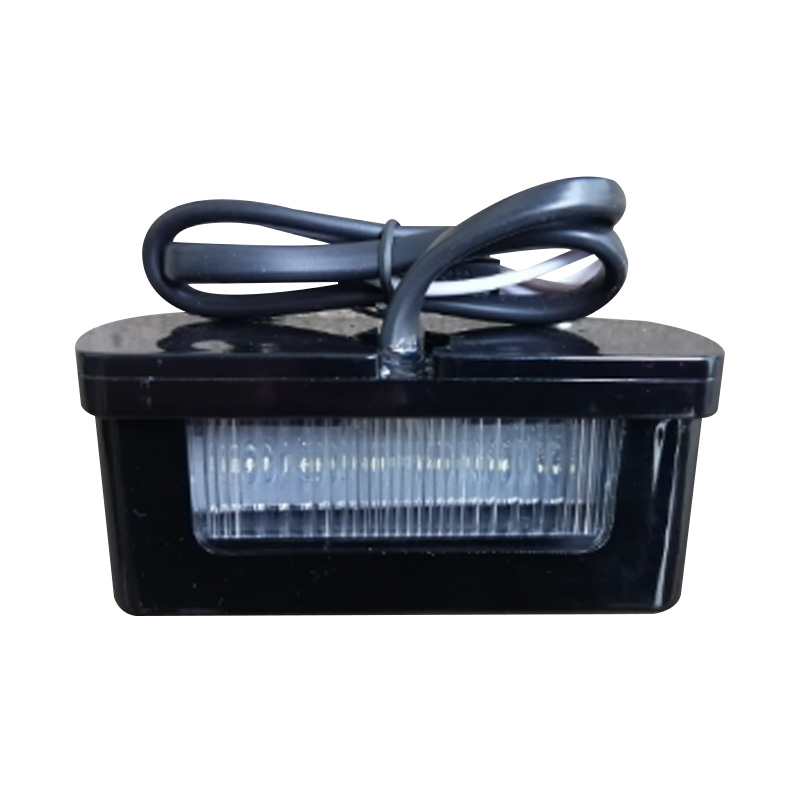 80×35 mm LED Number Plate LightTrailer nu...
80×35 mm LED Number Plate LightTrailer nu... -
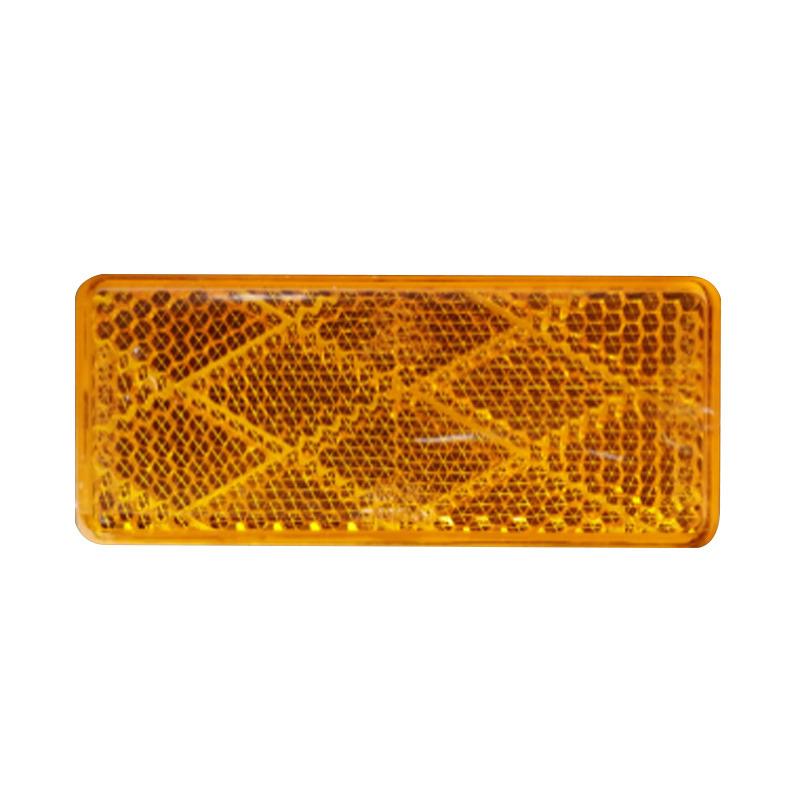 70×30 mm Reflector Stick On AmberReflectors...
70×30 mm Reflector Stick On AmberReflectors... -
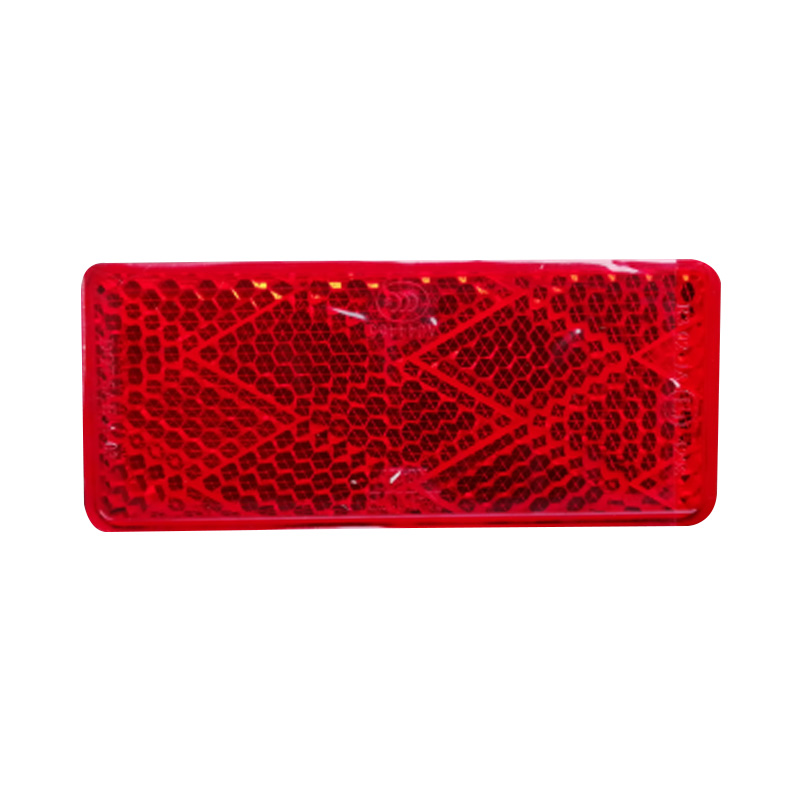 70×30 mm Reflector Stick On RedReflectors...
70×30 mm Reflector Stick On RedReflectors... -
 70×30 mm Reflector Stick On ClearReflectors...
70×30 mm Reflector Stick On ClearReflectors...
-
- Trailer Cage >
- Trailer Canvas Cover >
-
Trailer Drawbar Toolbox
>
-
 Side Open Trailer Drawbar Aluminum Toolbox with Fridge Slideavaiable f...
Side Open Trailer Drawbar Aluminum Toolbox with Fridge Slideavaiable f... -
 Top Opening Trailer Drawbar Aluminum Toolboxavaiable f...
Top Opening Trailer Drawbar Aluminum Toolboxavaiable f... -
 Checker Top Opening Trailer Drawbar Aluminum Toolboxavaiable f...
Checker Top Opening Trailer Drawbar Aluminum Toolboxavaiable f... -
 3/4 Angle Toolbox Trailer Drawbar Aluminum Toolboxavaiable f...
3/4 Angle Toolbox Trailer Drawbar Aluminum Toolboxavaiable f... -
 Aluminum Trailer Tongue Storage Toolbox with Lockavaiable f...
Aluminum Trailer Tongue Storage Toolbox with Lockavaiable f... -
 Checker 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Drawbar Aluminum Toolboxavaiable f...
Checker 3 Lid Ute Toolbox Trailer Drawbar Aluminum Toolboxavaiable f... -
 Aluminium 3 Lid Slides Trailer Drawbar Toolbox with Fridge Slideavaiable f...
Aluminium 3 Lid Slides Trailer Drawbar Toolbox with Fridge Slideavaiable f... -
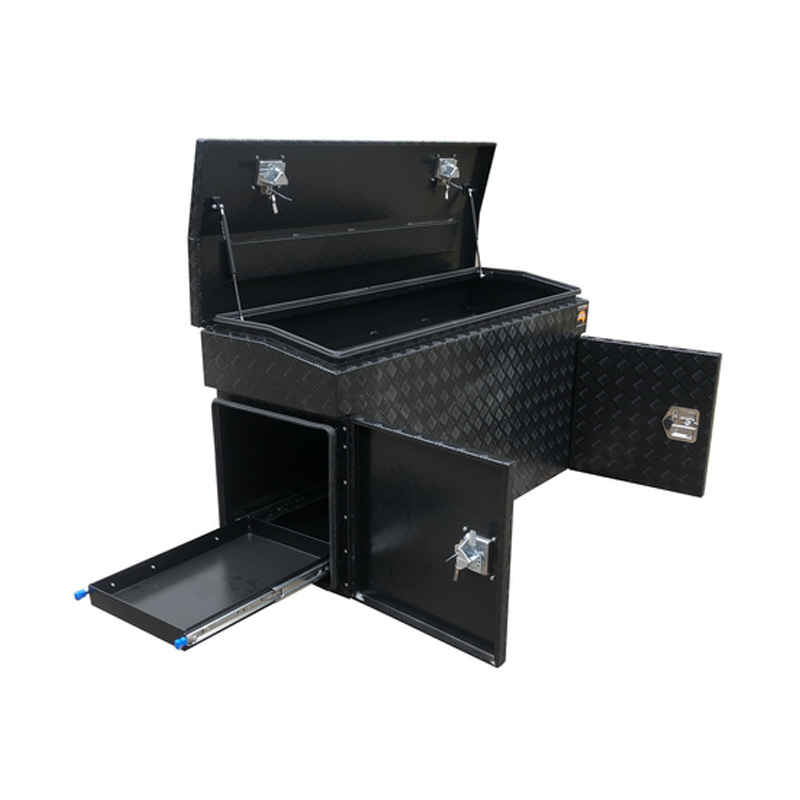 Black Aluminium Ute Toolbox Fridge Slide Trailer Drawbar Toolboxavaiable f...
Black Aluminium Ute Toolbox Fridge Slide Trailer Drawbar Toolboxavaiable f... -
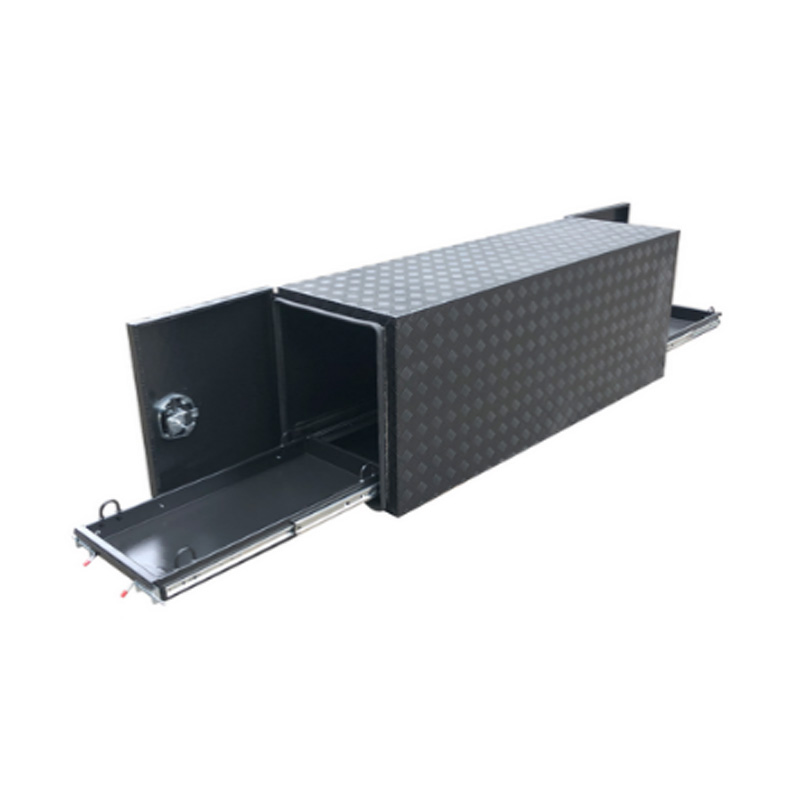 Black Trailer Drawbar Aluminum Toolbox with Fridge Slideavaiable f...
Black Trailer Drawbar Aluminum Toolbox with Fridge Slideavaiable f... -
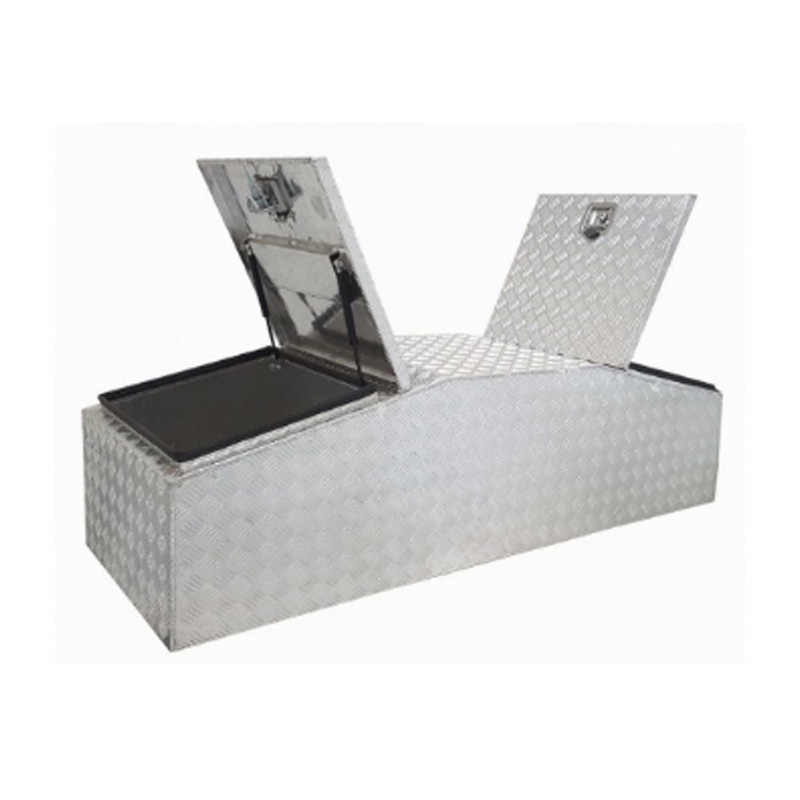 Gullwing 2 Lid Trailer Drawbar Aluminum Toolboxavaiable f...
Gullwing 2 Lid Trailer Drawbar Aluminum Toolboxavaiable f... -
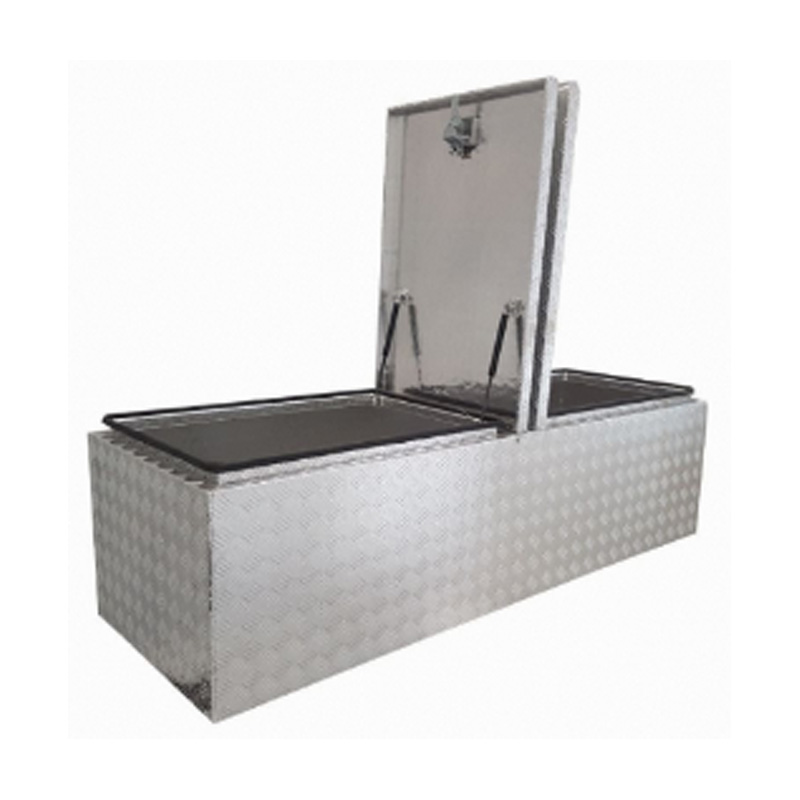 Checker Flat Top Dual 2 Lid Trailer Drawbar Aluminum Toolboxavaiable f...
Checker Flat Top Dual 2 Lid Trailer Drawbar Aluminum Toolboxavaiable f... -
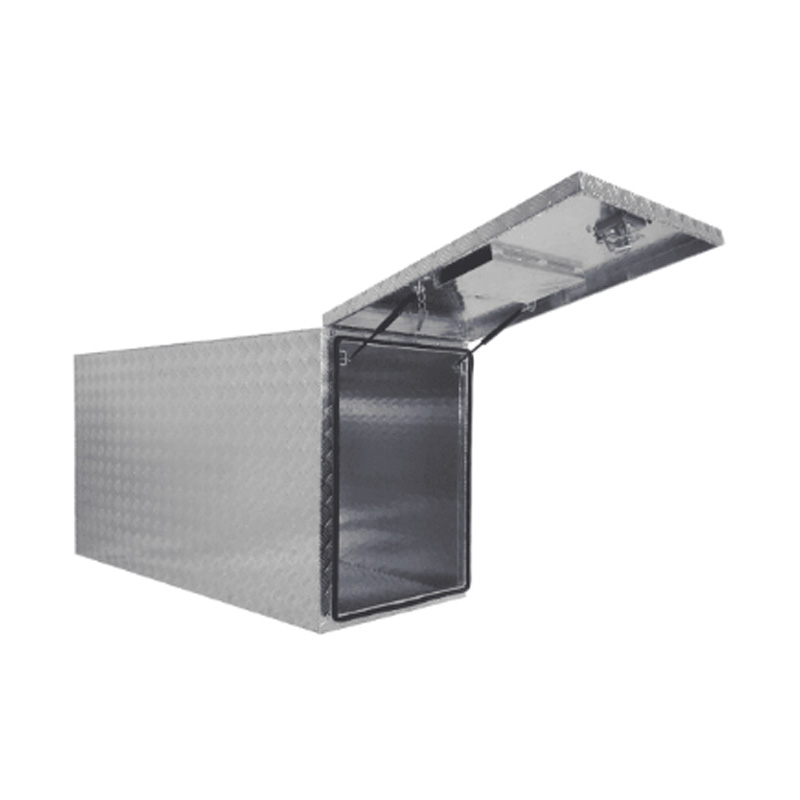 Full Side Opening Door Trailer Drawbar Aluminum Toolboxavaiable f...
Full Side Opening Door Trailer Drawbar Aluminum Toolboxavaiable f...
-
- Trailer Mower Box >
- Trailer H Bar >
- Trailer Spare Wheel Holder >
-
Toolbox Accessories
>
- Toolbox Mounting Kit >
-
Toolbox Locks
>
-
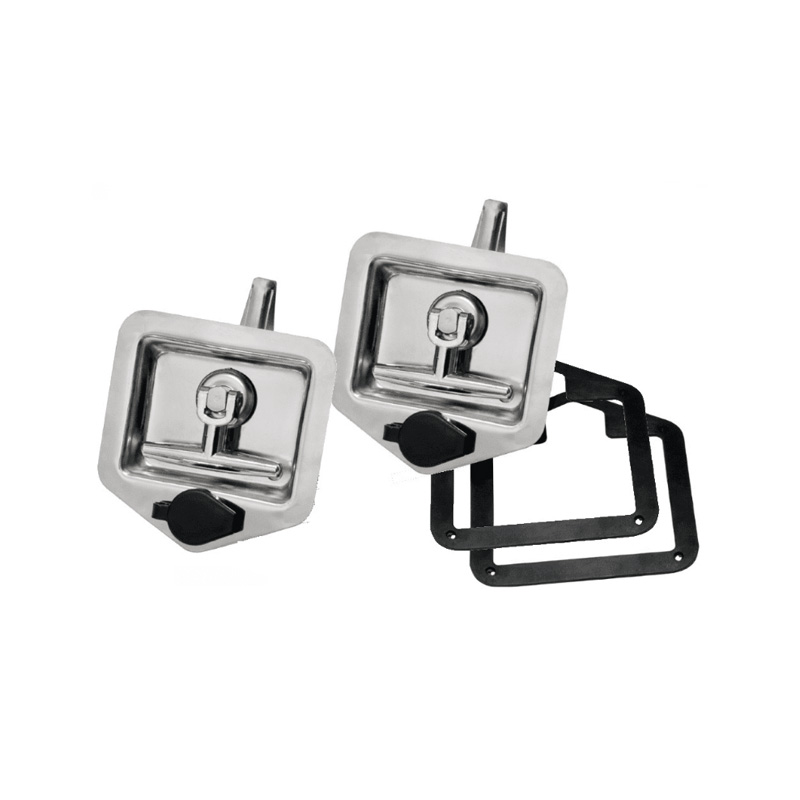 Stainless Steel T-Lock STUD MountMaterial: ...
Stainless Steel T-Lock STUD MountMaterial: ... -
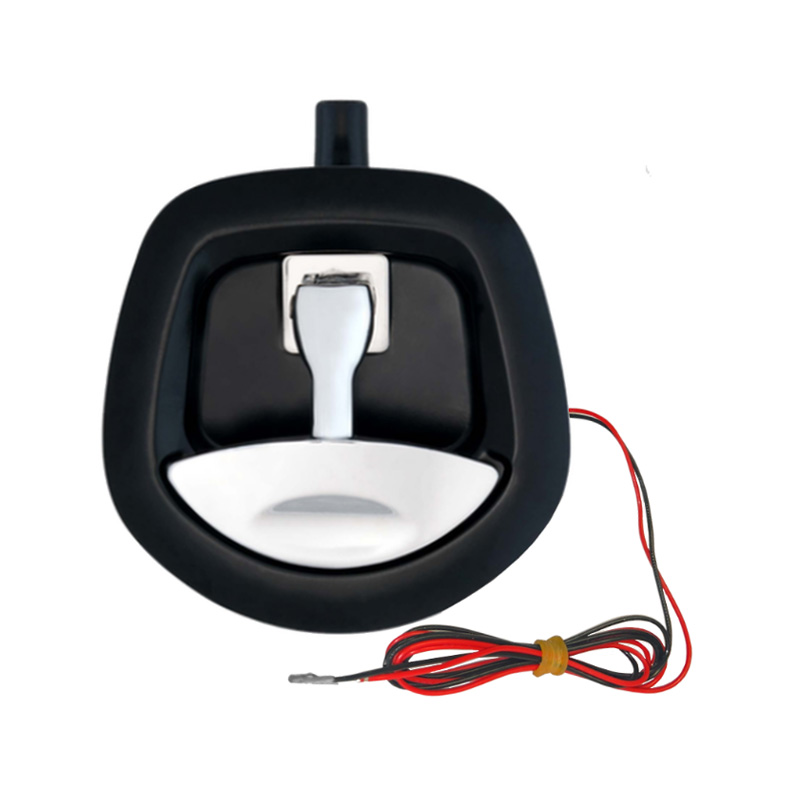 12V Recessed Folding Padlock Friendly Whale Tail Handle ACT-WTLOCKKey lockin...
12V Recessed Folding Padlock Friendly Whale Tail Handle ACT-WTLOCKKey lockin... -
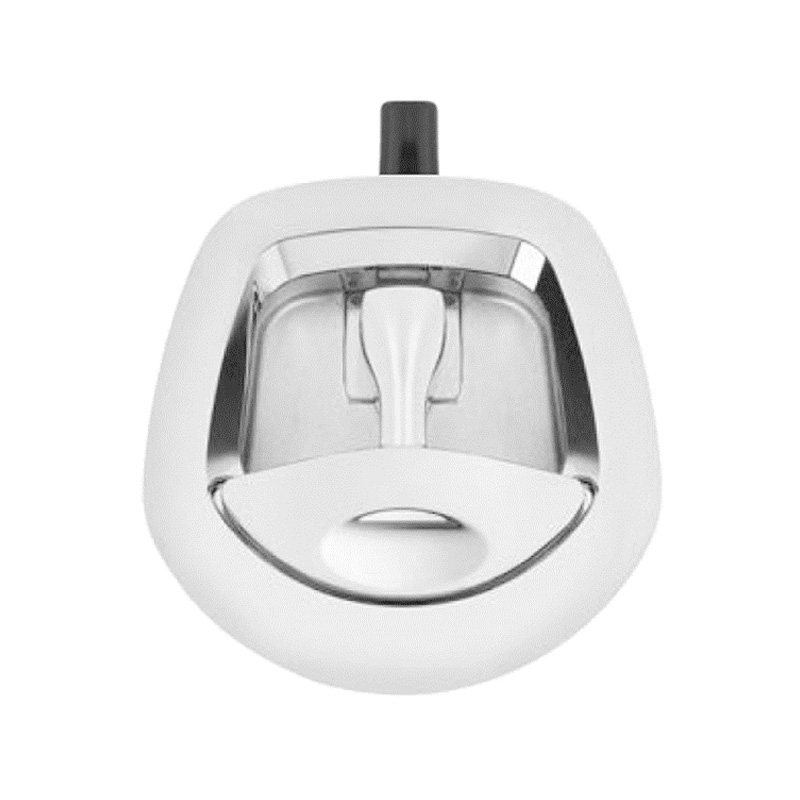 Whale Tail T-Lock Padlockable Whale Tail HandleKey lockin...
Whale Tail T-Lock Padlockable Whale Tail HandleKey lockin... -
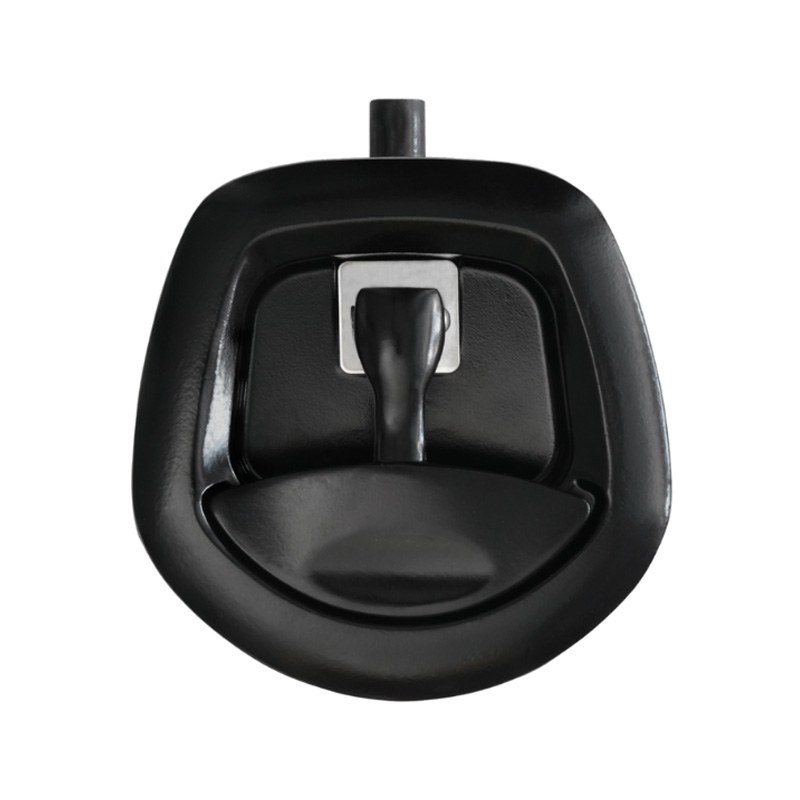 Black Whale Tail T-Lock Padlockable Whale Tail HandleKey lockin...
Black Whale Tail T-Lock Padlockable Whale Tail HandleKey lockin... -
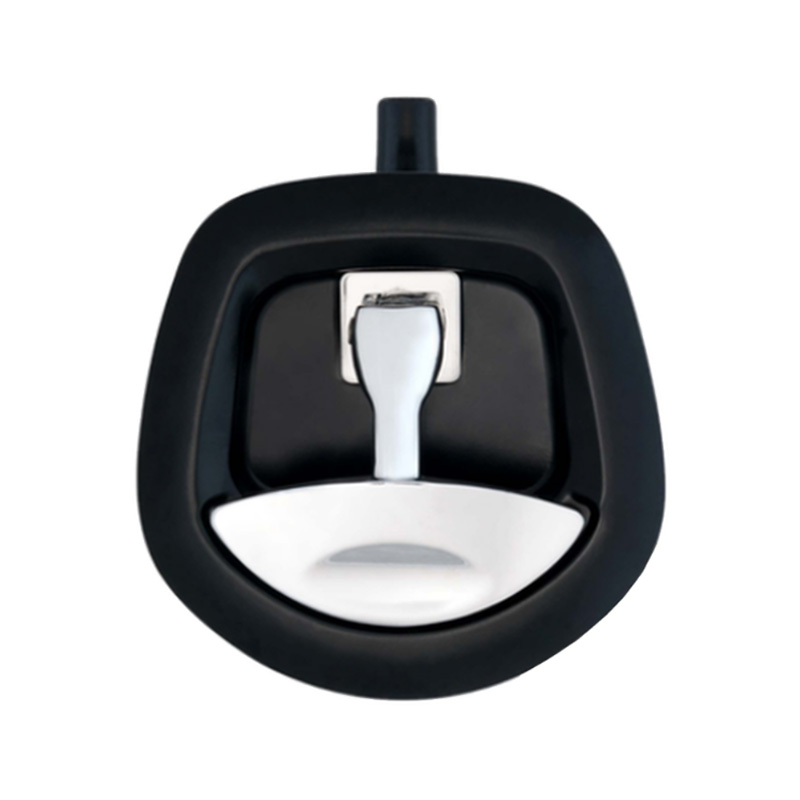 Chome & Black Whale Tail T-Lock Padlockable Whale Tail HandleKey lockin...
Chome & Black Whale Tail T-Lock Padlockable Whale Tail HandleKey lockin... -
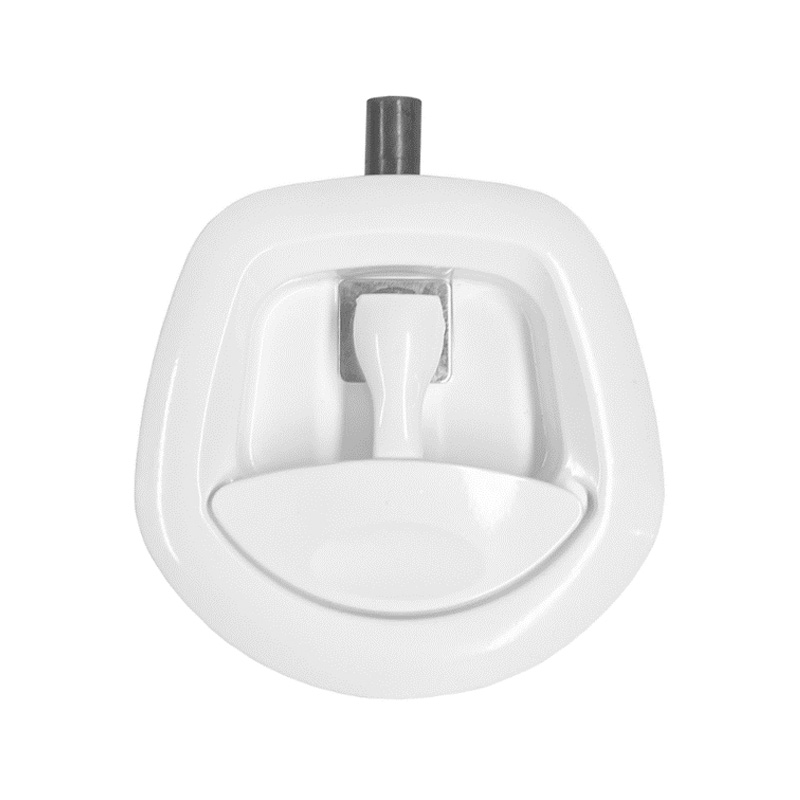 White Whale Tail T-Lock Padlockable Whale Tail HandleKey lockin...
White Whale Tail T-Lock Padlockable Whale Tail HandleKey lockin...
-
-
Toolbox Drawer Unites
>
-
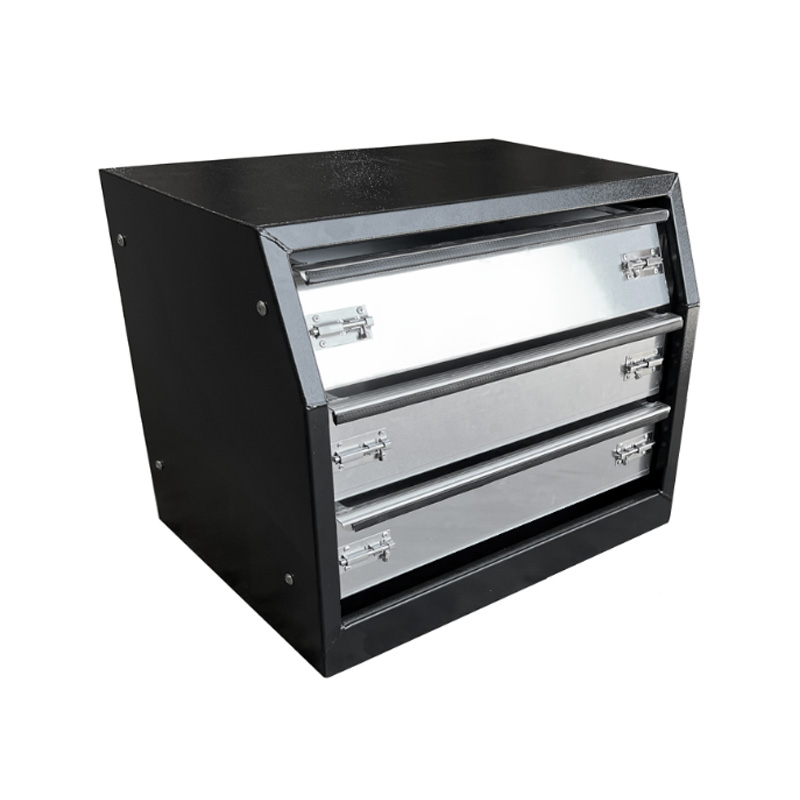 600 x 430 x 450mm Black Aluminium 3 Drawer Unit for Ute Truck Tool box Canopy Caravan Tool BoxThickness:...
600 x 430 x 450mm Black Aluminium 3 Drawer Unit for Ute Truck Tool box Canopy Caravan Tool BoxThickness:... -
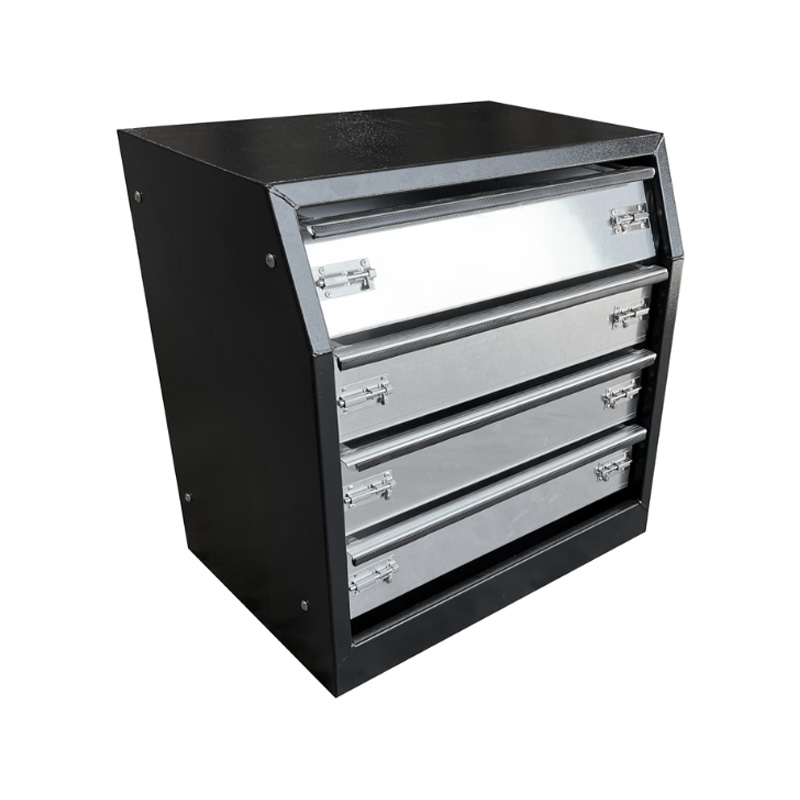 600 x 430 x 620mm Black Aluminium 4 Drawer Unit for Ute Truck Tool box Canopy Caravan Tool BoxThickness:...
600 x 430 x 620mm Black Aluminium 4 Drawer Unit for Ute Truck Tool box Canopy Caravan Tool BoxThickness:... -
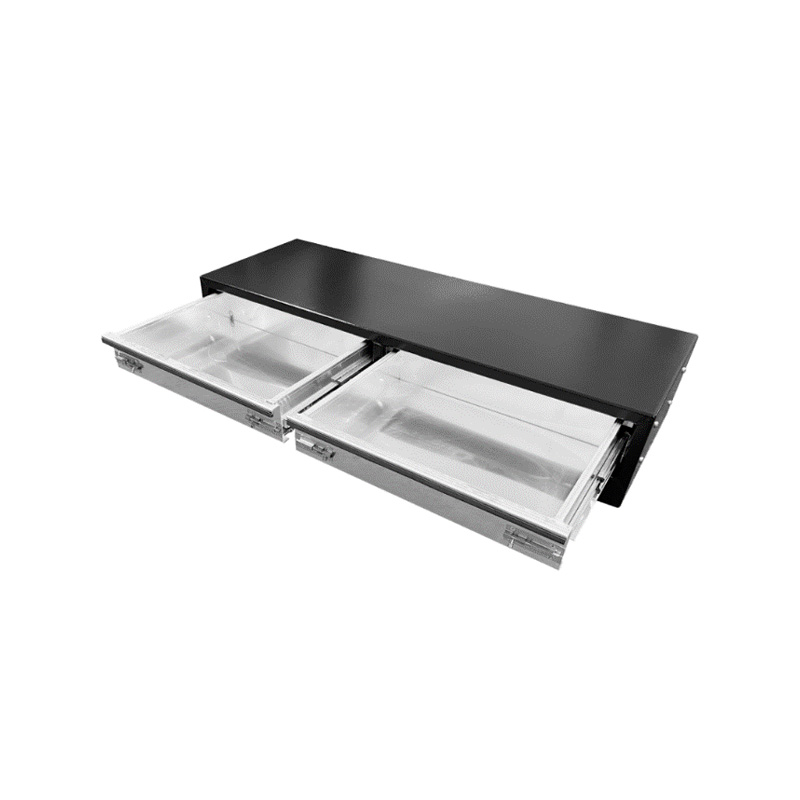 1020 x 440 x 230mm Black Aluminium 2 Drawer Unit for Ute Truck Tool box Canopy Caravan ToolboxThickness:...
1020 x 440 x 230mm Black Aluminium 2 Drawer Unit for Ute Truck Tool box Canopy Caravan ToolboxThickness:... -
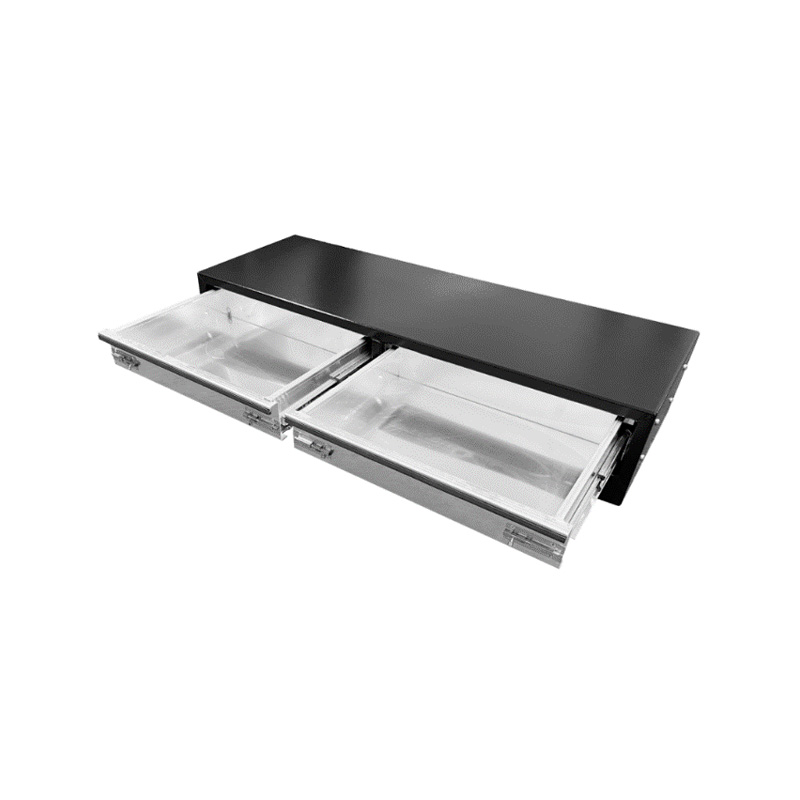 1220 x 440 x 230mm Black Aluminium 2 Drawer Unit for Ute Truck Tool box Canopy Caravan ToolboxThickness:...
1220 x 440 x 230mm Black Aluminium 2 Drawer Unit for Ute Truck Tool box Canopy Caravan ToolboxThickness:... -
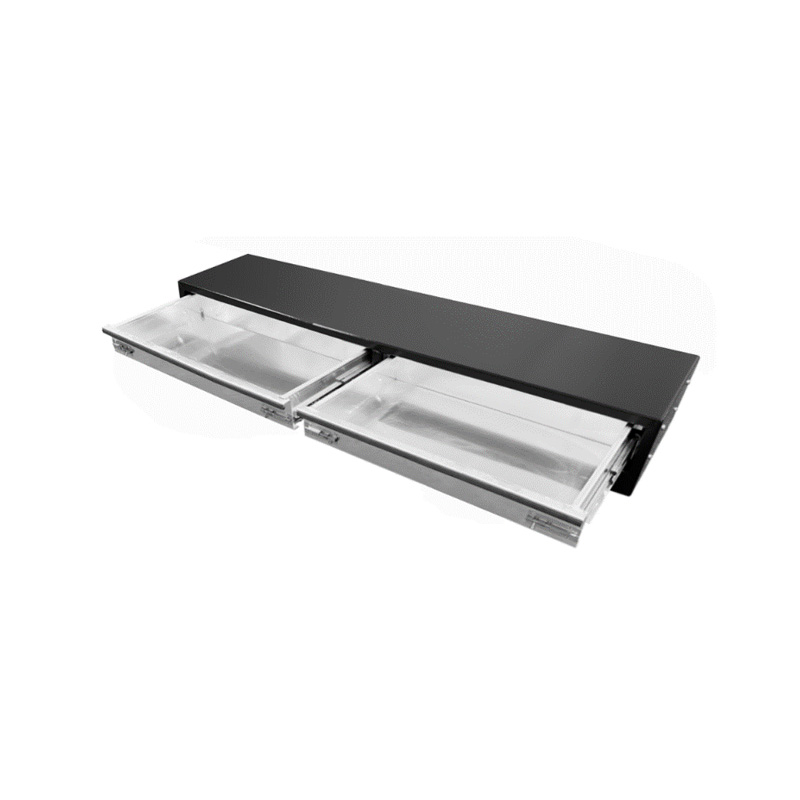 520 x 440 x 230mm Black Aluminium 2 Drawer Unit for Ute Truck Tool box Canopy Caravan ToolboxThickness:...
520 x 440 x 230mm Black Aluminium 2 Drawer Unit for Ute Truck Tool box Canopy Caravan ToolboxThickness:... -
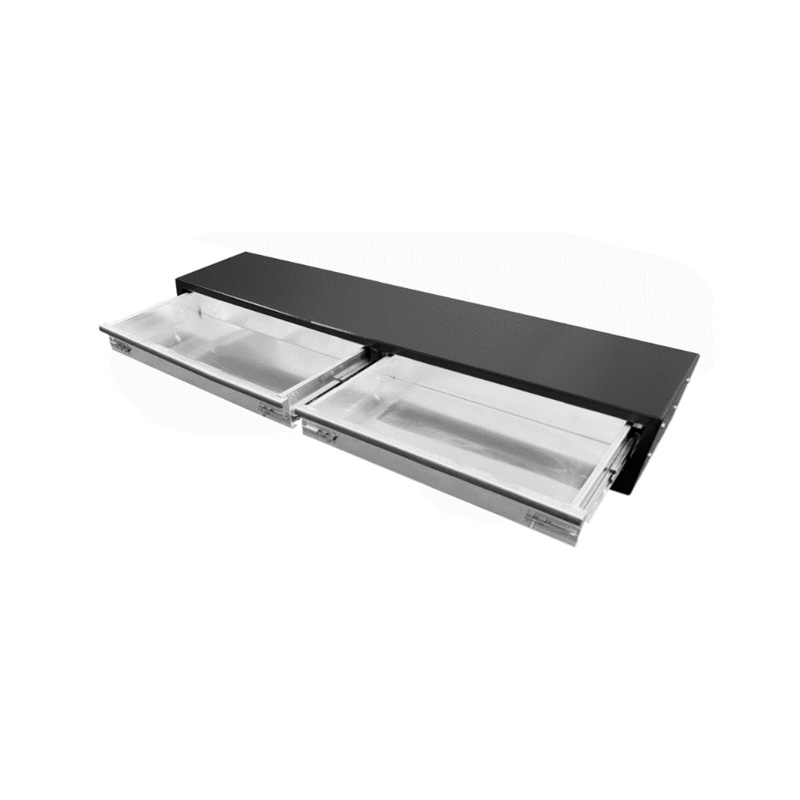 1920 x 440 x 230mm Black Aluminium 2 Drawer Unit for Ute Truck Tool box Canopy Caravan Tool BoxThickness:...
1920 x 440 x 230mm Black Aluminium 2 Drawer Unit for Ute Truck Tool box Canopy Caravan Tool BoxThickness:... -
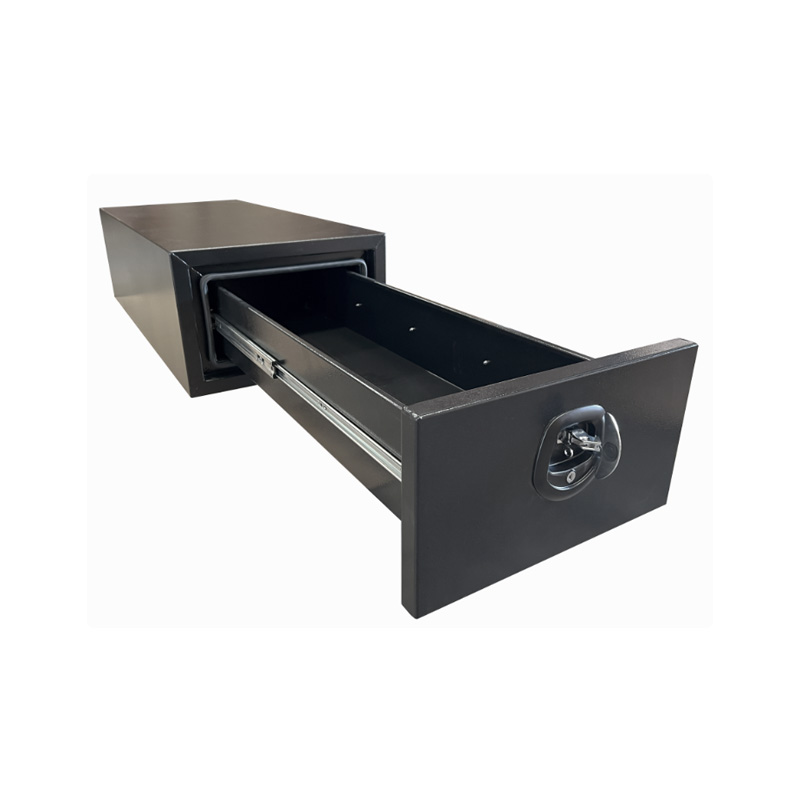 1400 x 600 x 380mm 1 Drawer Unit for Ute Truck Tool box Canopy Caravan ToolboxThickness:...
1400 x 600 x 380mm 1 Drawer Unit for Ute Truck Tool box Canopy Caravan ToolboxThickness:... -
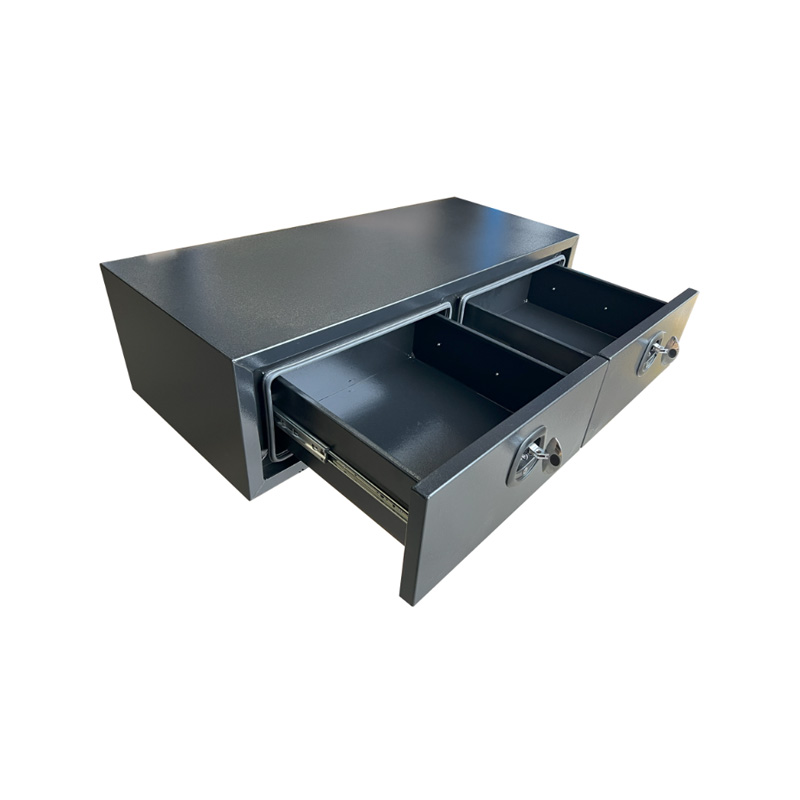 1400 x 600 x 380mm 2 Drawer Unit for Ute Truck Tool box Canopy Caravan ToolboxThickness:...
1400 x 600 x 380mm 2 Drawer Unit for Ute Truck Tool box Canopy Caravan ToolboxThickness:... -
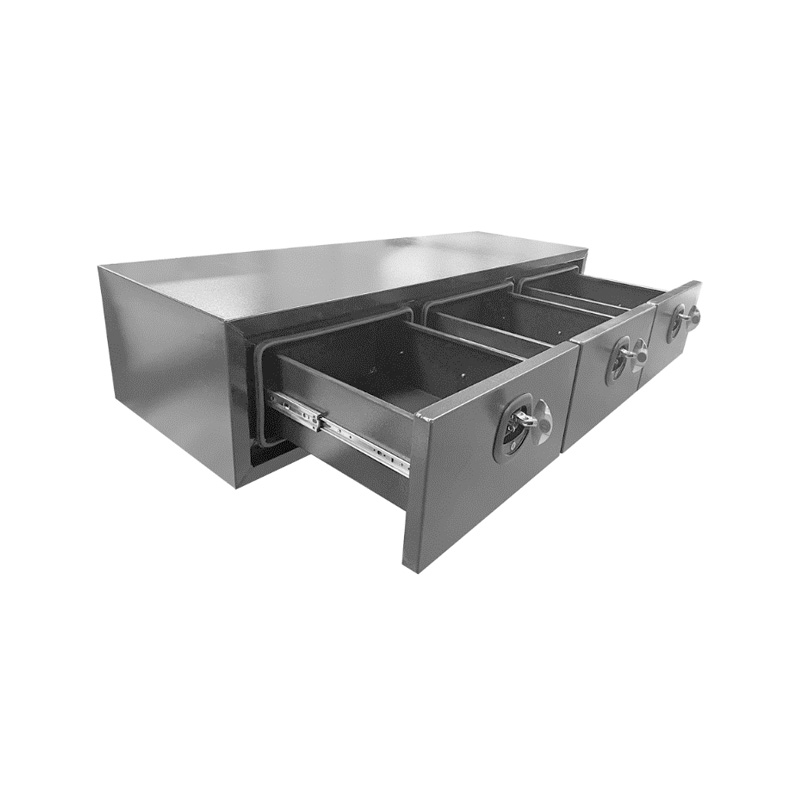 1700 x 600 x 380mm 3 Drawer Unit for Ute Truck Tool box Canopy Caravan ToolboxThickness:...
1700 x 600 x 380mm 3 Drawer Unit for Ute Truck Tool box Canopy Caravan ToolboxThickness:... -
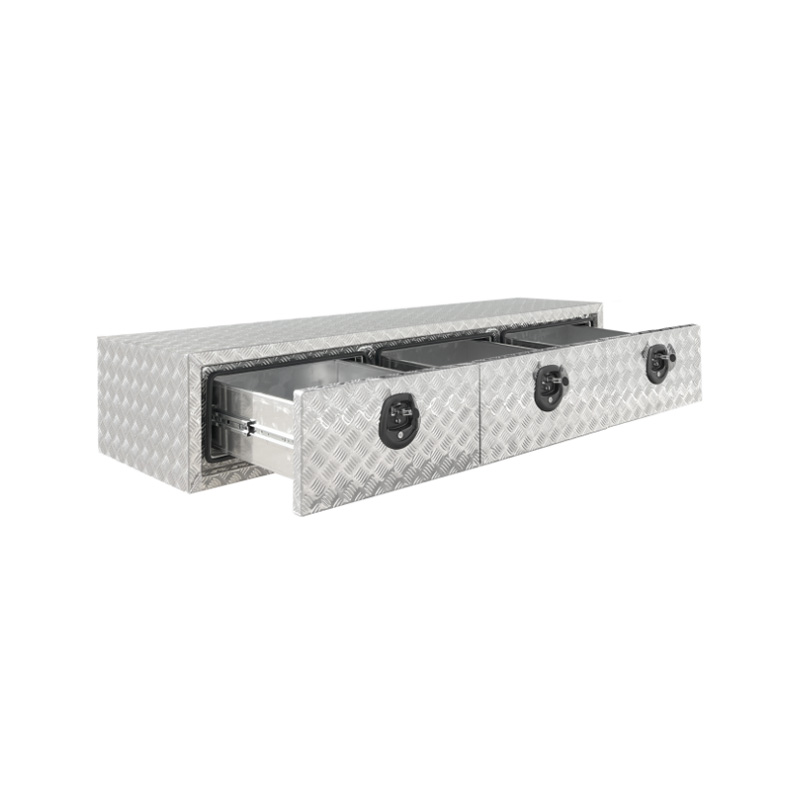 1900 x 600 x 380mm 3 Drawer Unit for Ute Truck Tool box Canopy Caravan ToolboxThickness:...
1900 x 600 x 380mm 3 Drawer Unit for Ute Truck Tool box Canopy Caravan ToolboxThickness:... -
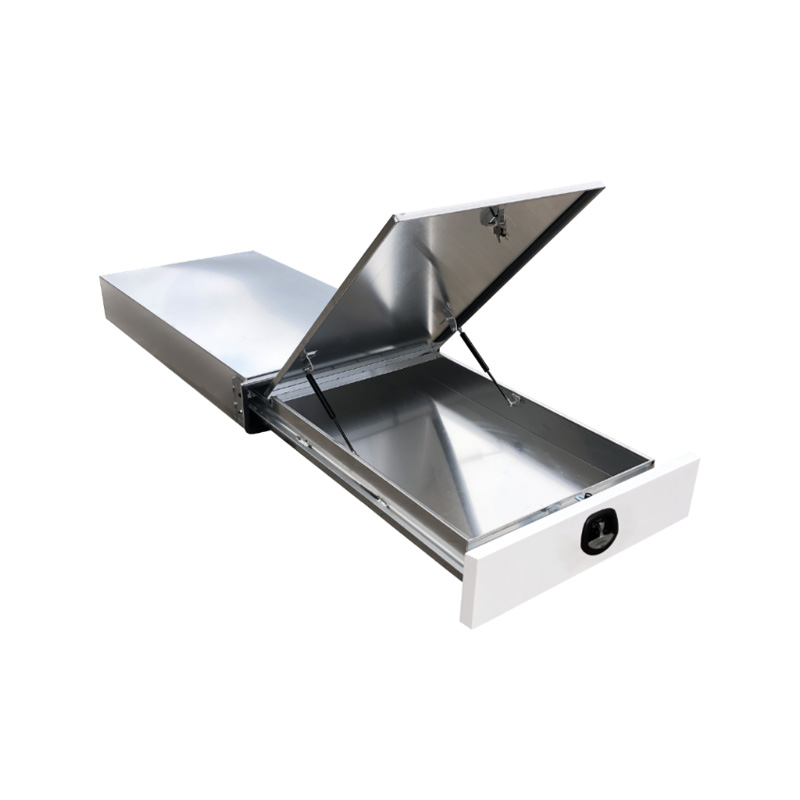 1.4m Aluminium Ute Tool box Under Tray Toolbox Trundle Roller Tray Slide Out Drawer Toolbox Benchtop LidThickness:...
1.4m Aluminium Ute Tool box Under Tray Toolbox Trundle Roller Tray Slide Out Drawer Toolbox Benchtop LidThickness:... -
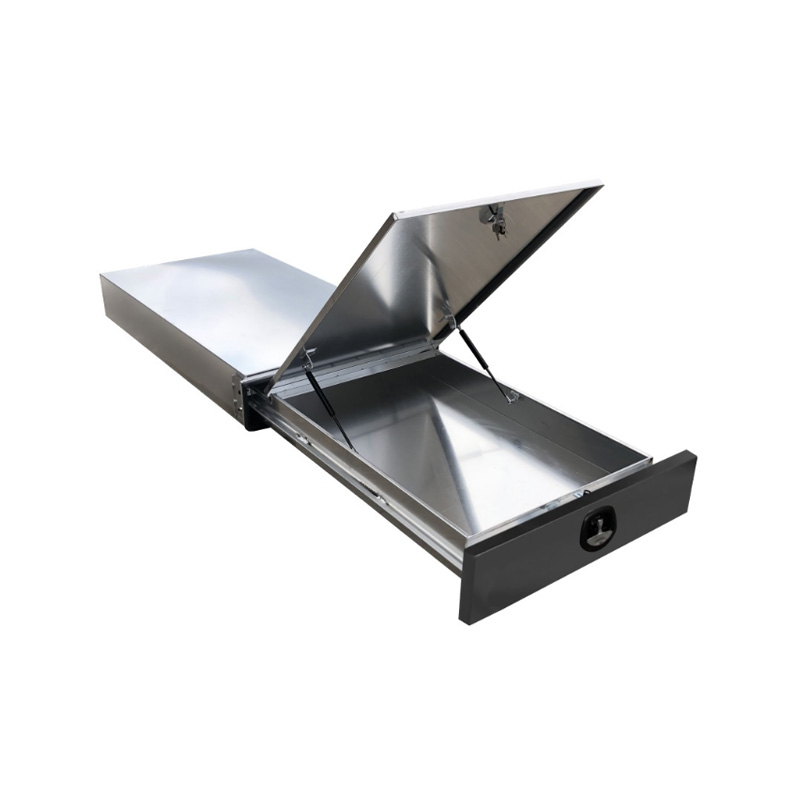 1.6m Aluminium Ute Tool box Under Tray Toolbox Trundle Roller Tray Slide Out Drawer Toolbox Benchtop LidThickness:...
1.6m Aluminium Ute Tool box Under Tray Toolbox Trundle Roller Tray Slide Out Drawer Toolbox Benchtop LidThickness:... -
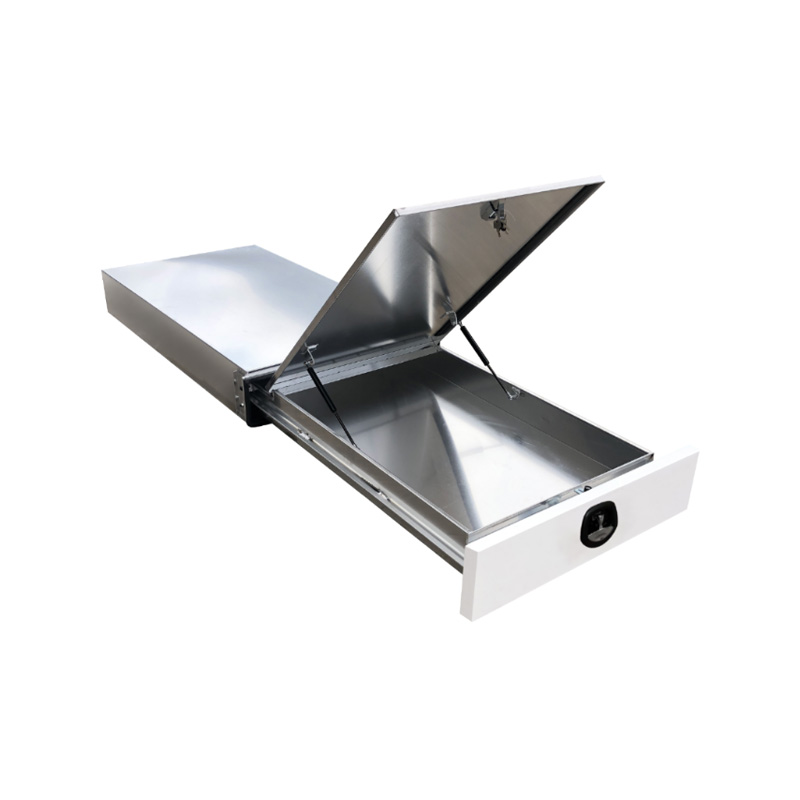 1.7m Aluminium Ute Tool box Under Tray Toolbox Trundle Roller Tray Slide Out Drawer Toolbox Benchtop LidThickness:...
1.7m Aluminium Ute Tool box Under Tray Toolbox Trundle Roller Tray Slide Out Drawer Toolbox Benchtop LidThickness:...
-
-
Toolbox Shelves
>
-
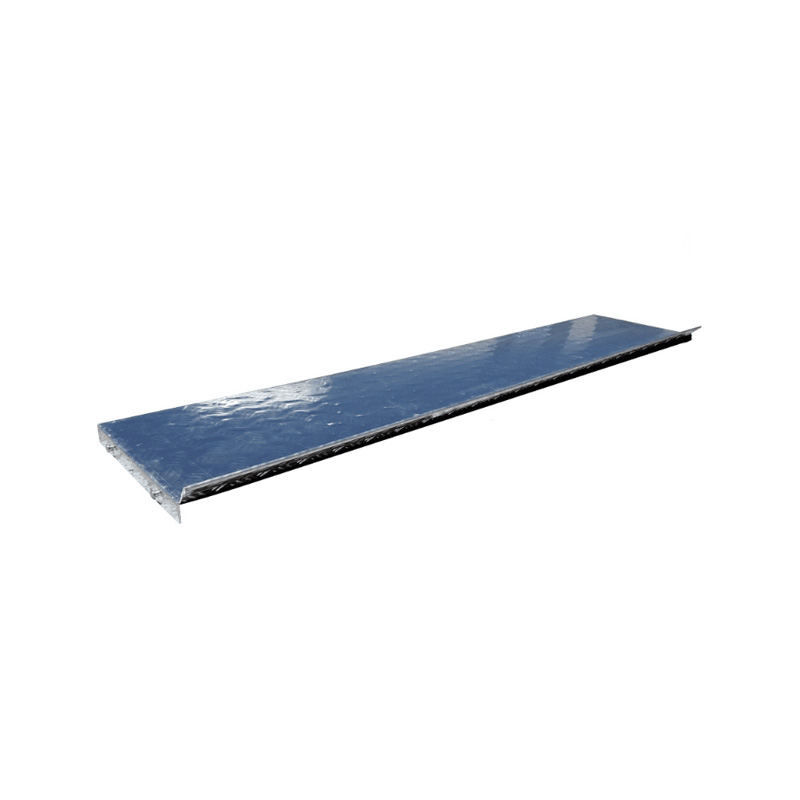 0.9m Shelf - For Aluminium Storage Toolbox Tool BoxThickness:...
0.9m Shelf - For Aluminium Storage Toolbox Tool BoxThickness:... -
 1.2m Shelf - For Aluminium Storage Toolbox Tool BoxThickness:...
1.2m Shelf - For Aluminium Storage Toolbox Tool BoxThickness:... -
 1.4m Shelf - For Aluminium Storage Toolbox Tool BoxThickness:...
1.4m Shelf - For Aluminium Storage Toolbox Tool BoxThickness:... -
 1.5m Shelf - For Aluminium Storage Toolbox Tool BoxThickness:...
1.5m Shelf - For Aluminium Storage Toolbox Tool BoxThickness:... -
 1.6m Shelf - For Aluminium Storage Toolbox Tool BoxThickness:...
1.6m Shelf - For Aluminium Storage Toolbox Tool BoxThickness:... -
 1.7m Shelf - For Aluminium Storage Toolbox Tool BoxThickness:...
1.7m Shelf - For Aluminium Storage Toolbox Tool BoxThickness:... -
 1.8m Shelf - For Aluminium Storage Toolbox Tool BoxThickness:...
1.8m Shelf - For Aluminium Storage Toolbox Tool BoxThickness:... -
 1.9m Shelf - For Aluminium Storage Toolbox Tool BoxThickness:...
1.9m Shelf - For Aluminium Storage Toolbox Tool BoxThickness:... -
 1.94m Shelf - For Aluminium Storage Toolbox Tool BoxThickness:...
1.94m Shelf - For Aluminium Storage Toolbox Tool BoxThickness:... -
 2.1m Shelf - For Aluminium Storage Toolbox Tool BoxThickness:...
2.1m Shelf - For Aluminium Storage Toolbox Tool BoxThickness:...
-
-
Gas Strut
>
-
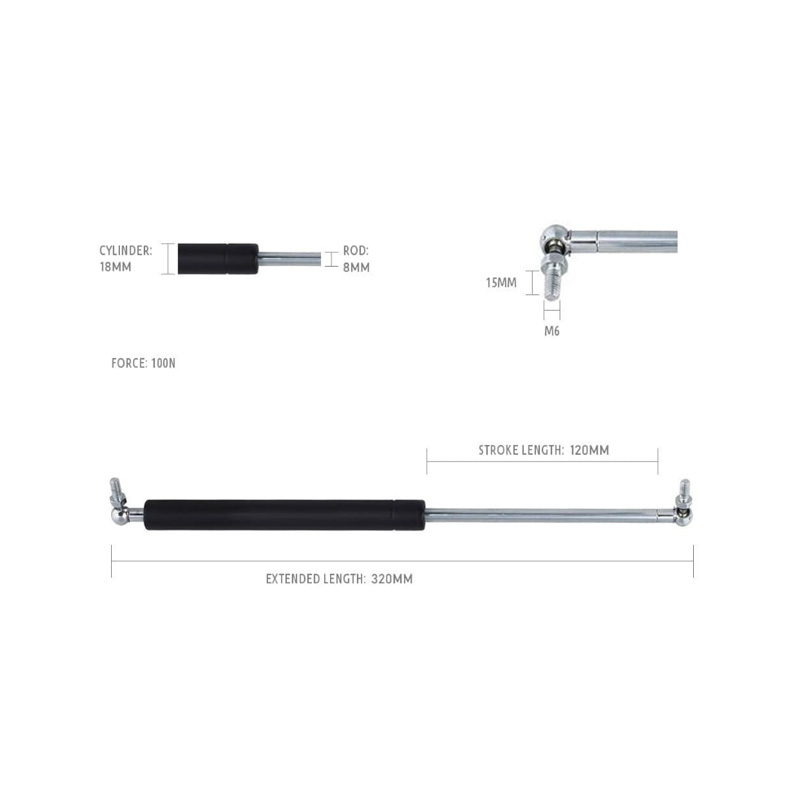 Gas Strut 120-320/100N GS120-320-100NExtended L...
Gas Strut 120-320/100N GS120-320-100NExtended L... -
 Gas Strut 120-320/180N GS120-320-180NExtended L...
Gas Strut 120-320/180N GS120-320-180NExtended L... -
 Gas Strut 120-320/300N GS120-320-300NExtended L...
Gas Strut 120-320/300N GS120-320-300NExtended L... -
 Gas Strut 120-320/380N GS120-320-380NExtended L...
Gas Strut 120-320/380N GS120-320-380NExtended L... -
 Gas Strut 230-540/260N GS230-540-260NExtended L...
Gas Strut 230-540/260N GS230-540-260NExtended L... -
 Gas Strut 230-540/300N GS230-540-300NExtended L...
Gas Strut 230-540/300N GS230-540-300NExtended L... -
 Gas Strut 230-540/350N GS230-540-350NExtended L...
Gas Strut 230-540/350N GS230-540-350NExtended L... -
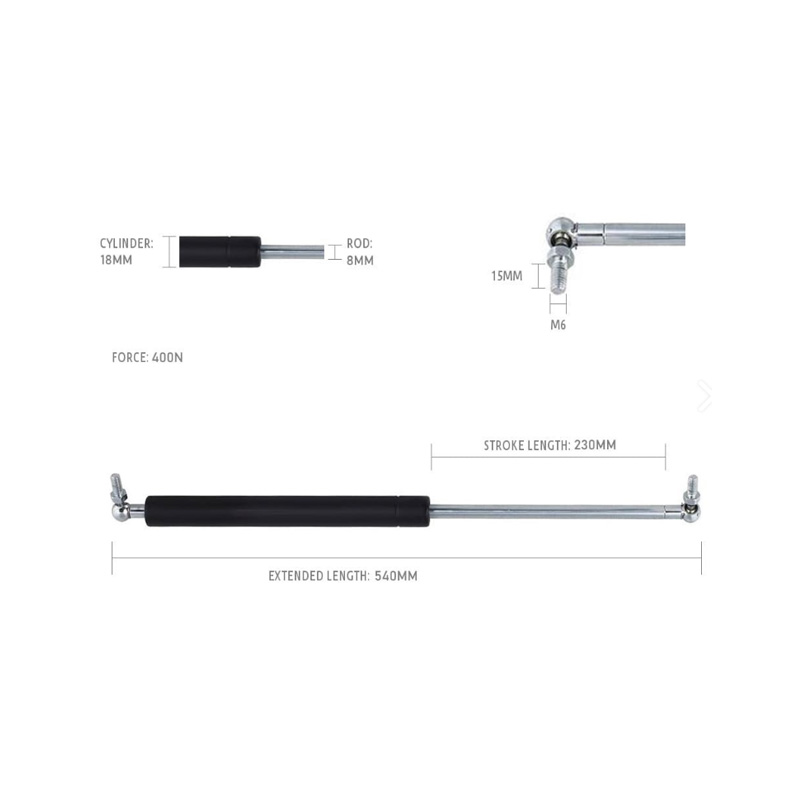 Gas Strut 230-540/400N GS230-540-400NExtended L...
Gas Strut 230-540/400N GS230-540-400NExtended L...
-
- Ladder Rack >
- Canopy Ladder >
- Toolbox Cargo Cage >
- Toolbox Rear Gate >
-
Fuel Gas Tool Holder
>
-
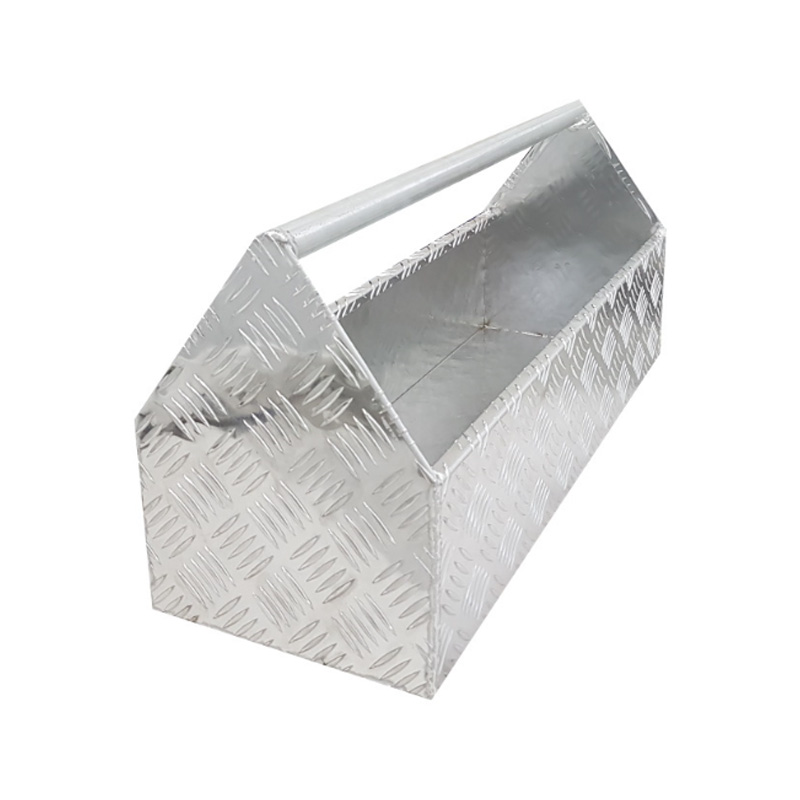 600 x 230 x 290mm Aluminium Tool Storage Handle Holder Heavy Duty ToteThickness:...
600 x 230 x 290mm Aluminium Tool Storage Handle Holder Heavy Duty ToteThickness:... -
 320 x 320 x 320mm Aluminium Checker Camping Camper 4x4 Ute Truck Trailer Gas Bottle HolderSize Lengt...
320 x 320 x 320mm Aluminium Checker Camping Camper 4x4 Ute Truck Trailer Gas Bottle HolderSize Lengt... -
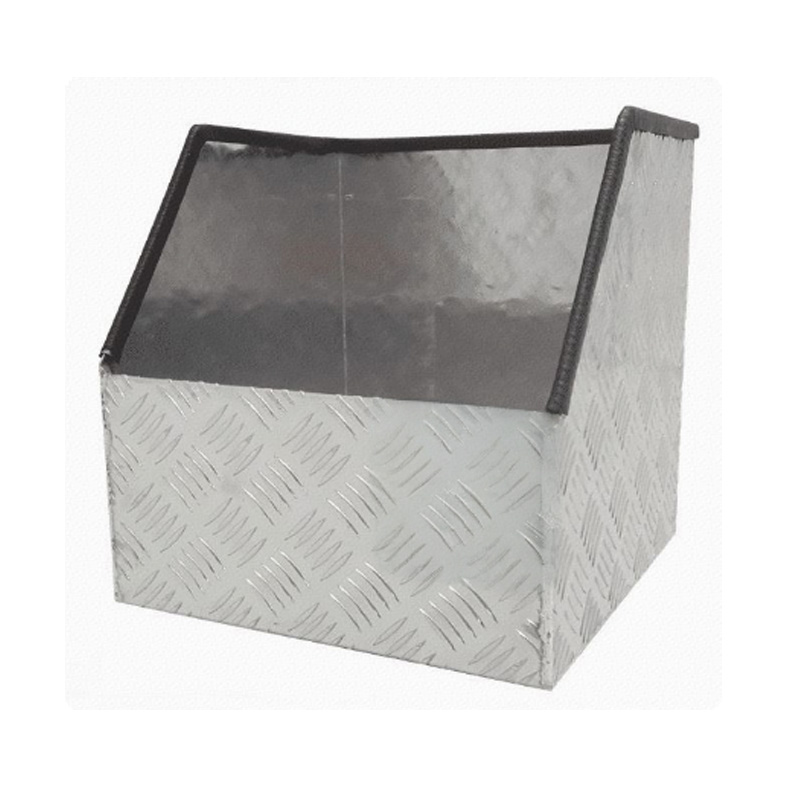
 450 x 230 x 300mm Aluminium Checker Camping Camper 4x4 Ute Truck Acetylene Oxy Gas Bottle Holder with DividerThickness:...
450 x 230 x 300mm Aluminium Checker Camping Camper 4x4 Ute Truck Acetylene Oxy Gas Bottle Holder with DividerThickness:... -
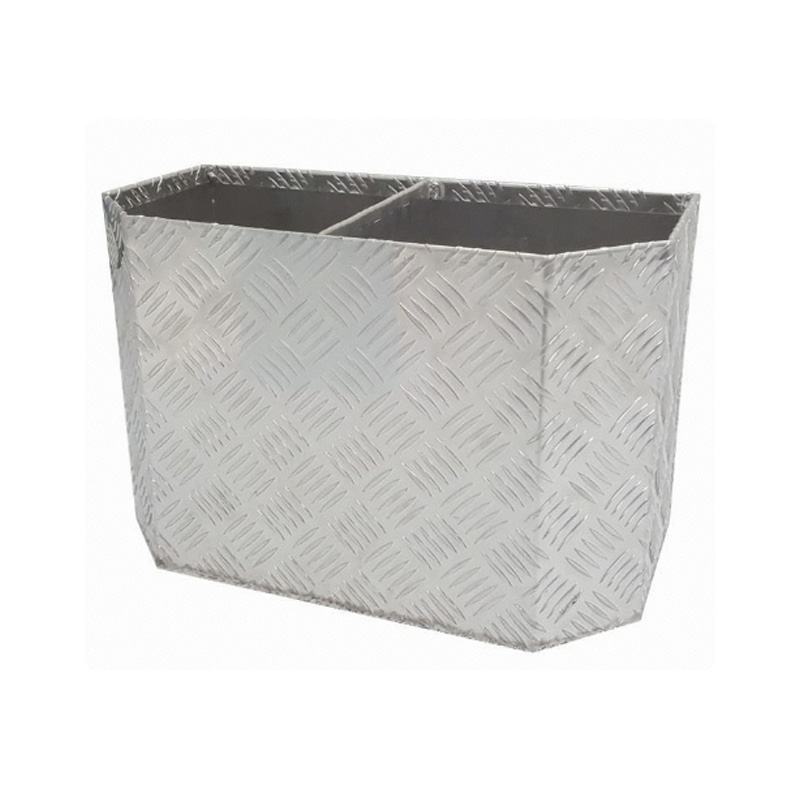
 450 x 230 x 380mm Aluminium Camping 4x4 Ute Truck Acetylene Oxy Gas Bottle Holder with DividerThickness:...
450 x 230 x 380mm Aluminium Camping 4x4 Ute Truck Acetylene Oxy Gas Bottle Holder with DividerThickness:... -
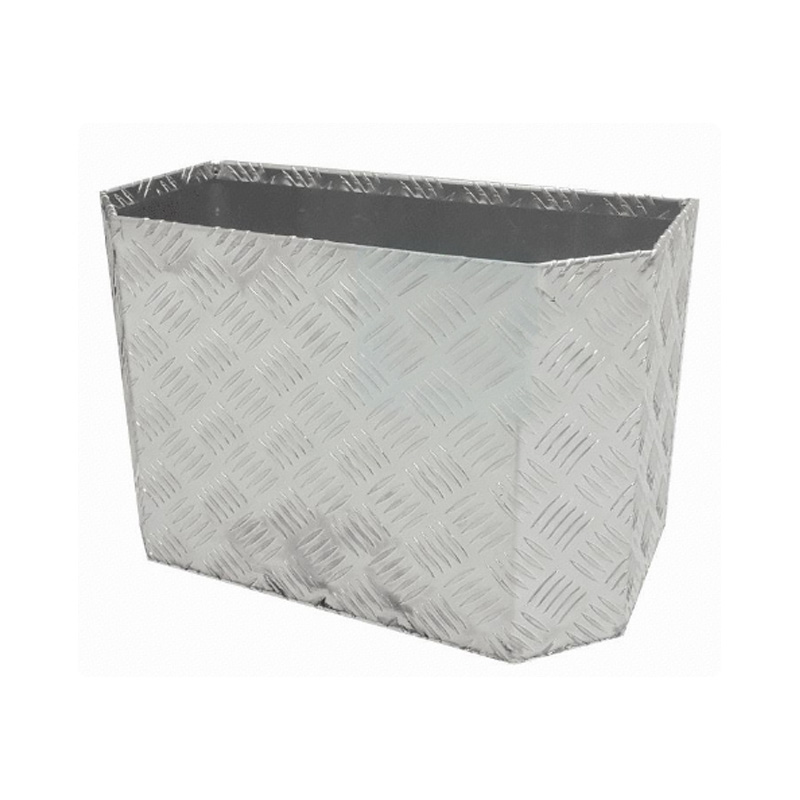 450 x 230 x 300mm Aluminium Checker Camping Camper 4x4 Ute Truck Acetylene Oxy Gas Bottle HolderThickness:...
450 x 230 x 300mm Aluminium Checker Camping Camper 4x4 Ute Truck Acetylene Oxy Gas Bottle HolderThickness:... -
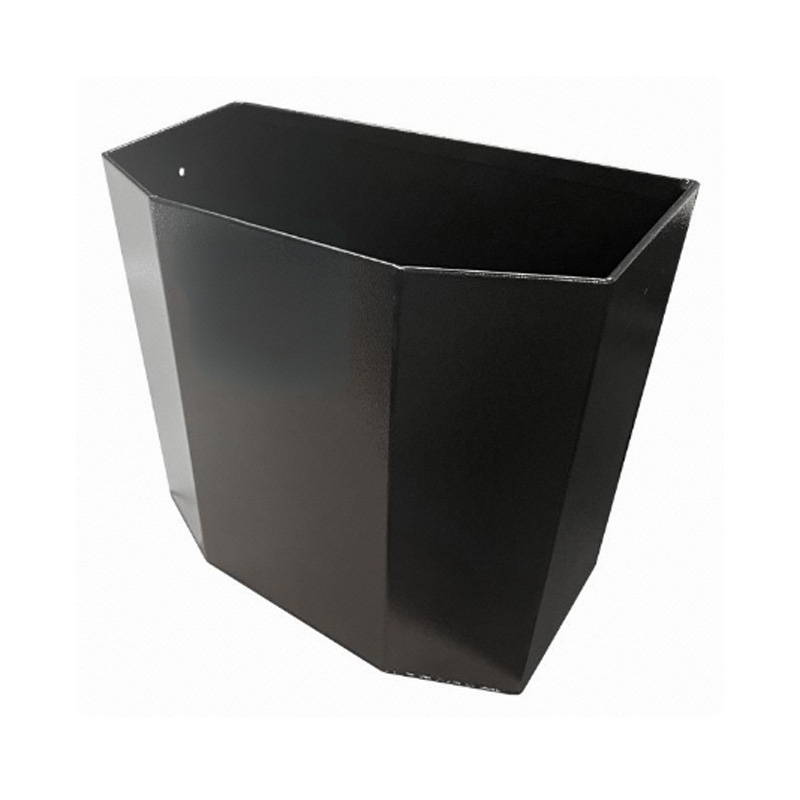 450 x 230 x 380mm Aluminium Camping 4x4 Ute Truck Acetylene Oxy Gas Bottle HolderSize Lengt...
450 x 230 x 380mm Aluminium Camping 4x4 Ute Truck Acetylene Oxy Gas Bottle HolderSize Lengt... -
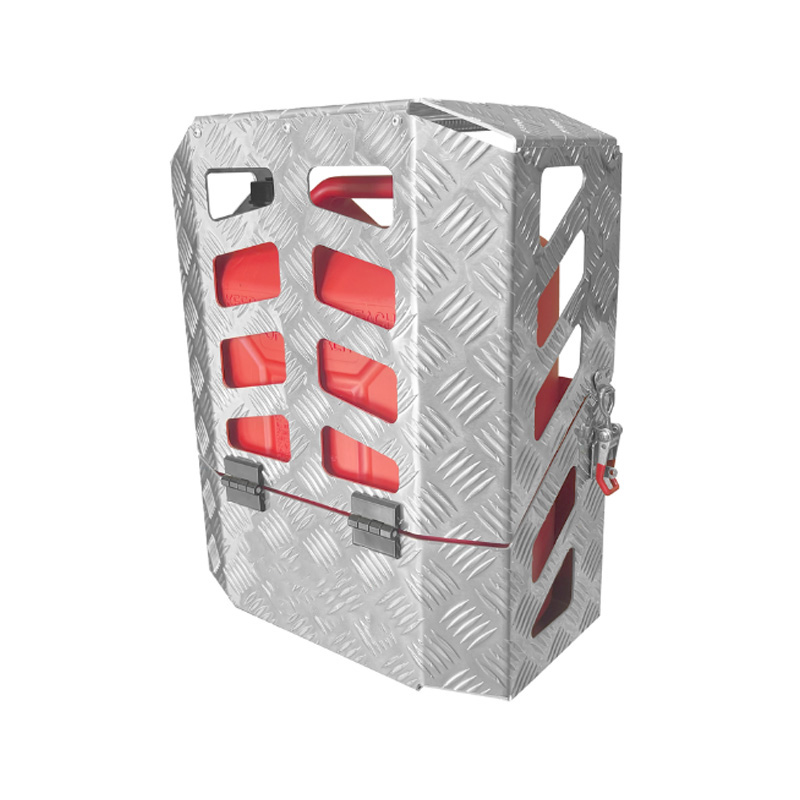 400 x 220 x 500mm Checker Aluminium Ute Camping Camper Jerry Can Bottle Holder Pad lockable Tool BoxThickness:...
400 x 220 x 500mm Checker Aluminium Ute Camping Camper Jerry Can Bottle Holder Pad lockable Tool BoxThickness:... -
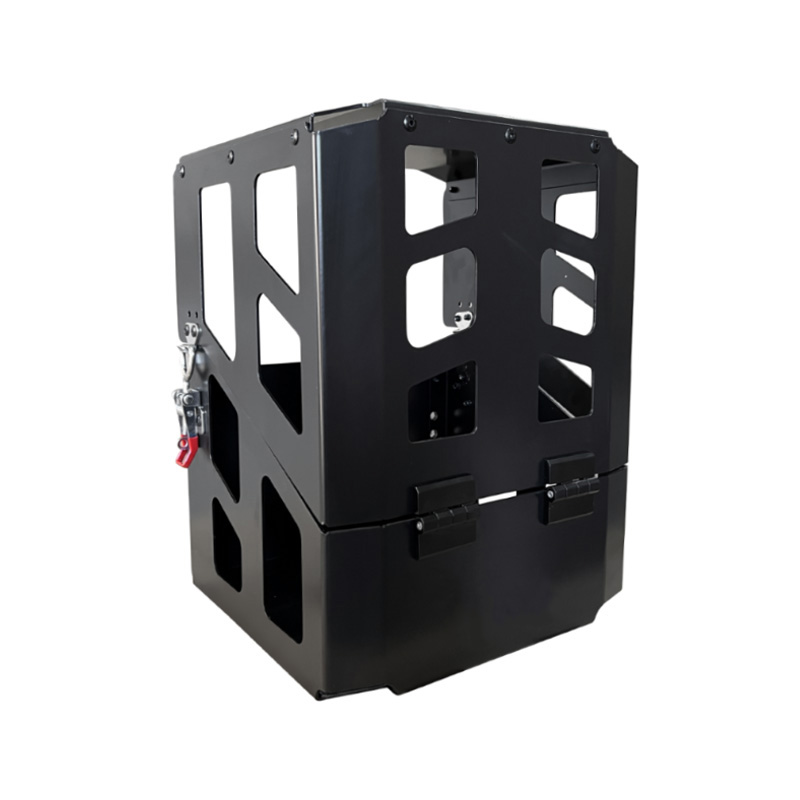 335 x 285 x 400mm 4.5kg Aluminium Gas Bottle HolderThickness:...
335 x 285 x 400mm 4.5kg Aluminium Gas Bottle HolderThickness:... -
 361 x 196 x 303mm Flat Aluminium Ute Camping Camper Jerry Can Bottle Holder Tool BoxThickness:...
361 x 196 x 303mm Flat Aluminium Ute Camping Camper Jerry Can Bottle Holder Tool BoxThickness:...
-
- Jack off Legs >
-
Trailers Accessories
>
- About
- News
- Contact
Web Menu
- Home
- TRAILERS
- TOOLBOXES
- ACCESSORIES
- About
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
When Did the Aluminium Toolbox Appear and How Did It Develop?
Early Origins and the Move Toward Metal Tool Storage

Tool storage has existed for centuries, with early craftspeople relying on wooden chests or leather pouches to carry tools. These materials were widely available and easy to shape, making them practical for the time. However, they also had limitations: wood absorbed moisture and could become heavy when damp, and leather softened or cracked depending on the environment. As industrial work expanded in the late 1800s and early 1900s, workers needed storage options that could withstand new kinds of tasks, such as factory labor, mechanical repair, and construction.
The idea of a metal toolbox began to take shape when steel and tin containers became more common for industrial use. In the early 20th century, metal storage boxes were used for durable goods, ammunition, and equipment. These designs influenced the generation of metal toolboxes, which appeared in the mid-20th century. While these early versions were mainly made from steel, they set the foundation for later aluminium designs. Steel toolboxes provided durability but were relatively heavy, especially when loaded with tools.
The aluminium toolbox emerged as an alternative when workers sought strong yet lighter storage solutions. Although aluminium had been used in transportation and aviation since the early 1900s, it took a few decades before manufacturing costs lowered enough to make aluminium consumer products—including toolboxes—more accessible.
Introduction of Aluminium and Material Advancements
Aluminium toolboxes started gaining recognition around the mid to late 20th century, as aluminium processing became more efficient. The material offered several properties that suited professional work: lower density compared to steel, natural corrosion resistance, and good formability. These qualities made aluminium competitive in industries such as construction, automotive repair, and utility work.
Manufacturers soon tailored alloys specifically for storage products. Aluminium alloys containing small amounts of magnesium or silicon offered enhanced strength while remaining lightweight. This shift allowed toolboxes to withstand frequent handling and exposure to outdoor environments without significant deterioration.
Another key advancement was the use of patterned aluminium sheets. Diamond plate, also called checker plate, became a defining feature of many aluminium toolboxes. The raised pattern improved grip, reduced slipping, and enhanced surface rigidity. Over time, both polished and matte finishes were introduced to satisfy appearance and functional needs.
These material improvements were part of a broader trend toward efficient, long-lasting storage options, driven by changing expectations in manual labor environments.
Structural Improvements and Evolving Designs
As aluminium toolboxes gained popularity, their structural design evolved to meet new demands. Early versions were simple rectangular boxes with hinged lids. Over time, designers introduced more sophisticated configurations suitable for different tasks and installation locations.
One significant development was the integration of reinforced corners and edges. Because aluminium is softer than steel, reinforcement increased impact resistance and extended lifespan. Hinges, latches, and lock mechanisms were also upgraded to reduce wear during repeated opening and closing.
Another major shift was the diversification of toolbox styles. Instead of a single model, manufacturers introduced side-mount boxes for trucks, cross-bed boxes, underbody storage units, portable hand-carry toolboxes, and jobsite chests. This variety supported changing work environments, especially as utility vehicles became central to many trades.
Weather sealing also became more important as toolboxes increasingly served outdoor applications. Rubber gaskets, overlapping lids, and improved welding techniques helped reduce water intrusion. Meanwhile, internal organization improved with removable trays, dividers, and foam inserts designed for tool protection.
These structural enhancements show how aluminium toolboxes transitioned from simple containers to specialized storage systems.
Modern Applications and Future Trends
Today, aluminium toolboxes are widely used across multiple industries. Construction workers rely on them to store heavy-duty tools, while contractors use them in vehicles to protect equipment during transportation. Outdoor enthusiasts adopt aluminium boxes for camping gear, aid supplies, or off-road storage. The material's resistance to moisture and temperature changes makes it suitable for both indoor and outdoor conditions.
In recent years, manufacturers have incorporated modern production technologies such as CNC forming, laser cutting, and automated welding. These methods increase precision and allow for customized shapes that fit specific vehicles or tasks. Powder coating, anodizing, and color finishing have also expanded design possibilities, enabling users to match toolboxes with equipment or personal style preferences.
Looking ahead, development may continue toward more ergonomic designs, hybrid-material structures, and improved security systems. Integration of smart features, such as electronic locks or inventory-tracking compartments, reflects ongoing innovation in storage solutions.
Post a comment
- GET A QUOTE
- PRODUCTS
- TRAILERS
- TOOLBOXES
- ACCESSORIES
- CONTACT US
-
-
 +86-0579-82795522
+86-0579-82795522 -
 +86-13362901332(Jack)
+86-13362901332(Jack)
-

-
 No. 1533 Huaxi Road, Jinhua City, Zhejiang Province, China
No. 1533 Huaxi Road, Jinhua City, Zhejiang Province, China
-
- MOBILE SITE











































































 English
English  Español
Español  русский
русский 


