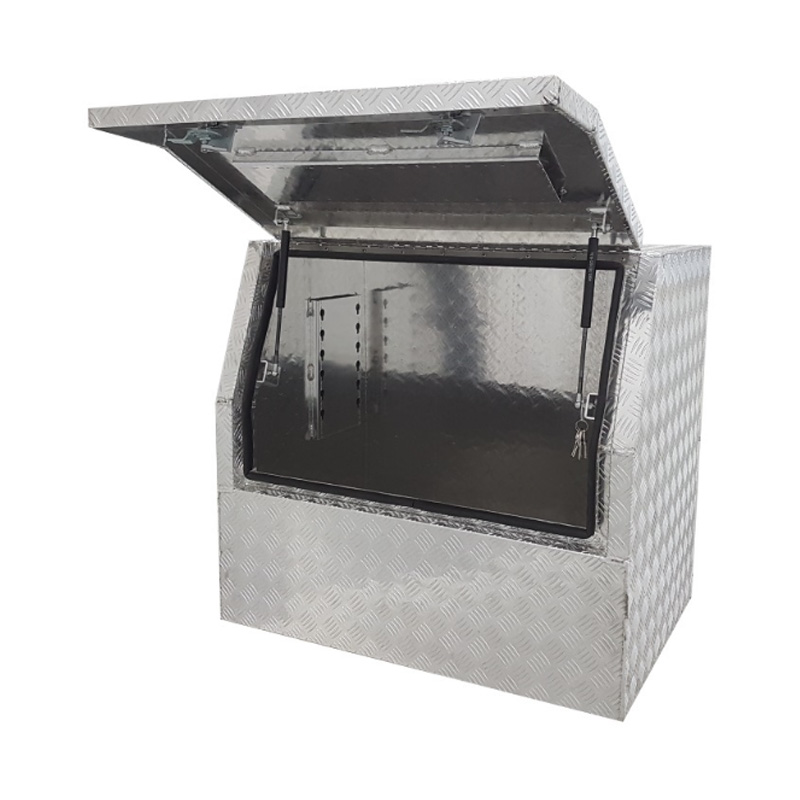
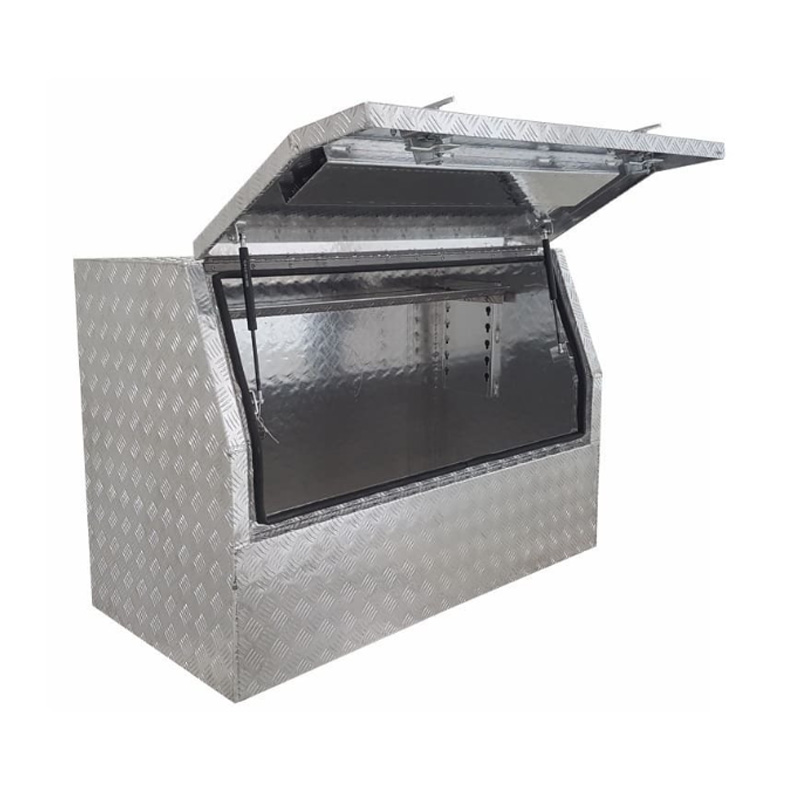
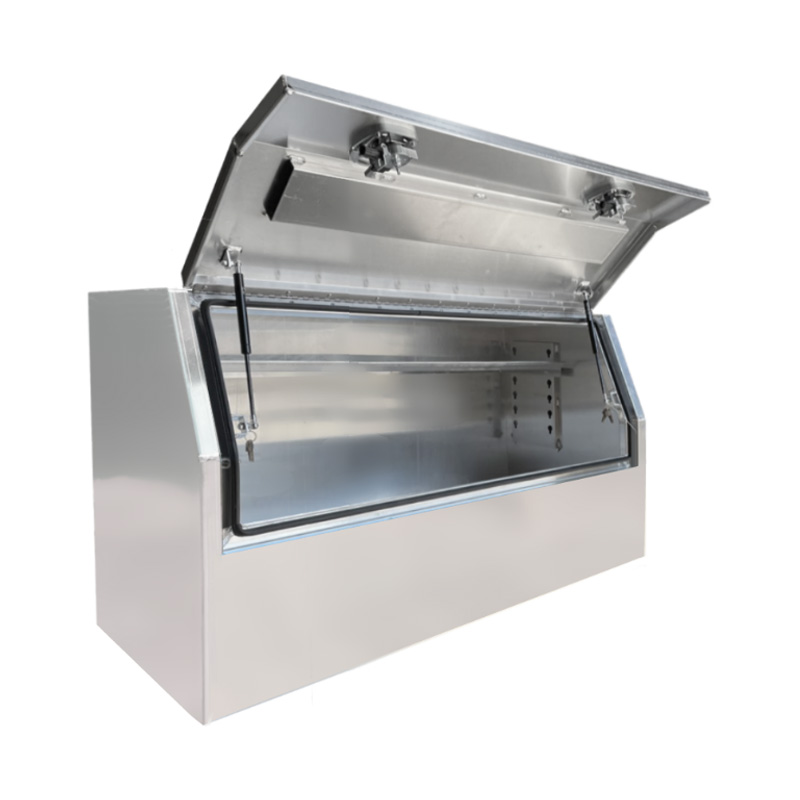
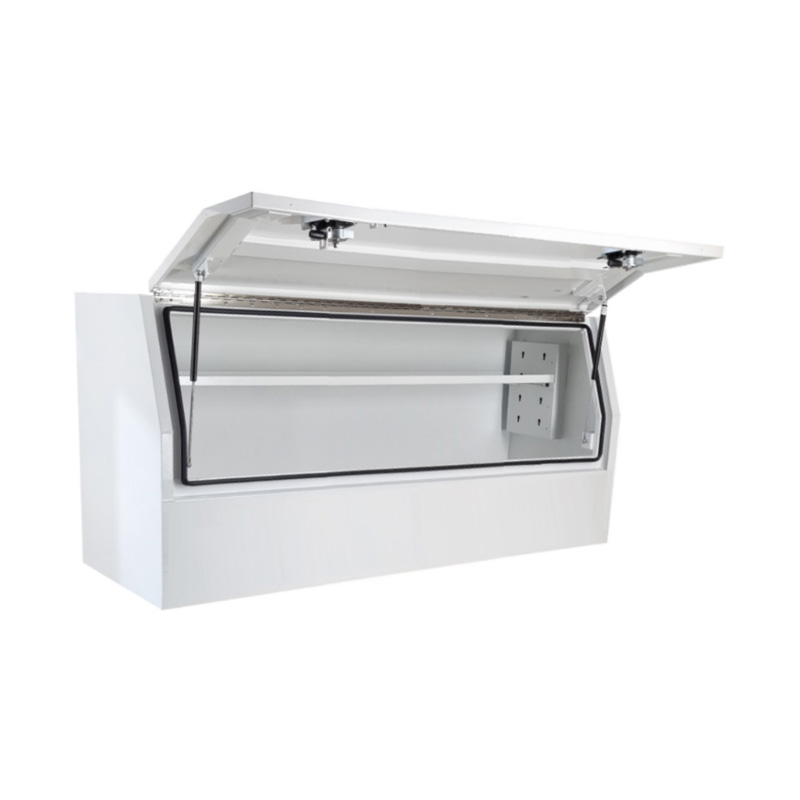
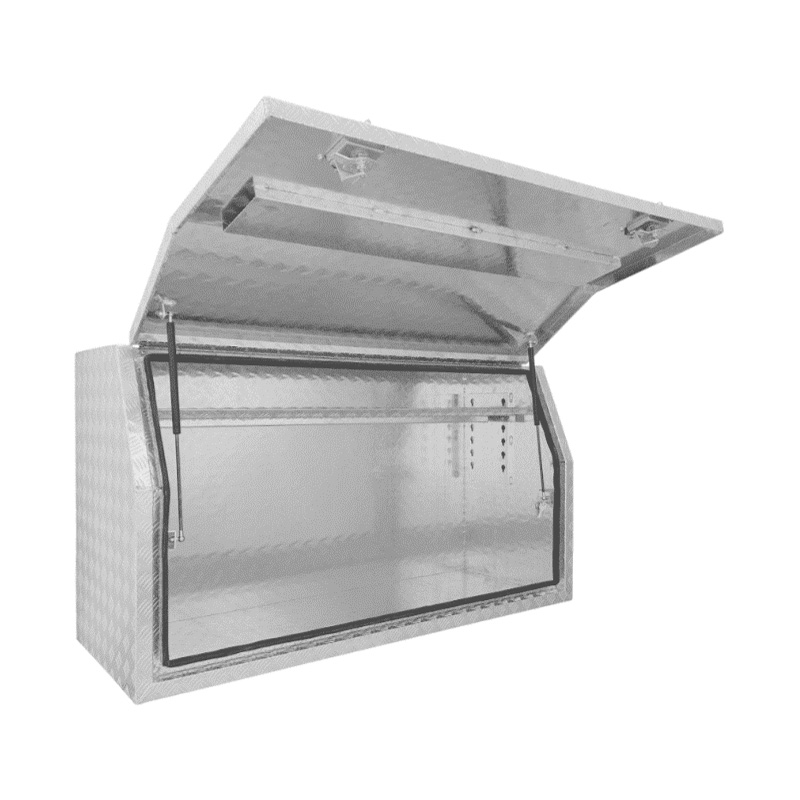
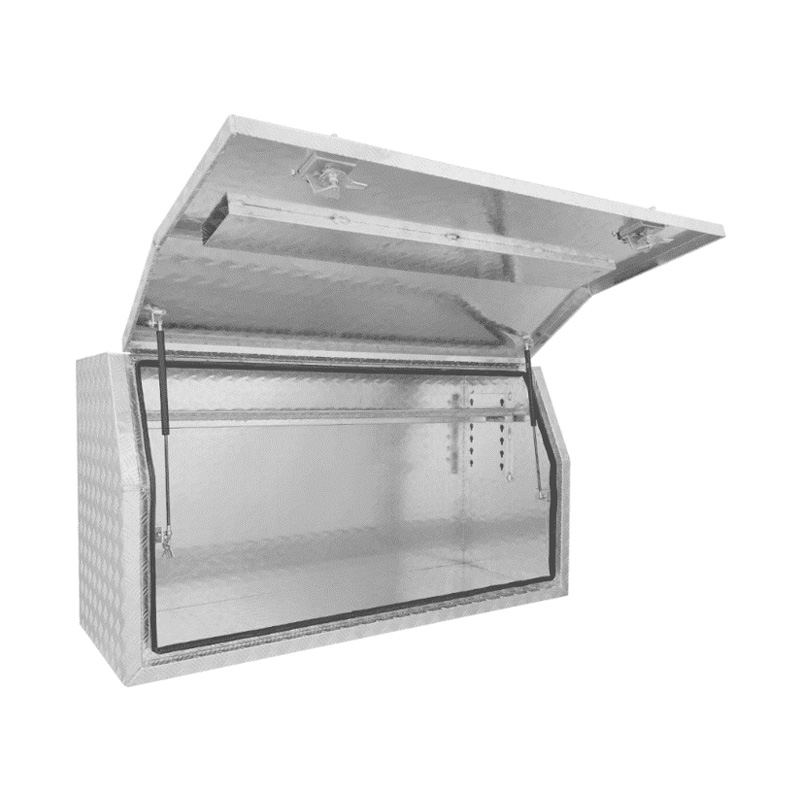
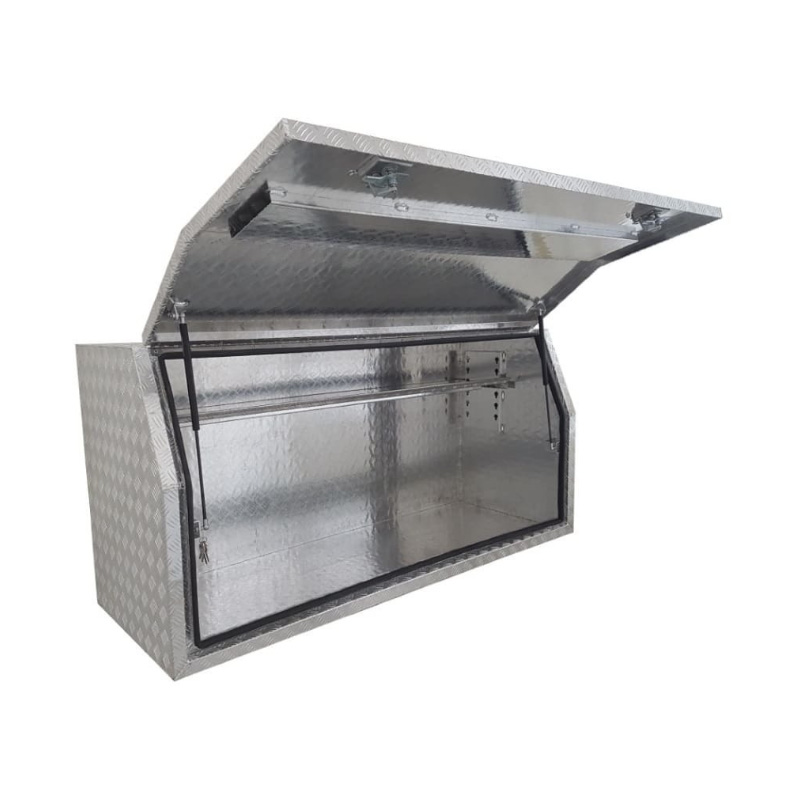
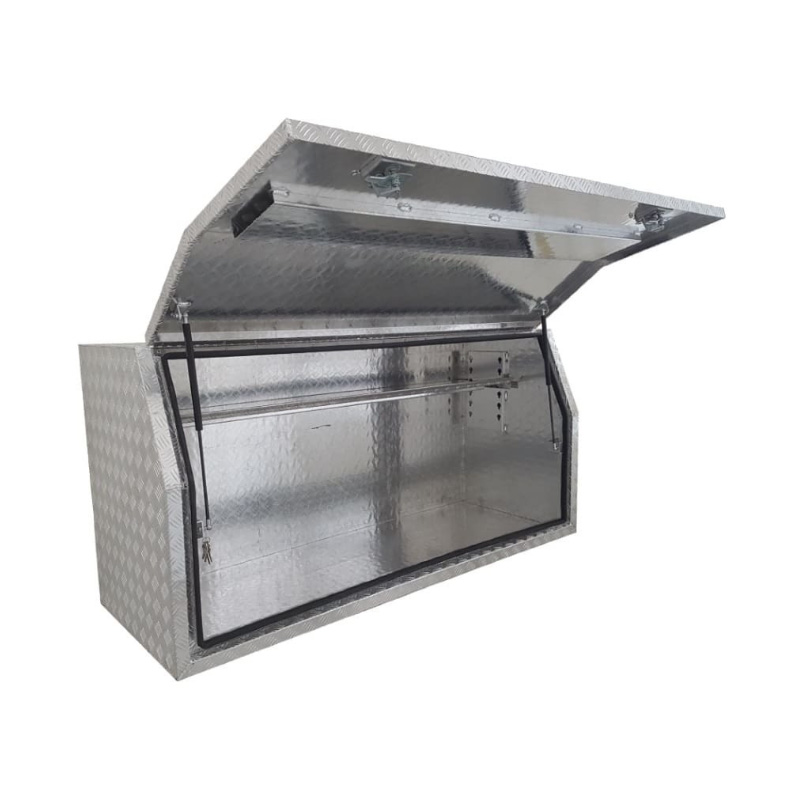
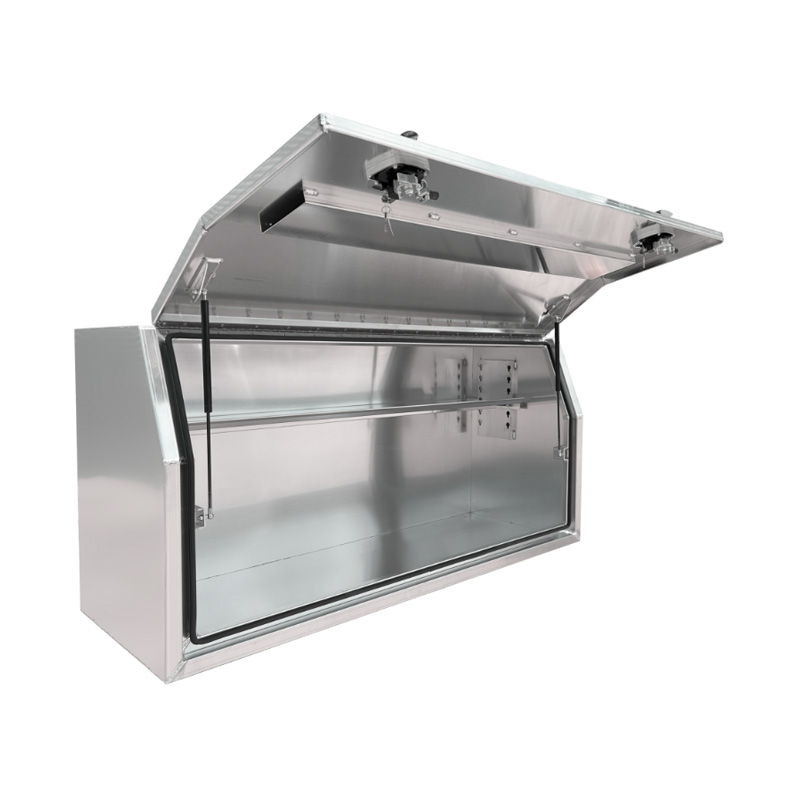
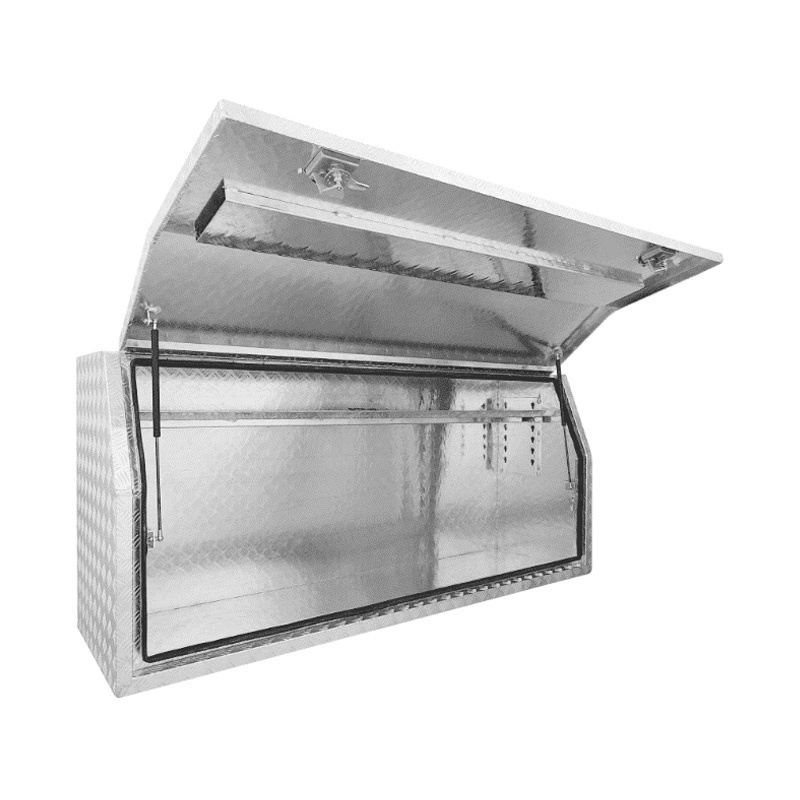
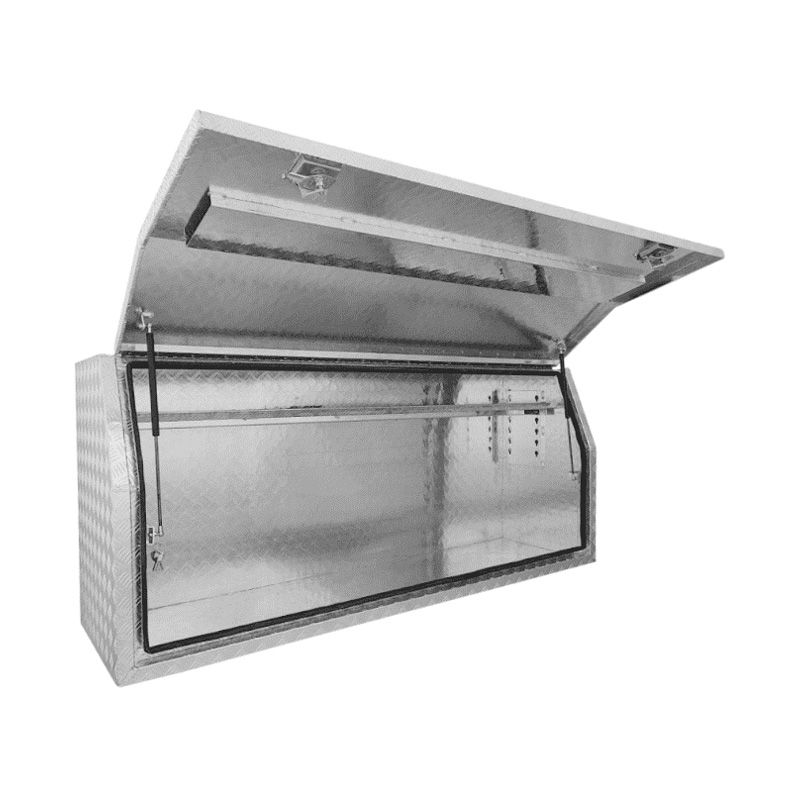
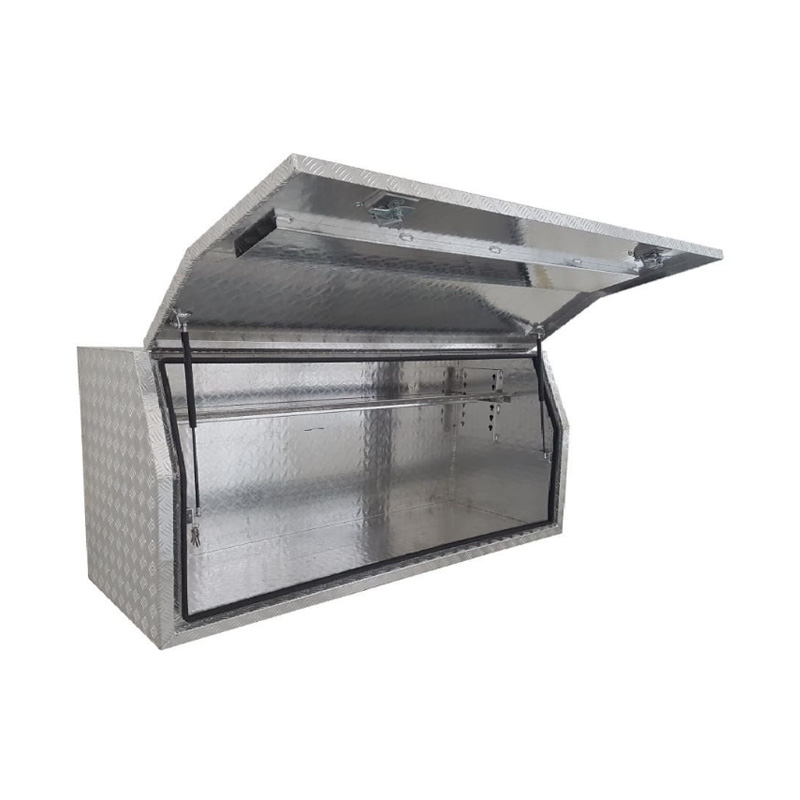
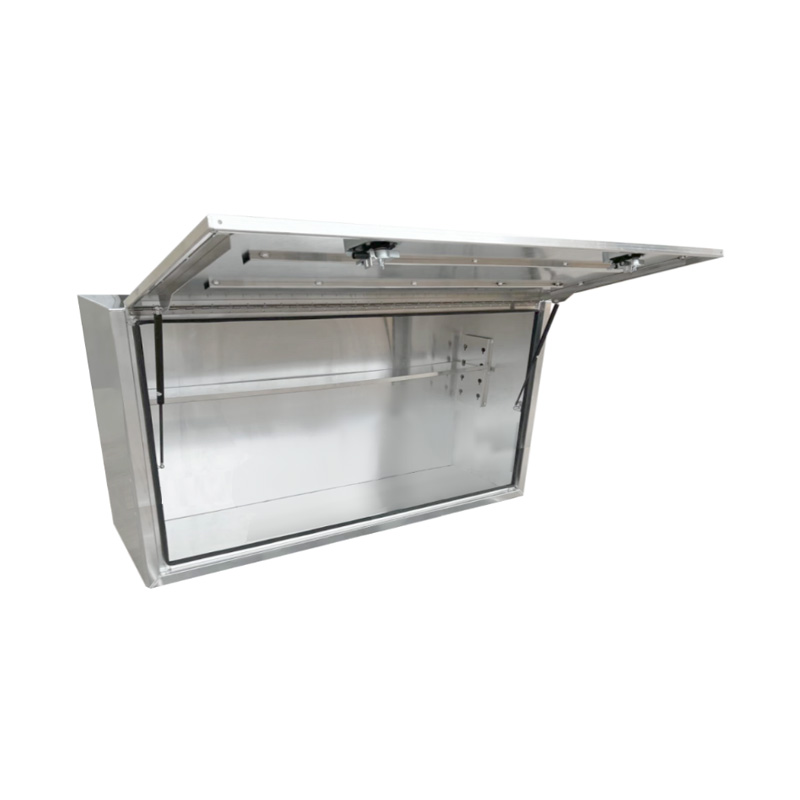
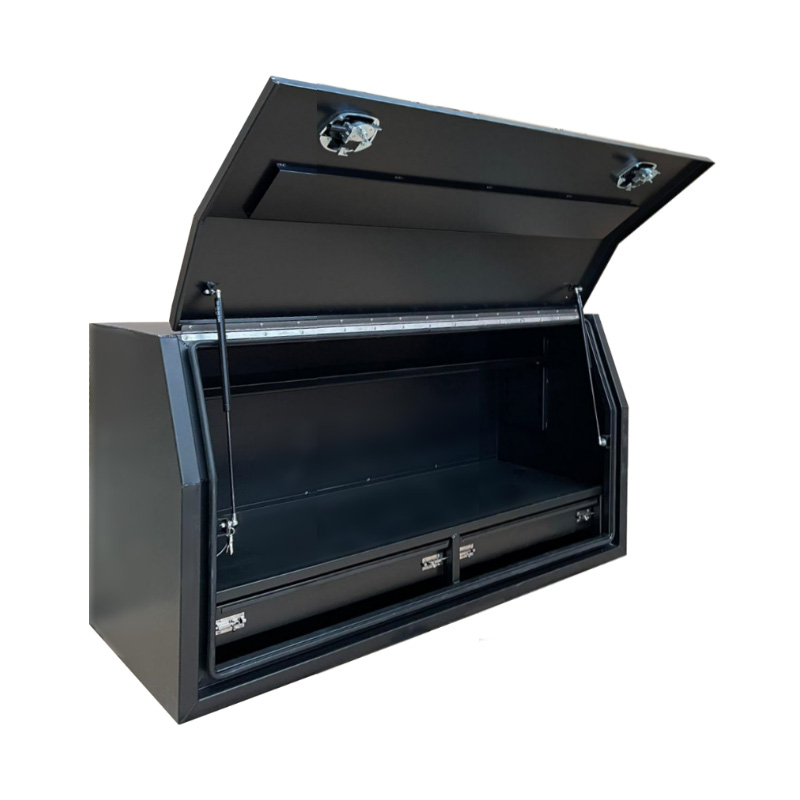
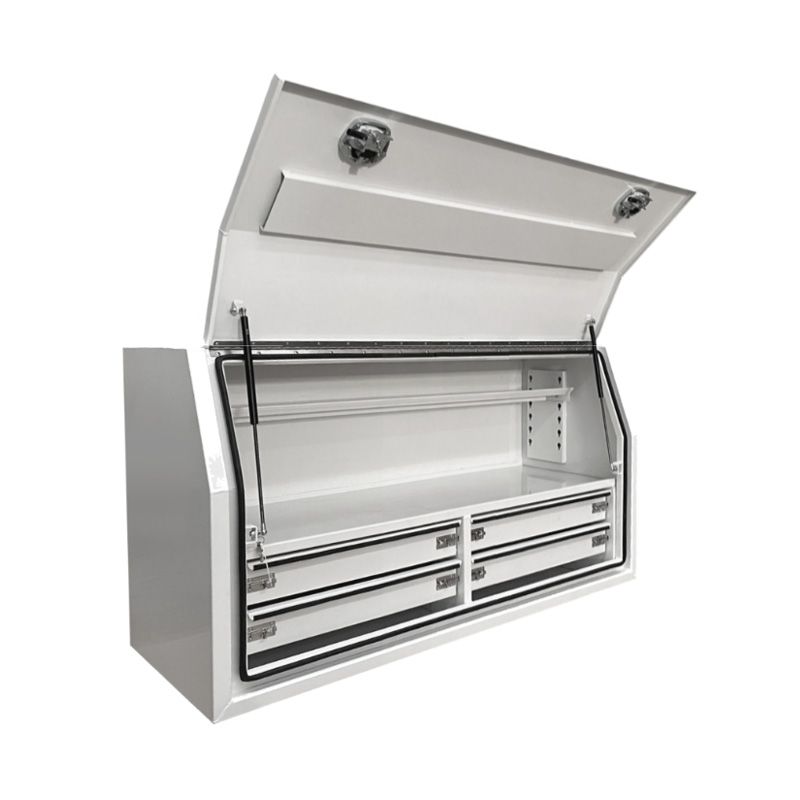
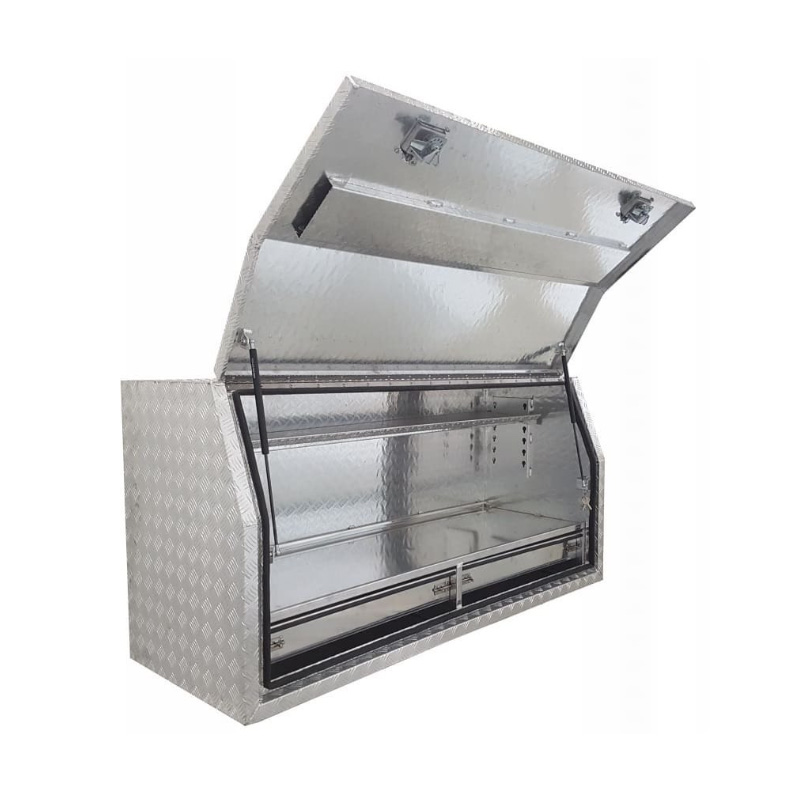
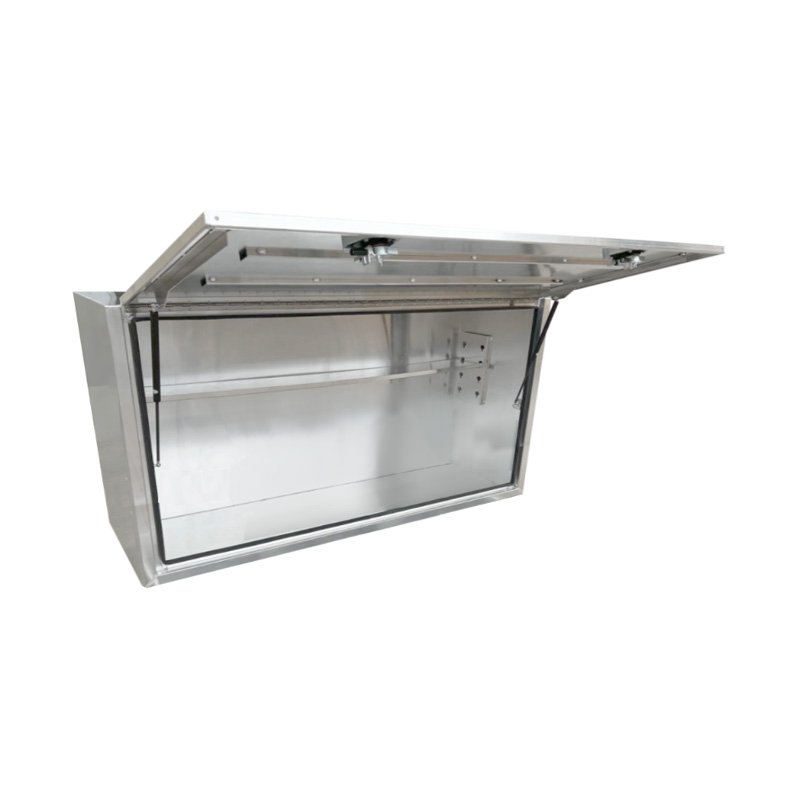
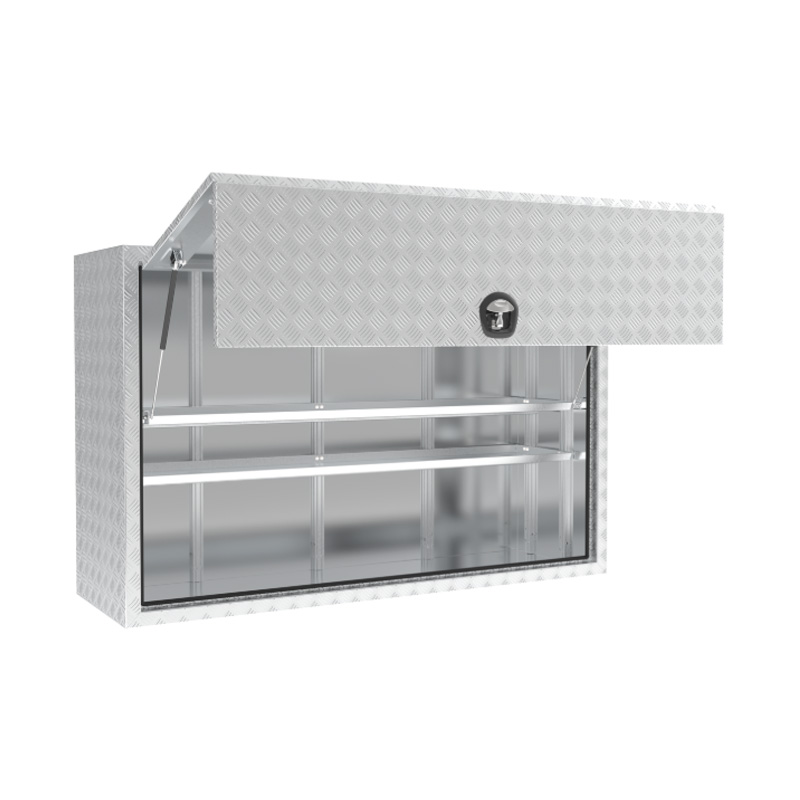
Material Properties: Strength vs. Weight One of the significant differences between Aluminum Ute Canopy Toolboxes and those made from other materials (such as steel or plastic) lies in the material pr...
READ MORETrailer accessories encompass a wide range of components designed to improve towing performance, safety, and cargo management. From structural elements like axles, springs, and wheels to supporting parts such as jockey wheels, couplers, brakes, and mudguards, each accessory plays a key role in ensuring stable towing and efficient operation. Additional items like trailer cages, canvas covers, drawbar toolboxes, mower boxes, and spare wheel holders provide added storage, load protection, and equipment security. Lighting systems and H bars contribute to visibility and cargo support, meeting both practical and regulatory requirements. By selecting the right combination of components, trailer owners can tailor their setup to meet specific needs and operating environments. Investing in durable, well-engineered accessories ensures longer service life.
-
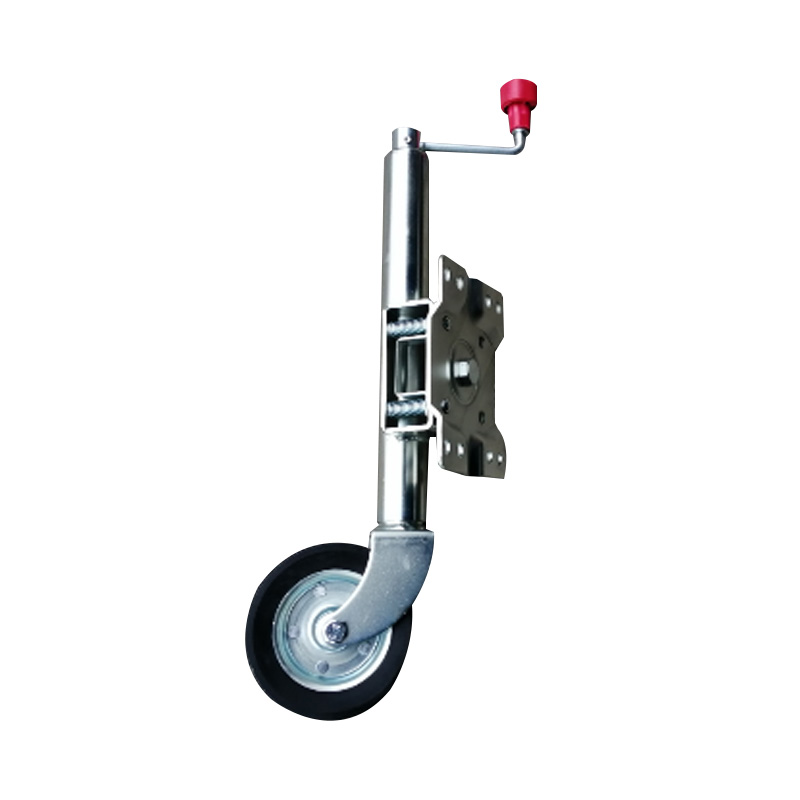
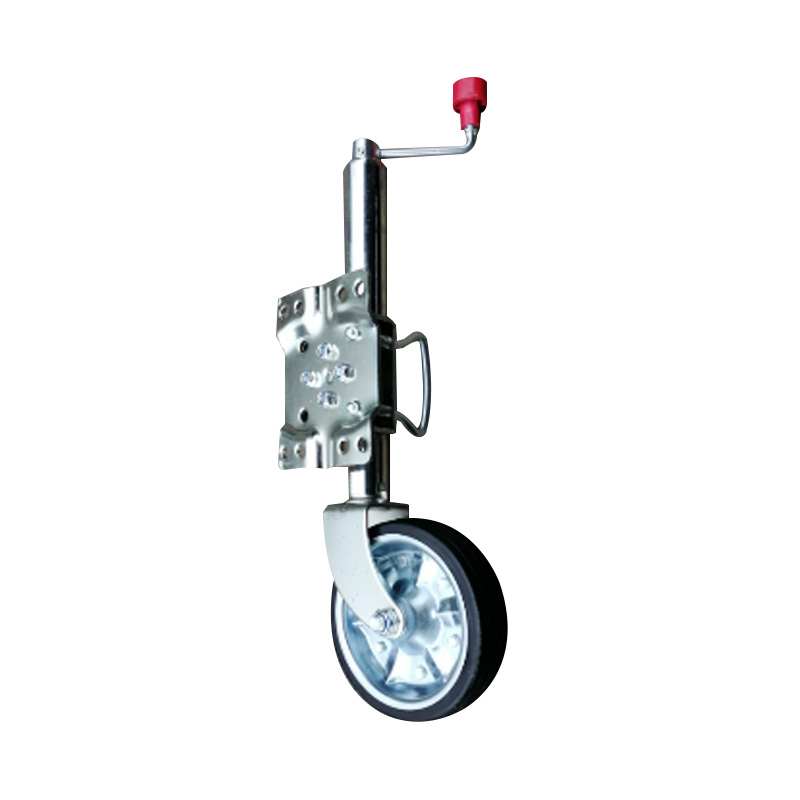
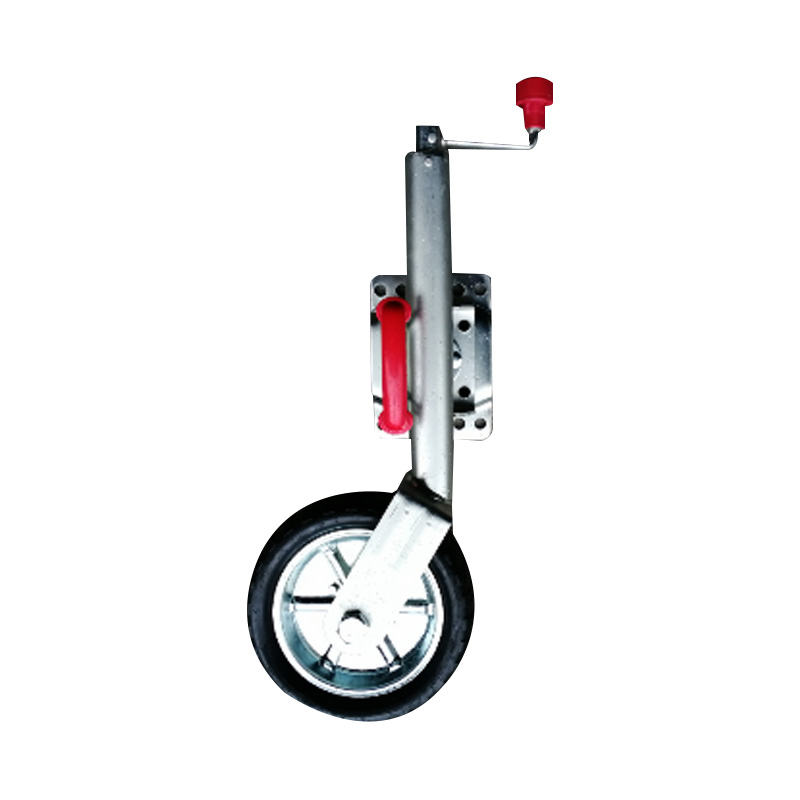
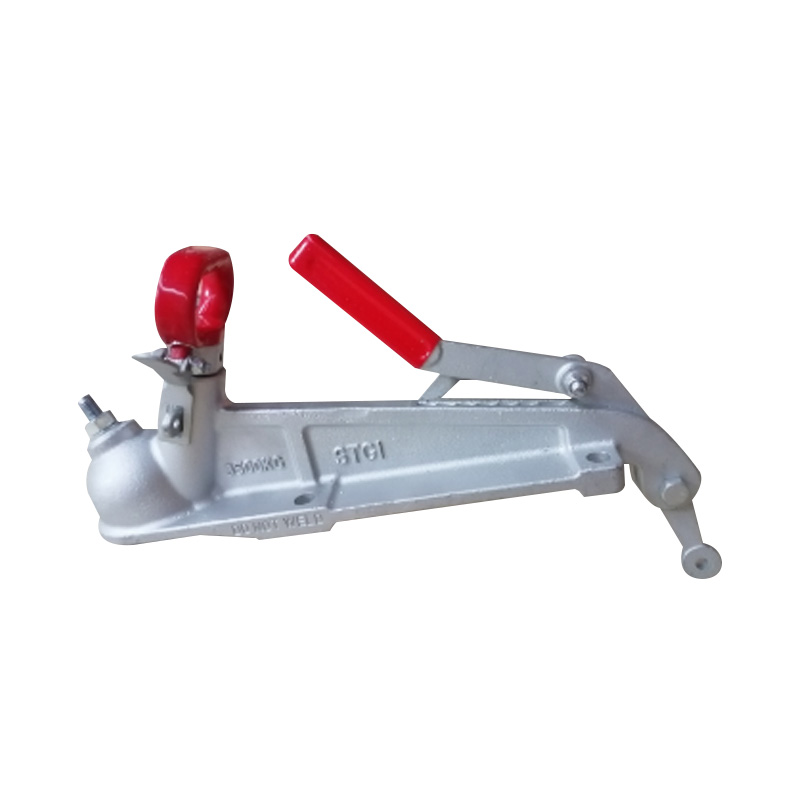
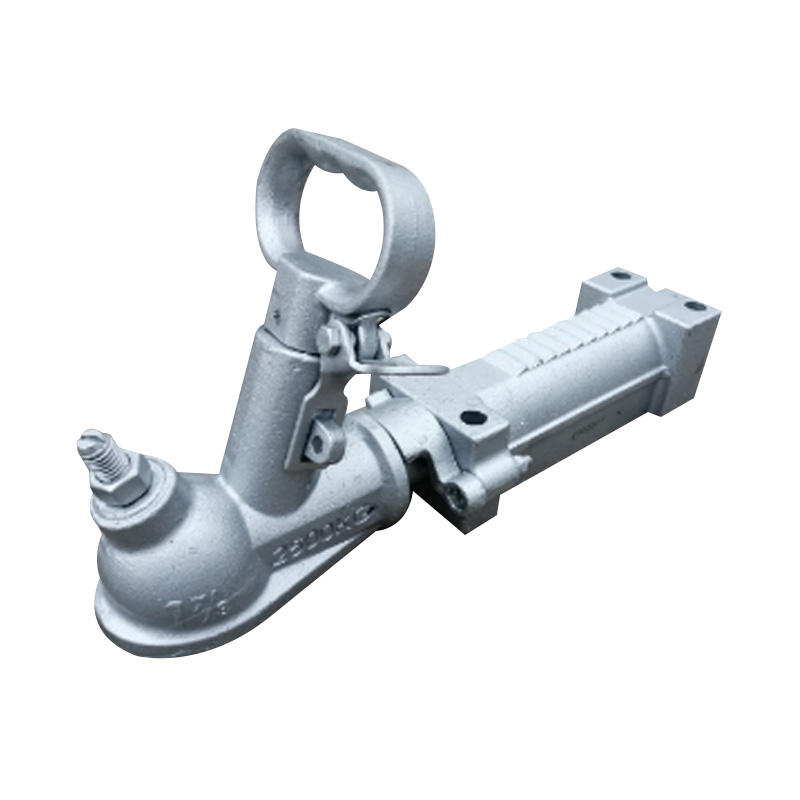
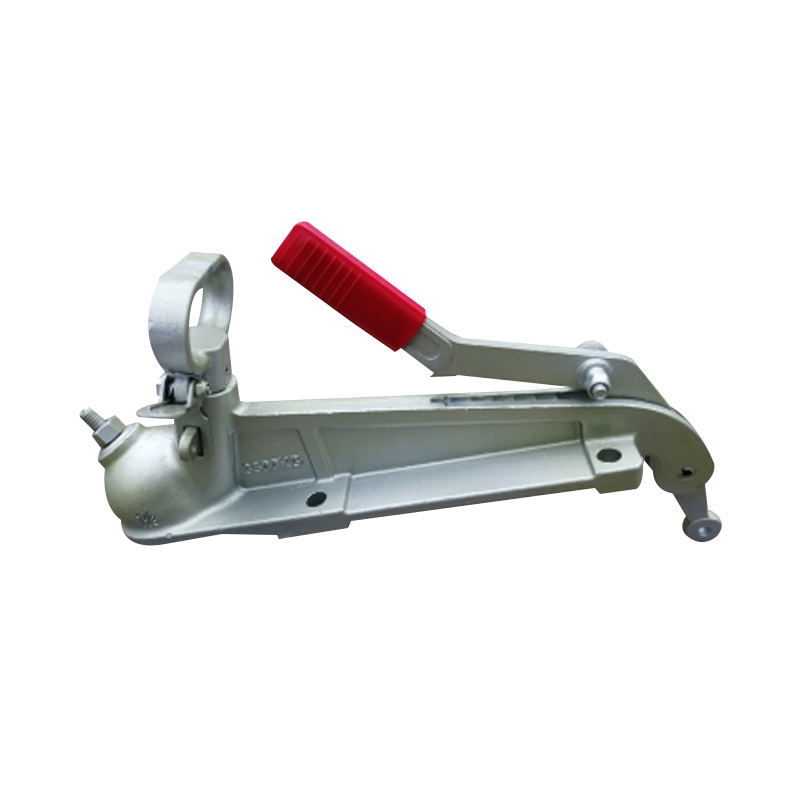
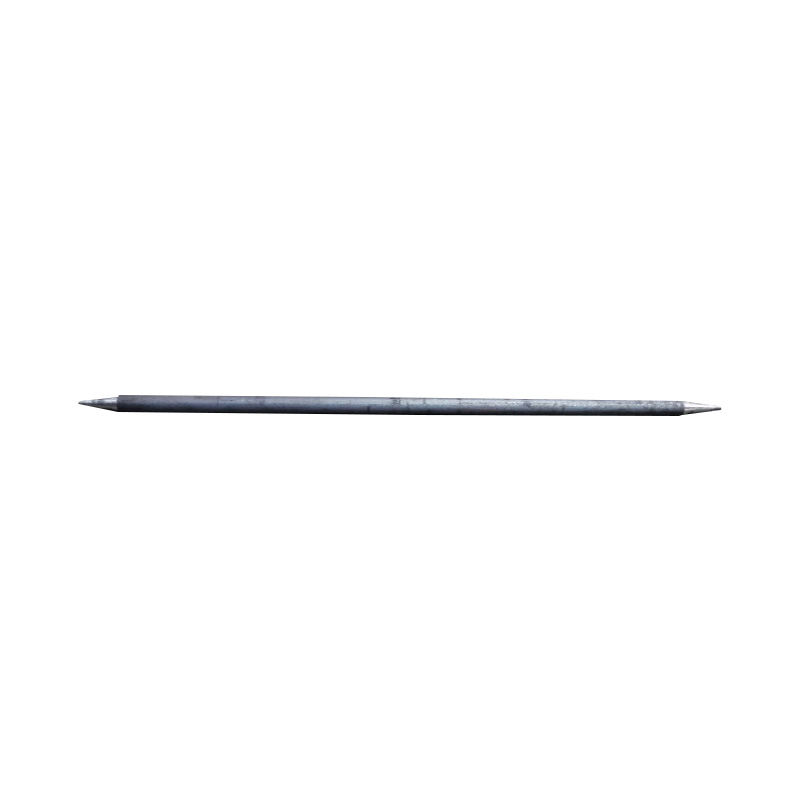
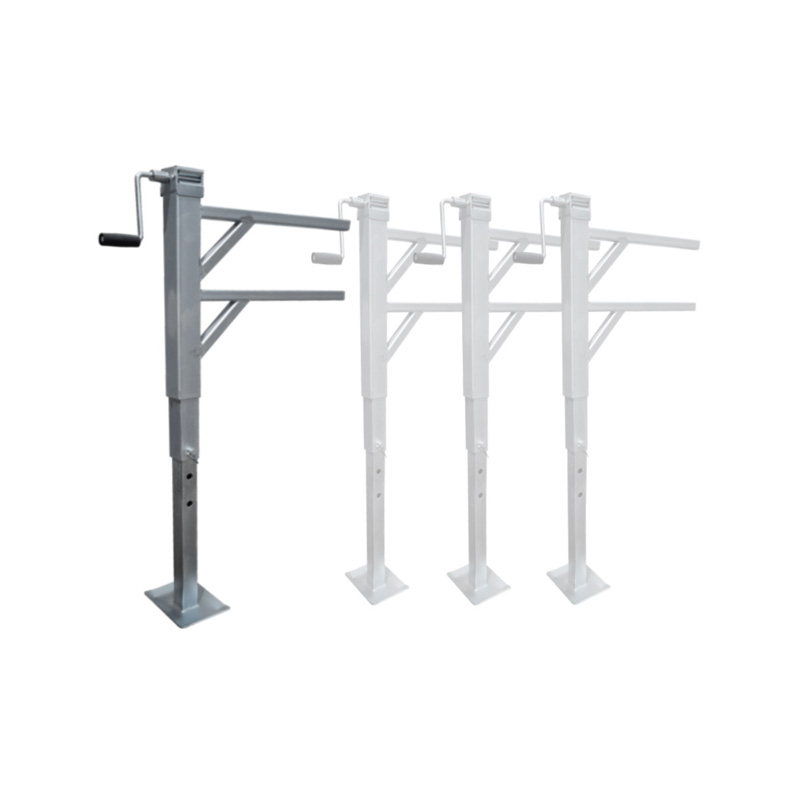
Trailer Jockey Wheel
A trailer jockey wheel is a height-adjustable, retractable wheel mounted on the drawbar or A-frame of a trailer, engineered to support the trailer tongue when disconnected from a towing vehicle and improve maneuverability during coupling, storage, or repositioning operations. By lifting or lowering the nose using its integrated screw or swivel bracket, the jockey wheel facilitates precise alignment with the towing hitch and eases the effort required to connect or disconnect the trailer, while its caster action allows smooth movement in any direction—ideal for tight spaces or uneven terrain. These wheels are constructed to carry a specified static nose load—ranging from several hundred kilograms on light models to over 700 kg on heavy-duty units—and feature sleeve diameters typically between 42 mm and 60 mm, ensuring compatibility with different trailer classes. -
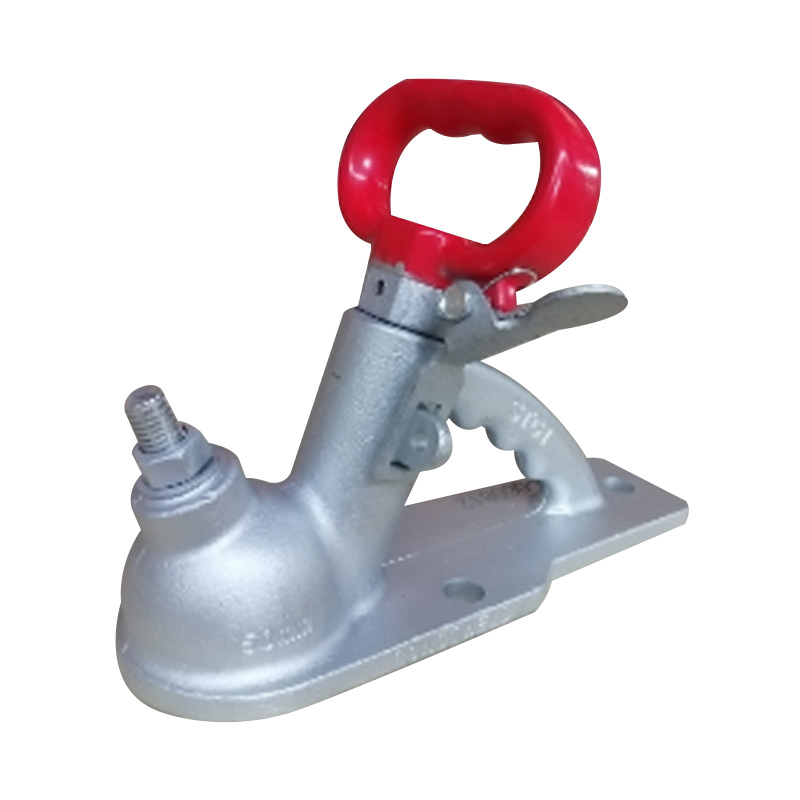
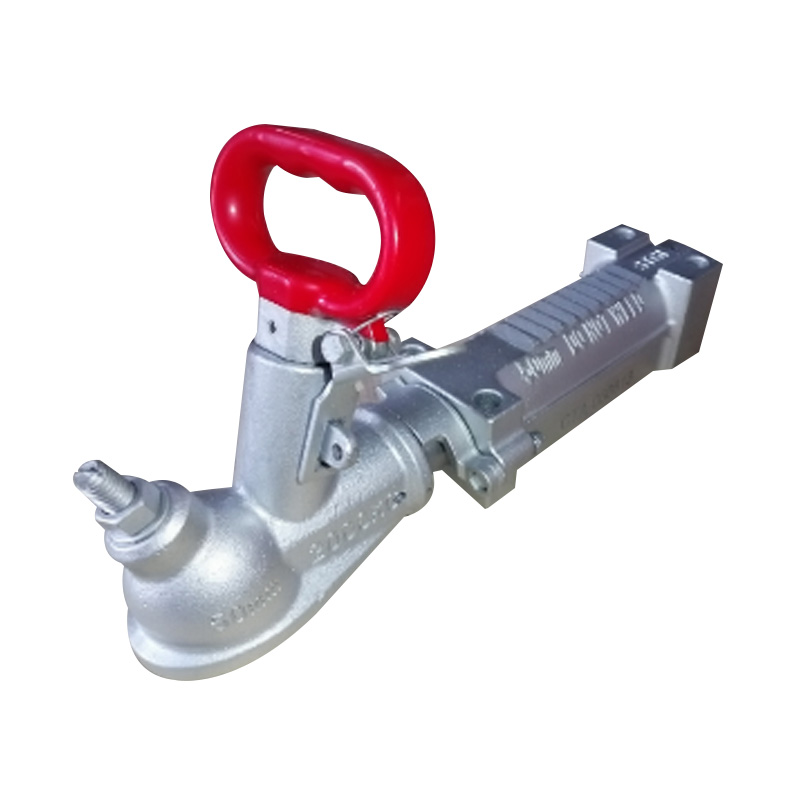
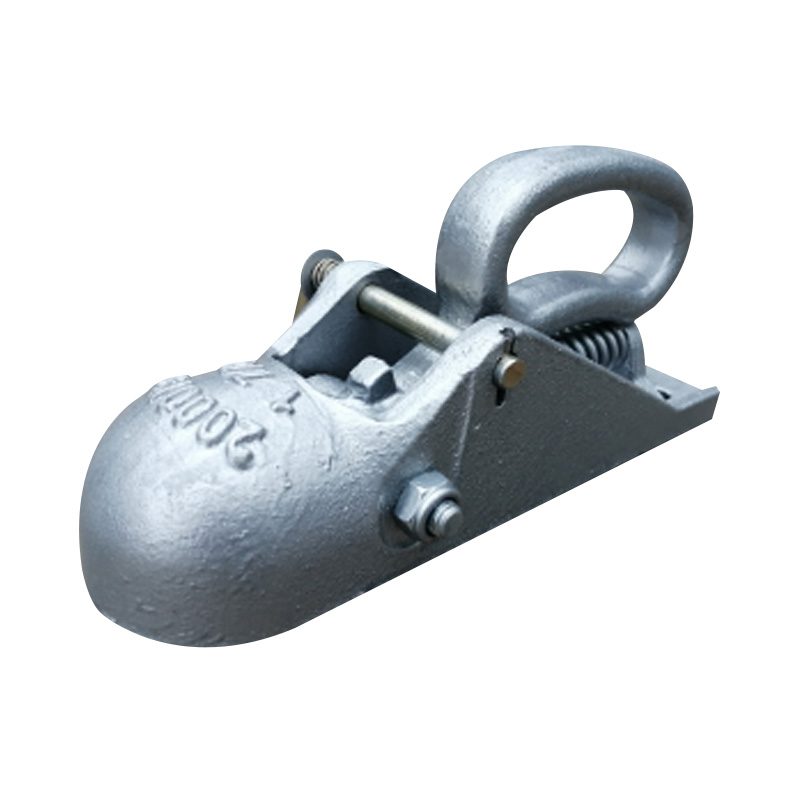
Trailer Coupler
A trailer coupler is a critical mechanical component that joins the trailer’s tongue to the tow vehicle’s hitch ball, enabling secure towing and effective load transfer; it must match the hitch ball size (commonly 2") and the trailer’s Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) to ensure safe operation. Constructed from high-strength steel—often with powder or zinc coating—the coupler employs a latch mechanism (such as the patented wedge-latch design) that locks firmly over the hitch ball to maintain connection under dynamic loading. Adjustable-height couplers accommodate various towing setups, helping to keep the trailer and tow vehicle level, which is key to reducing sway and uneven tyre wear. Whether bolt-on or weld-on, the coupler’s design must comply with established safety standards, and its materials and construction influence both longevity and maintenance frequency. -
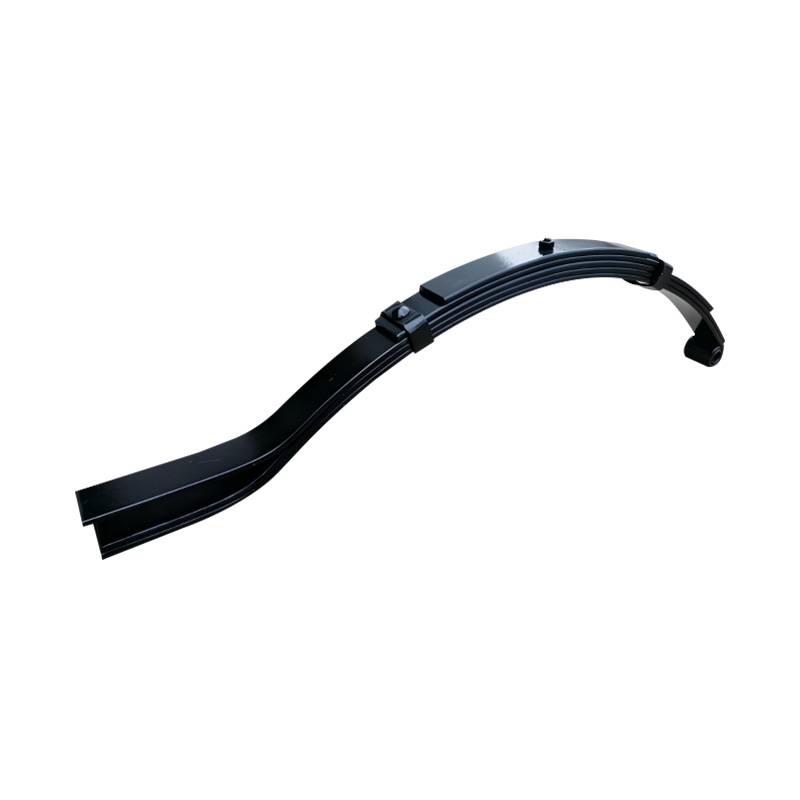
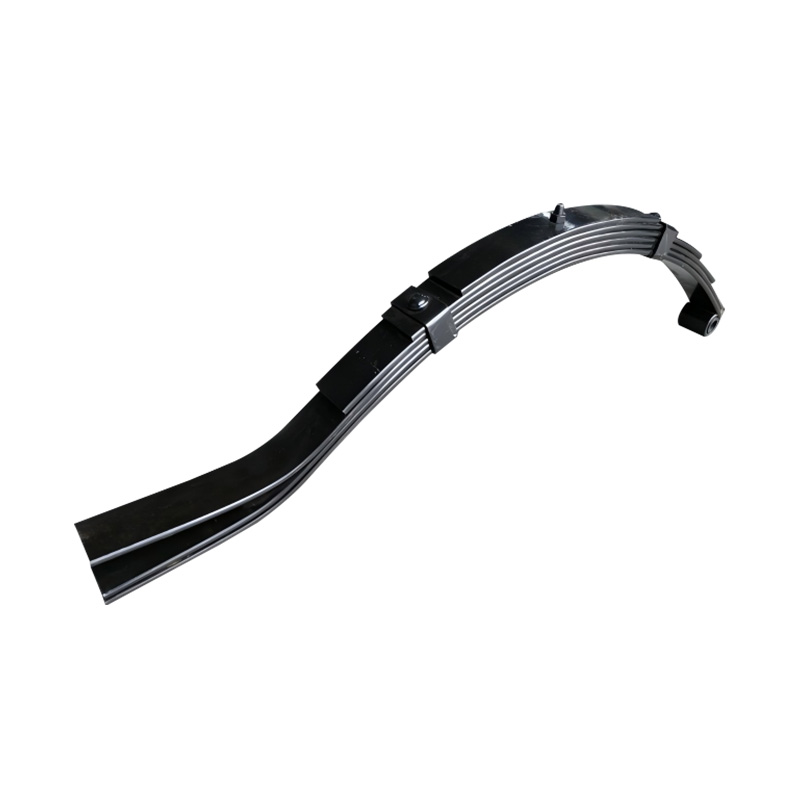
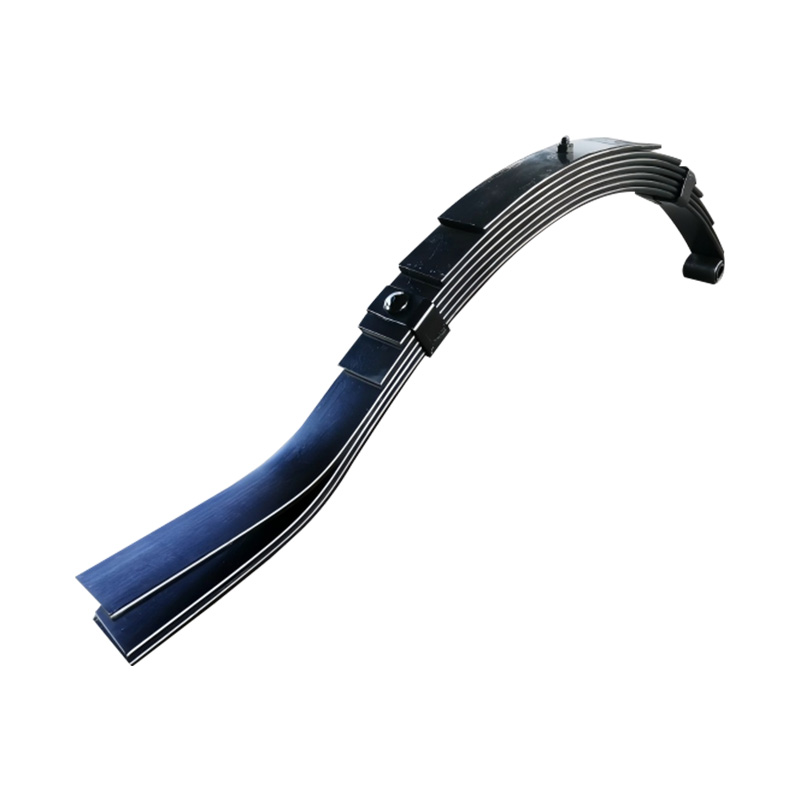
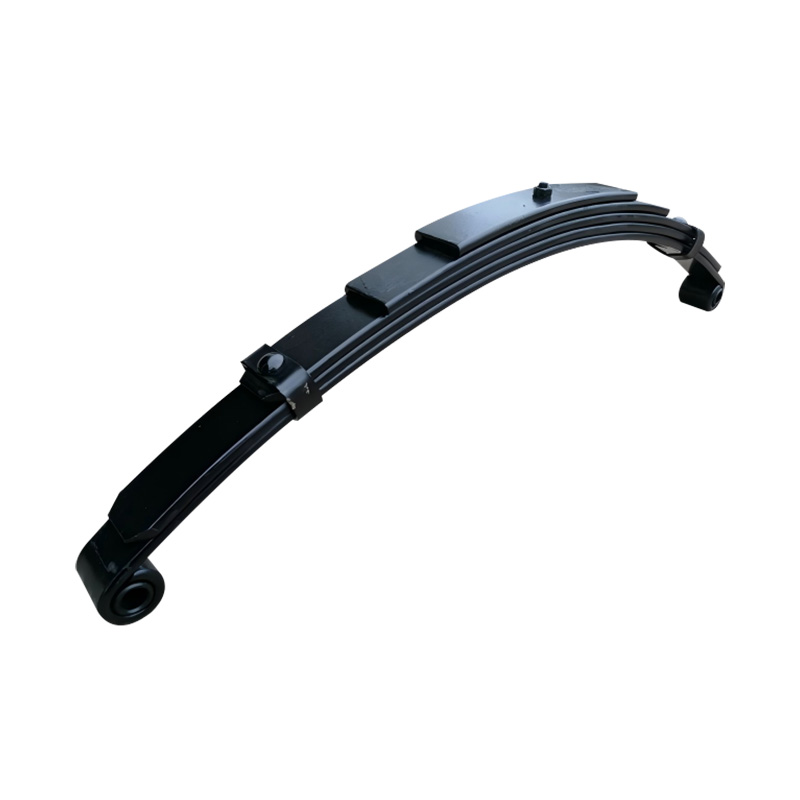
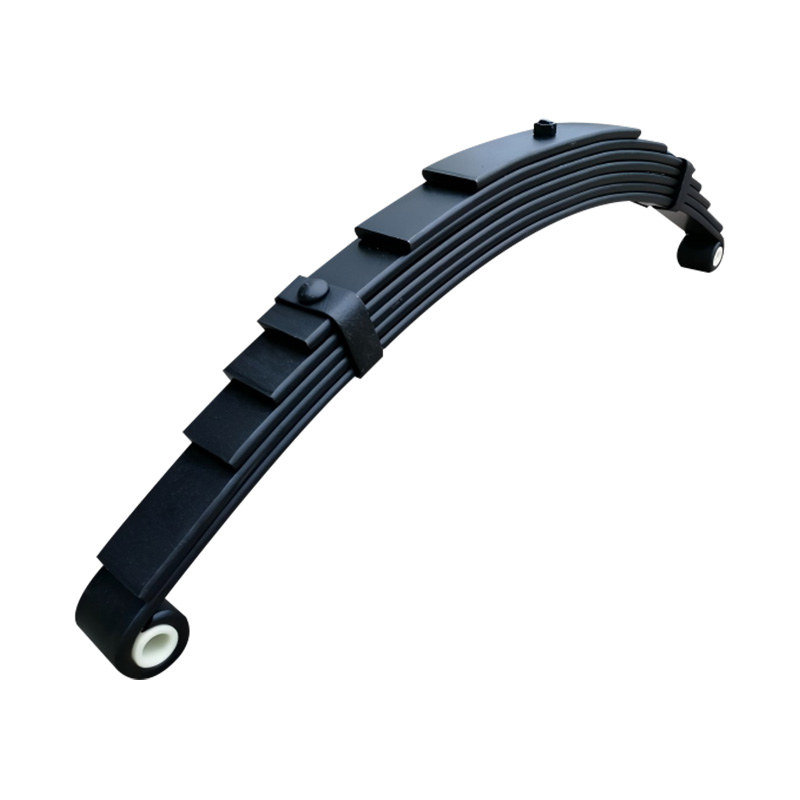
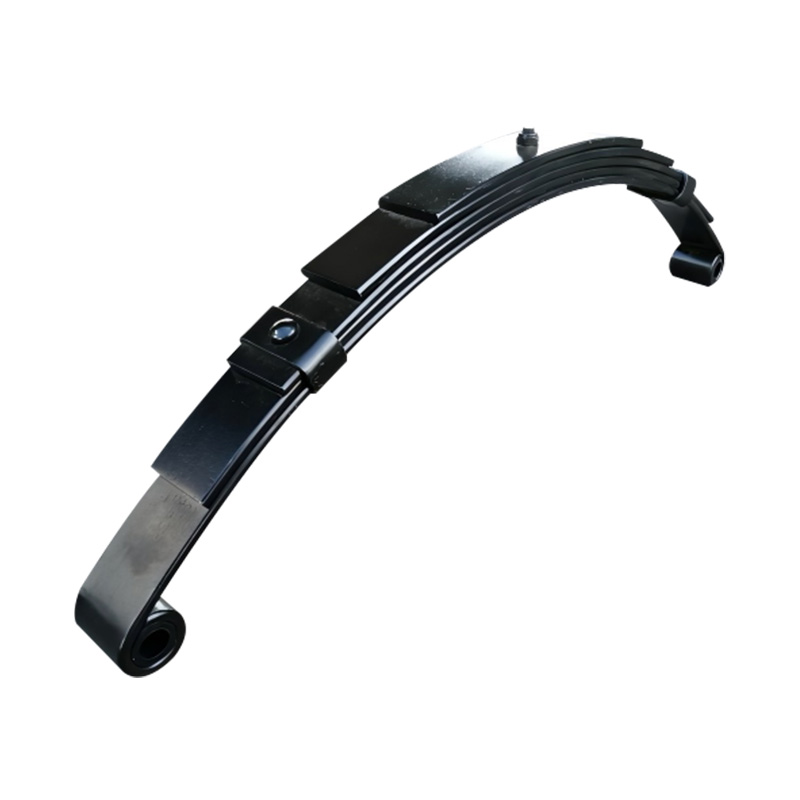
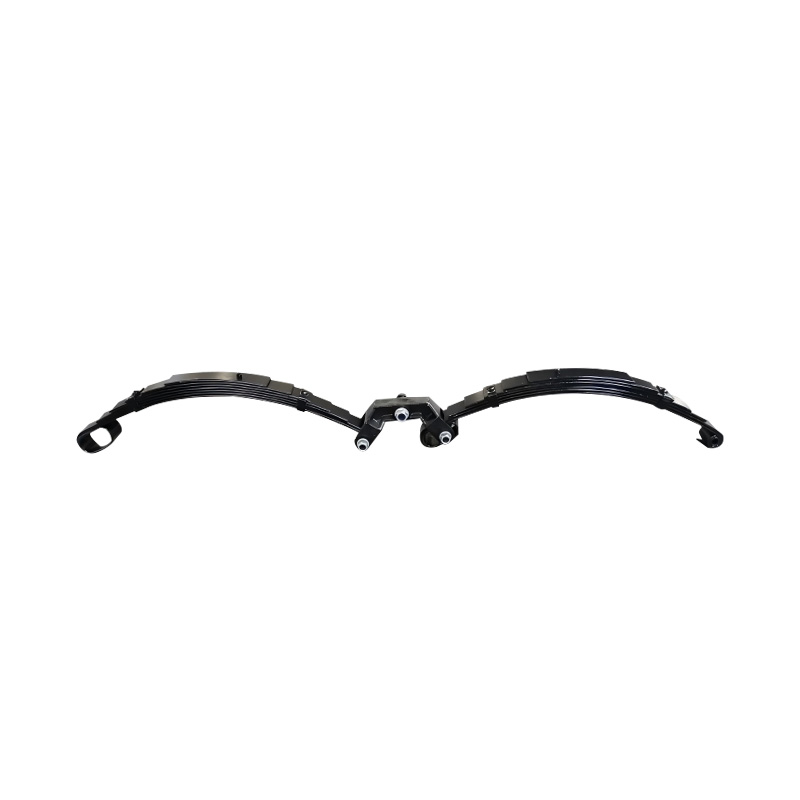
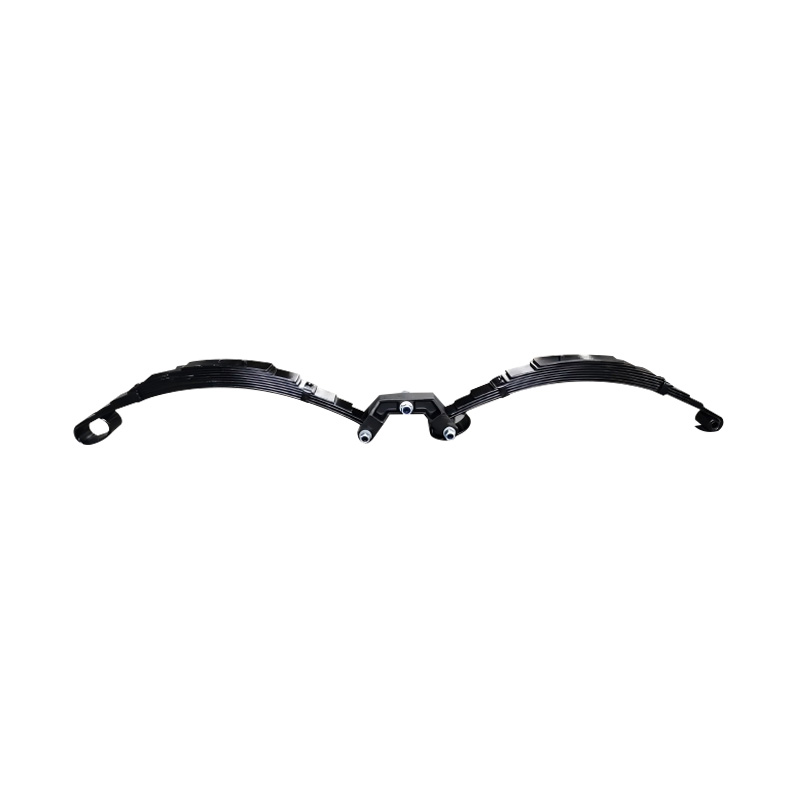
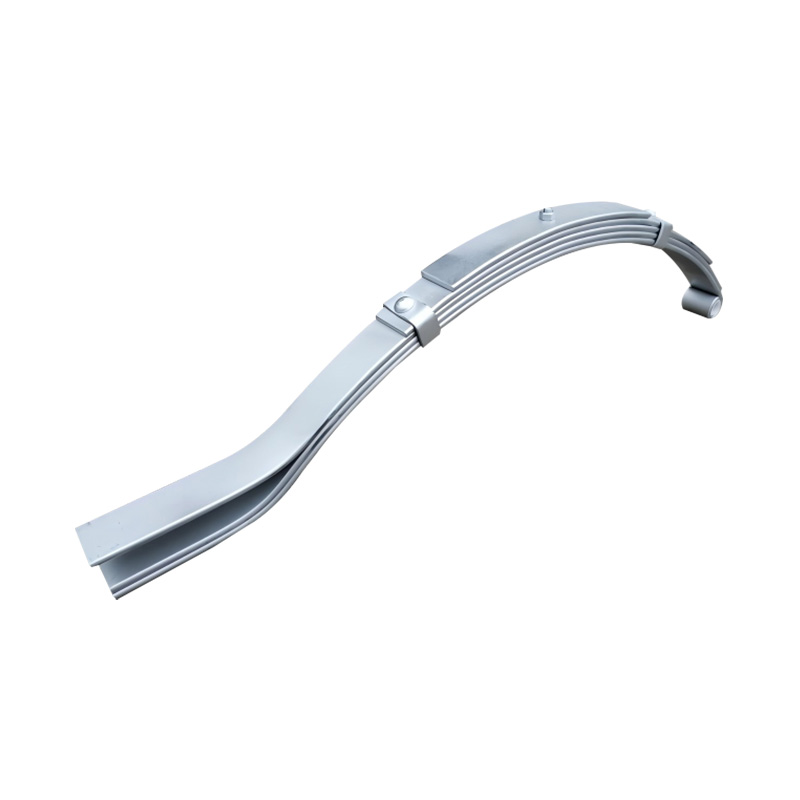
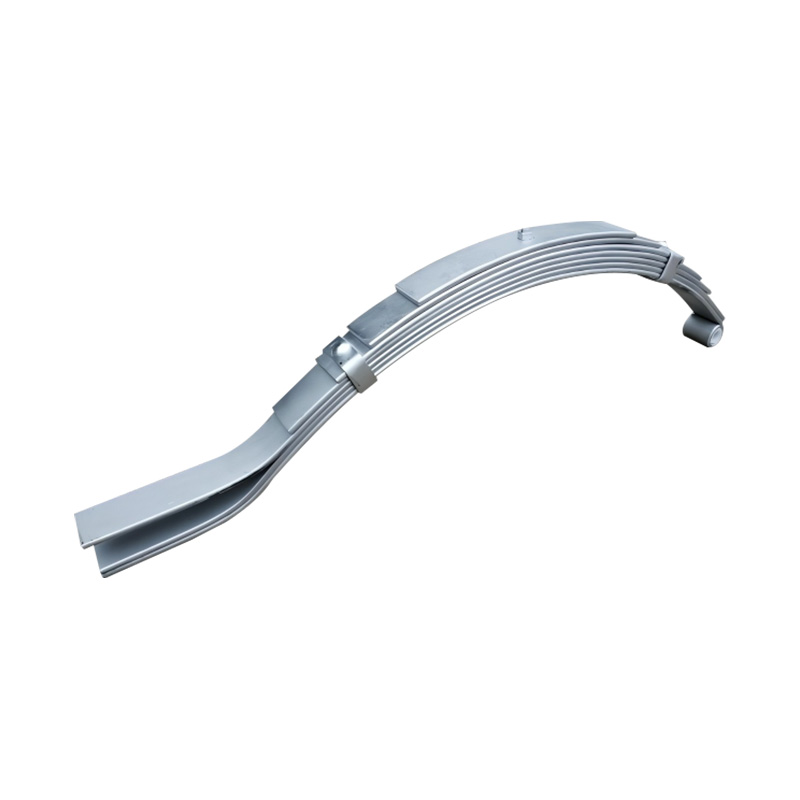
Trailer Spring
Trailer springs—typically in the form of leaf springs—are engineered assemblies of curved steel plates (leaves) designed to flex under load, absorbing shocks and maintaining stability when hauling cargo over uneven terrain. A standard leaf spring pack may contain anywhere from one to seven leaves, each tempered to balance strength and flexibility. When the trailer traverses bumps or dips, the springs flatten and flex, dissipating energy and reducing stress on the frame and axle, thus preserving structural integrity and ensuring cargo remains secure. The spring’s arc shape and number of leaves directly correlate to load capacity: heavier trailers require more leaves or thicker steel, while lighter trailers can use simpler, single-leaf designs. Eye-to-eye springs are common on lighter utility trailers, while slipper-type configurations are preferred in heavier applications for their self-locating pads and streamlined footprint. -
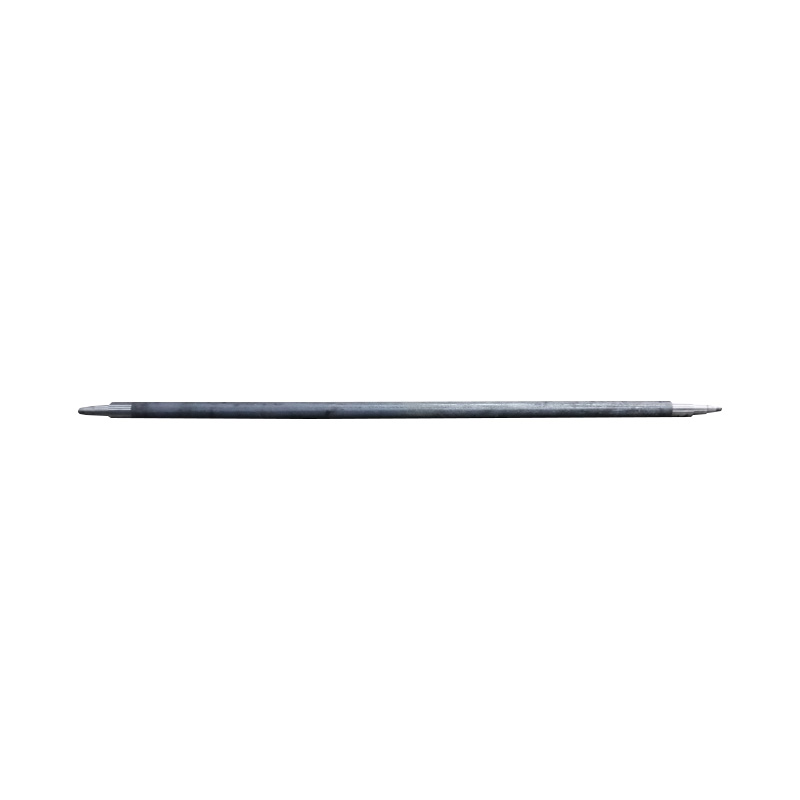
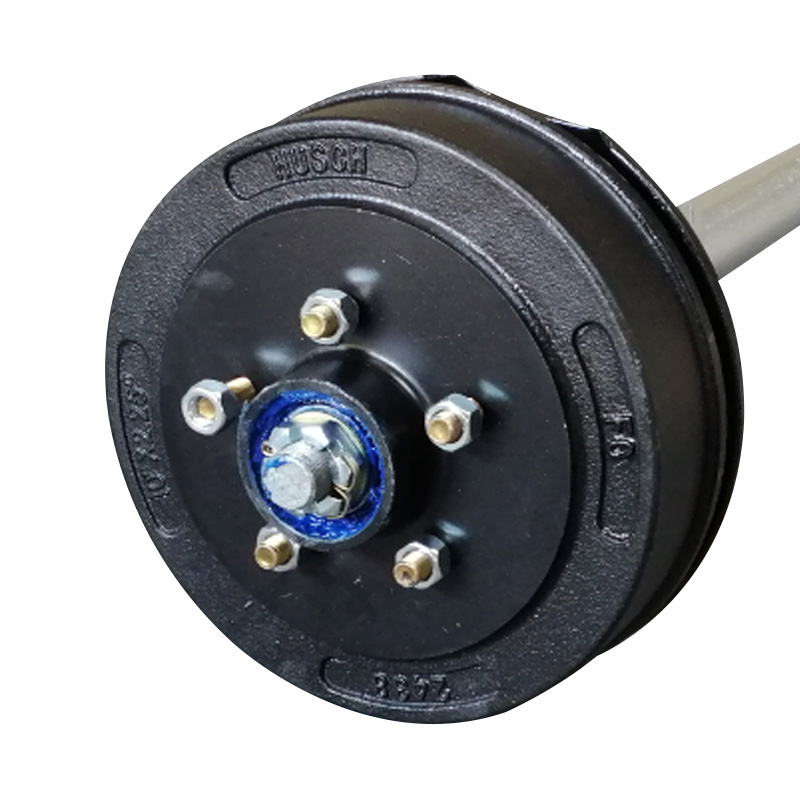
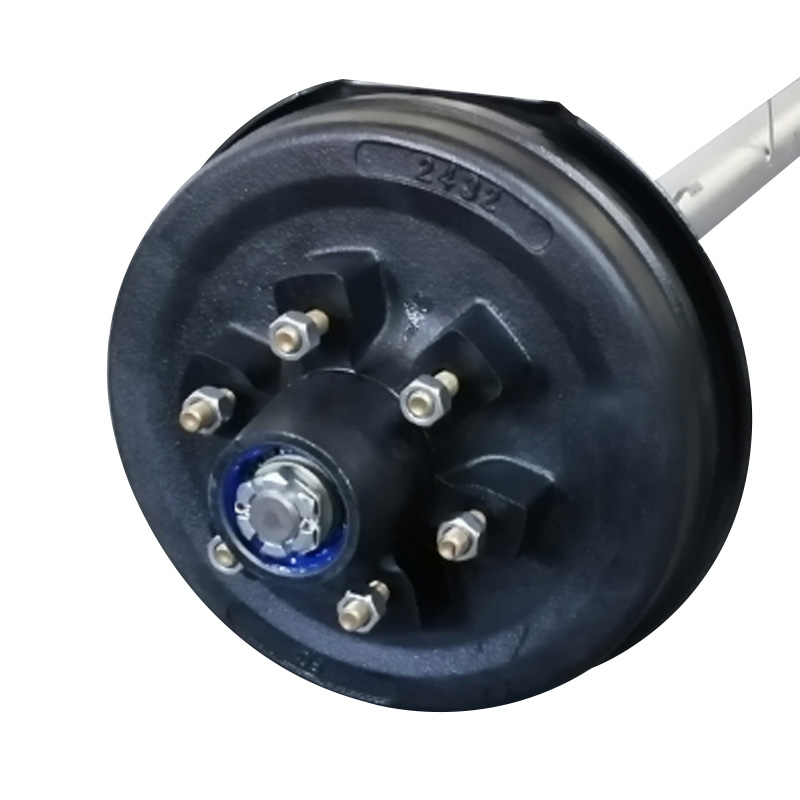
Trailer Axle
A trailer axle serves as the central load-bearing shaft that connects the wheels and transfers the trailer's cargo weight onto the ground, playing a fundamental role in both structural support and ride dynamics. There are primarily two axle systems: spring (leaf-spring) axles and torsion axles. Spring axles use leaf spring packs mounted beneath or above the beam, offering robust, cost-effective suspension with straightforward maintenance and parts replacement. Torsion axles encapsulate individual trailing arms and rubber cords inside a sealed tube, delivering independent suspension and smoother ride quality with fewer metal-on-metal wear points. Axles can be straight for even deck height, drop-style to lower load-leveling, or overslung/underslung depending on clearance and stability requirements. They are available in configurations ranging from single to tandem or triple axles, depending on weight distribution needs. -
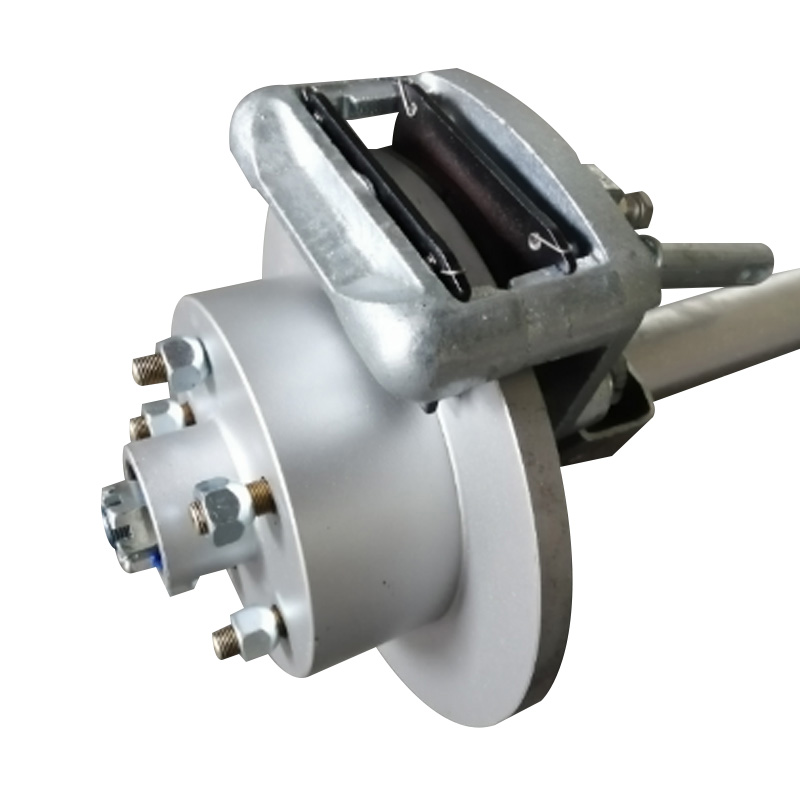
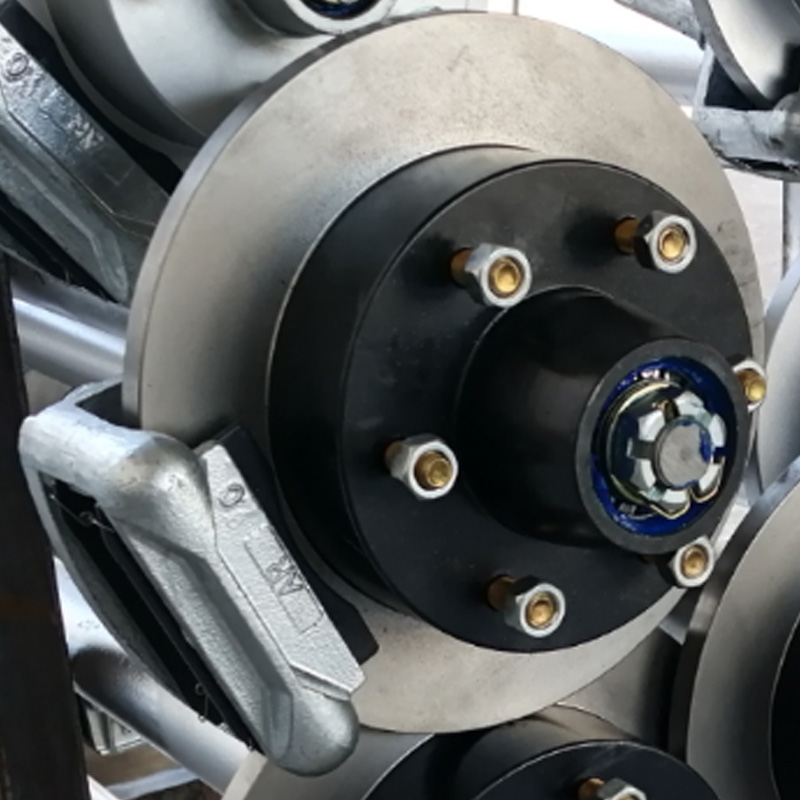
Trailer Brake
A trailer brake system is a vital component for any towed load, ensuring controlled deceleration, enhanced safety, and compliance with vehicle regulations. These systems are generally divided into three main types—electric (or electric drum), hydraulic, and electric-over-hydraulic. Electric drum brakes utilize an electromagnetic coil activated by a brake controller signal, forcing shoes against a rotating drum. Hydraulic brakes rely on fluid pressure generated within a surge actuator on the trailer, translating towing vehicle deceleration into mechanical force on drum or disc assemblies. Electric-over-hydraulic systems combine the responsive control of electric braking with the power of hydraulic actuation, delivering stronger and smoother stopping performance—though requiring both wiring and fluid lines. Choosing the proper brake system depends on trailer weight, usage frequency, towing terrain, cost, and maintenance preference to guarantee optimal performance and compliance. -
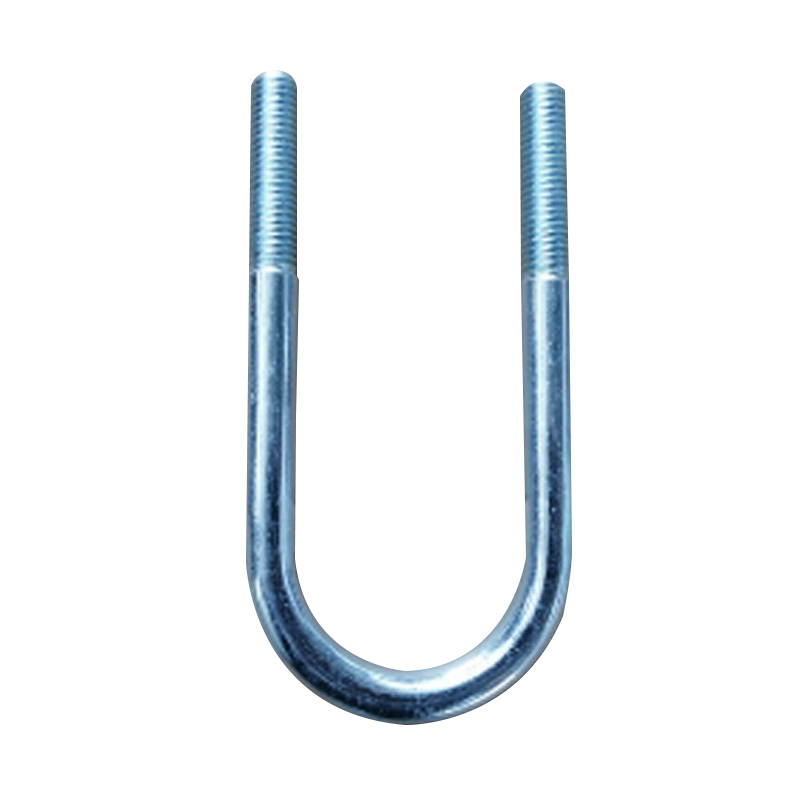
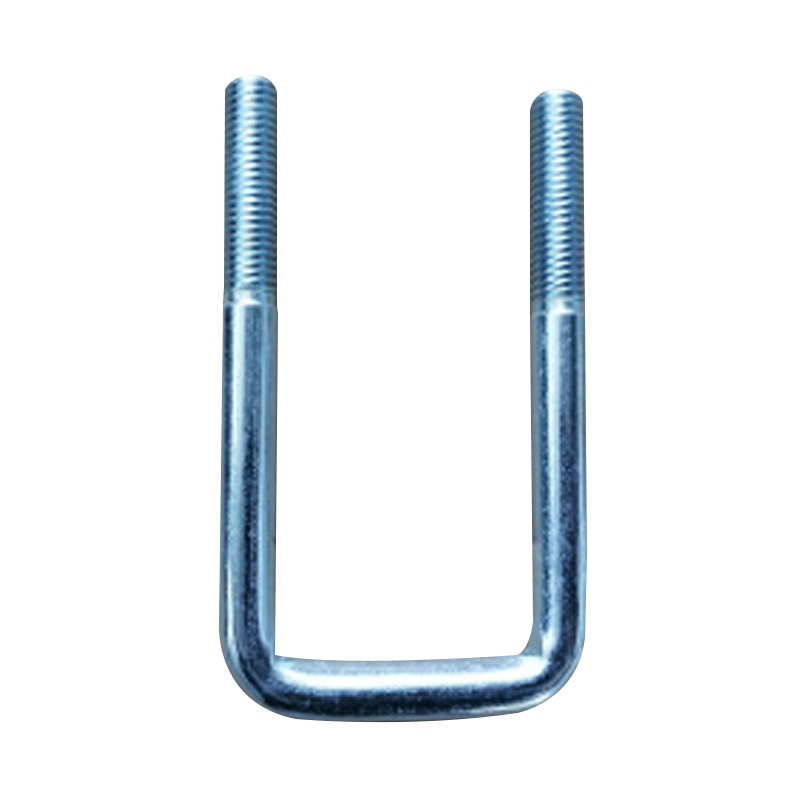
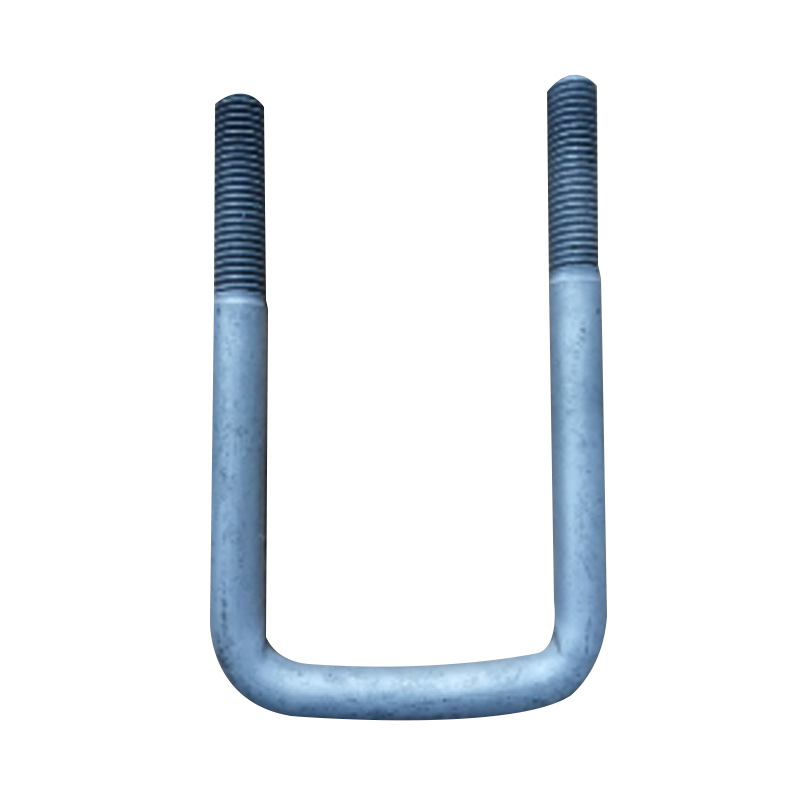
Trailer U Bolt
A trailer U-bolt is a curved fastener manufactured to precise specifications, engineered to clamp the leaf spring pack to the trailer axle and maintain suspension alignment under dynamic loads. These components are typically crafted from high-strength steel—available in raw, zinc-plated, hot-dip galvanized, or stainless finishes—to resist corrosion and maintain clamping force in environments ranging from road salt to freshwater exposure. The critical dimensions—thread diameter, inside width, and leg length—must match the axle tube size, spring width, and mount plate thickness. Proper installation involves using torque-specified nuts, lock washers or plates, and periodic re-torque checks, as steel U-bolts stretch during initial installation or under heavy load, which may loosen the clamp over time. -
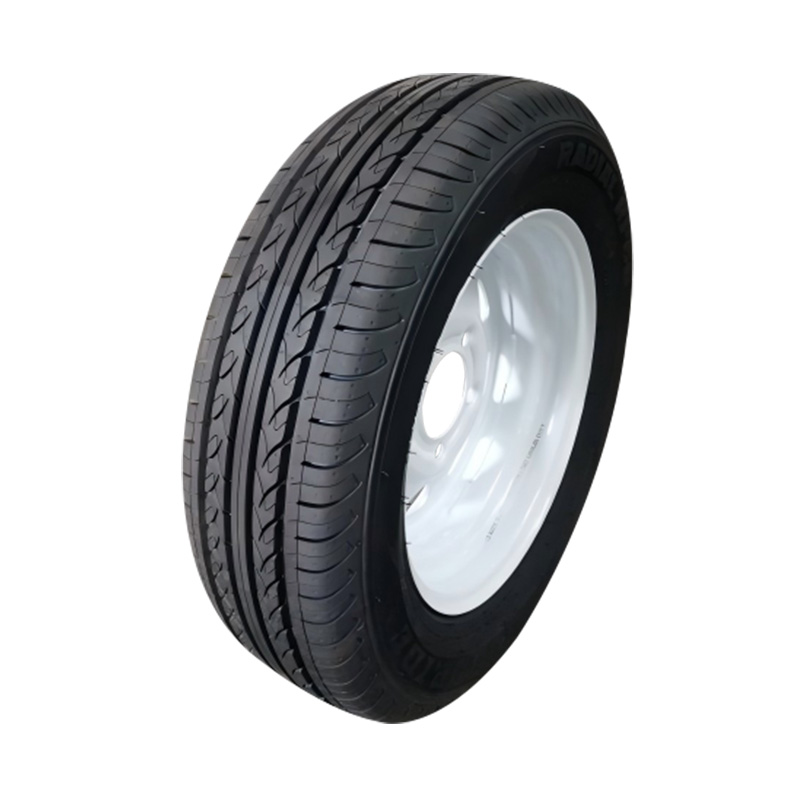
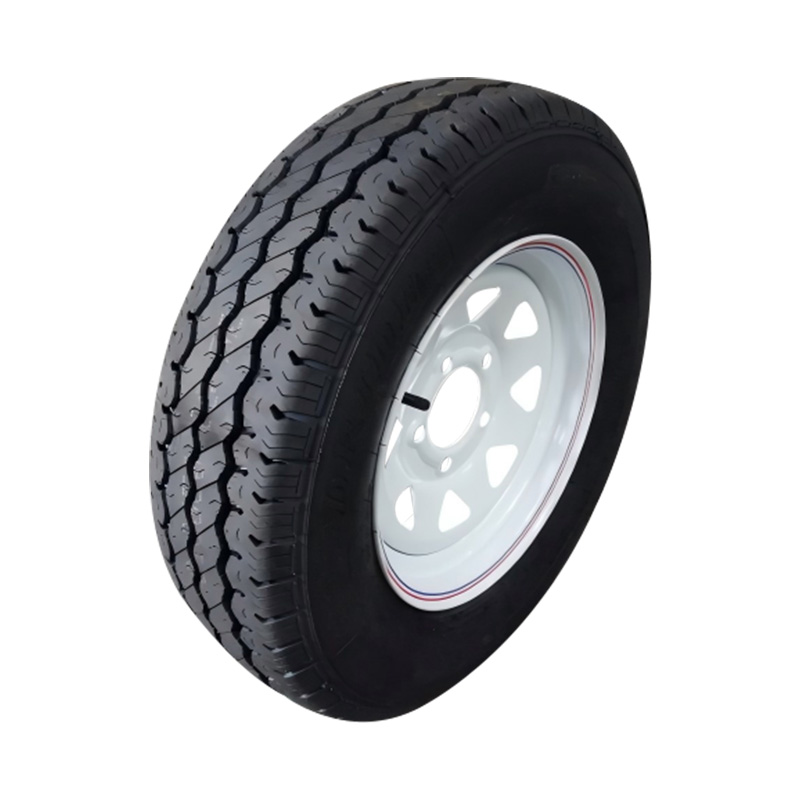
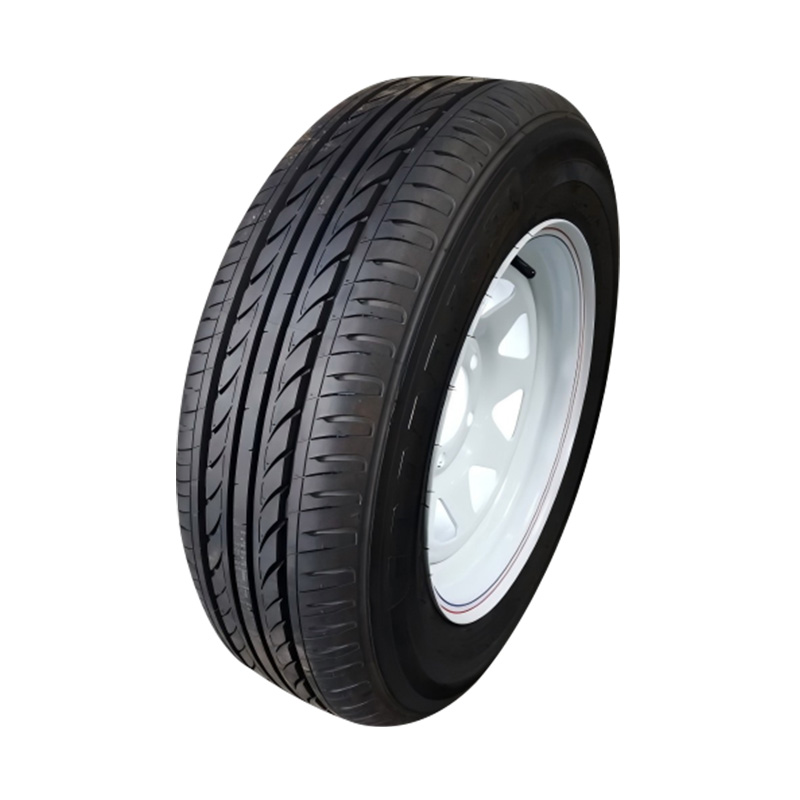
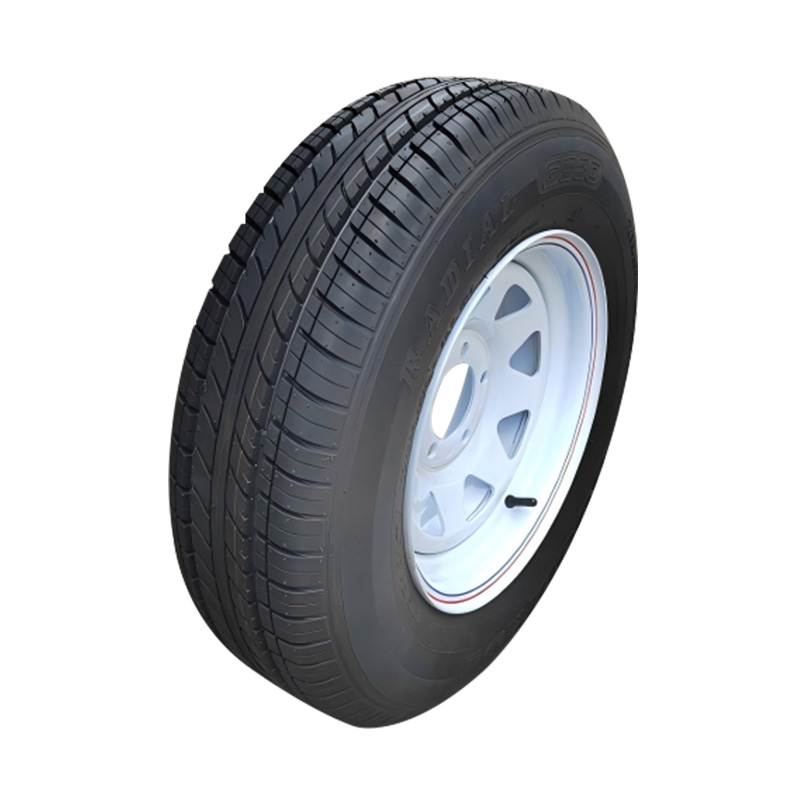
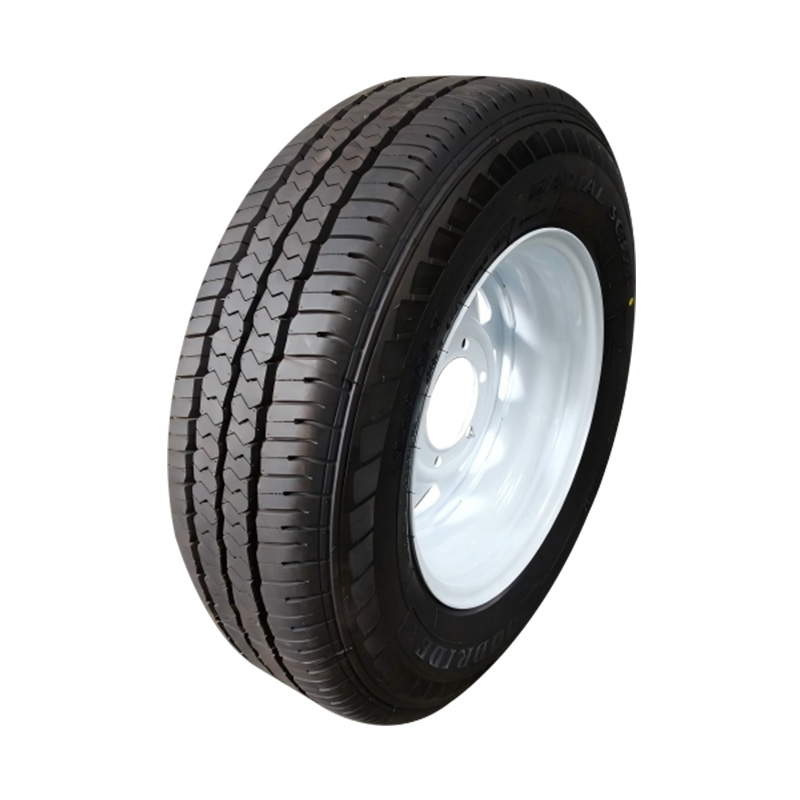
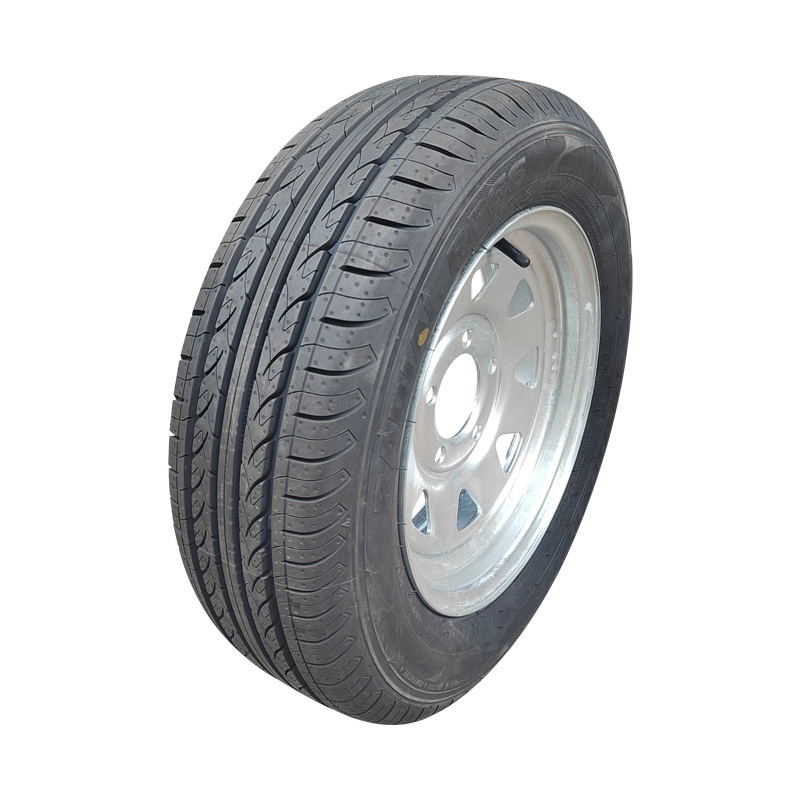
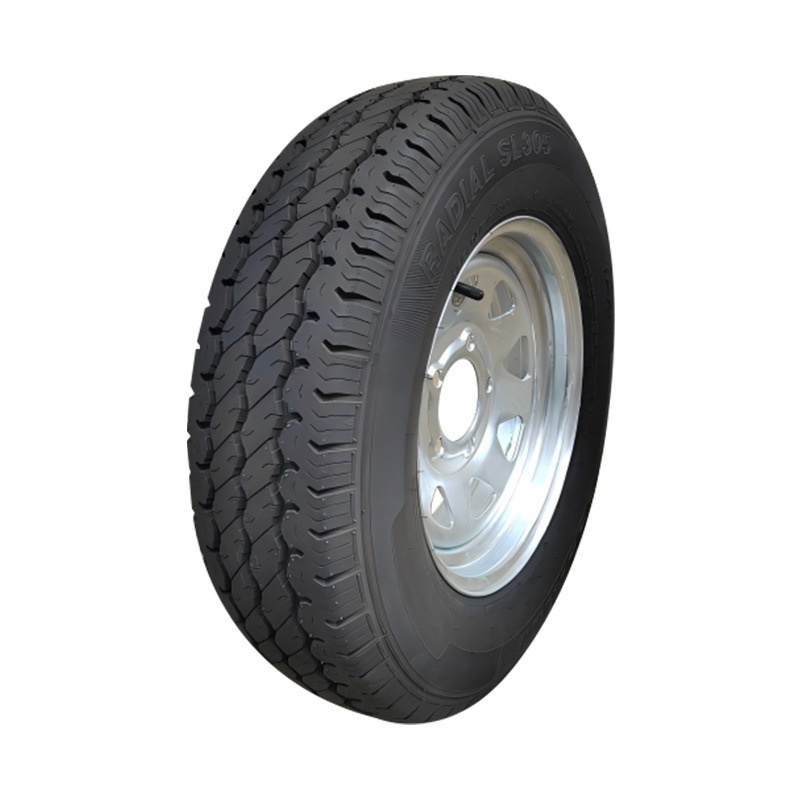
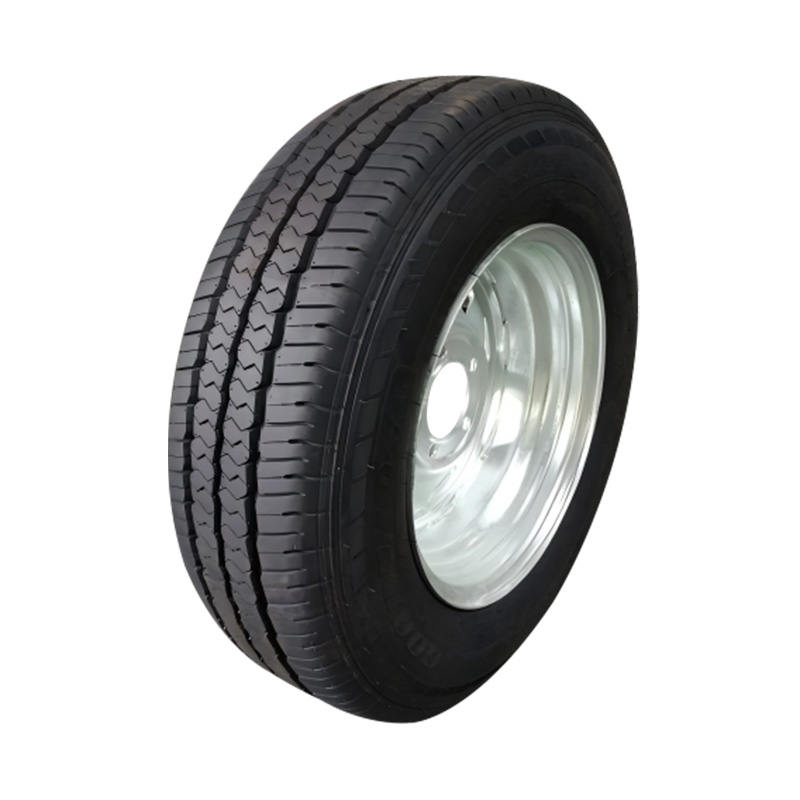
Trailer Wheel
A trailer wheel is a specialized wheel assembly designed to support the load of a trailer and transmit forces between the axle and the road surface, which includes the rim and hub, studs, lug nuts, and sometimes an integrated brake hub. These wheels vary in diameter—common sizes range from 8″ to 16″—and are built with load ratings that must match or exceed the trailer’s Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) to ensure safety and avoid overloading. Trailer wheels bolt to the axle hubs using standard patterns—often 4‑, 5‑, or 6‑lug—and are aligned using pilot centers or hub-centric designs to maintain proper tracking and reduce vibration. Wheels used on brake-equipped trailers may contain integrated brake drums or disc mounting surfaces, enabling braking functionality. -
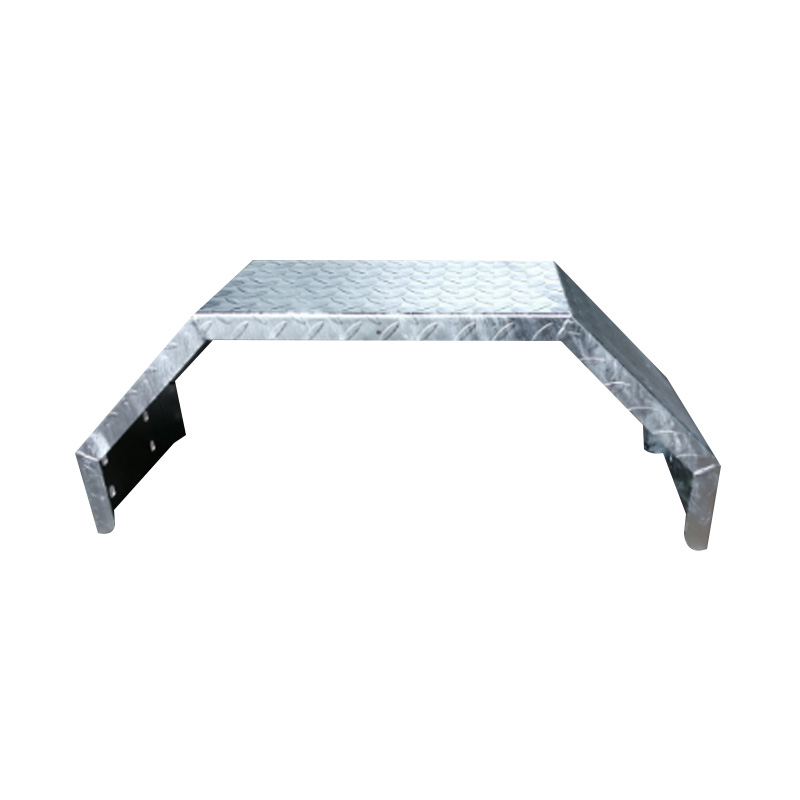
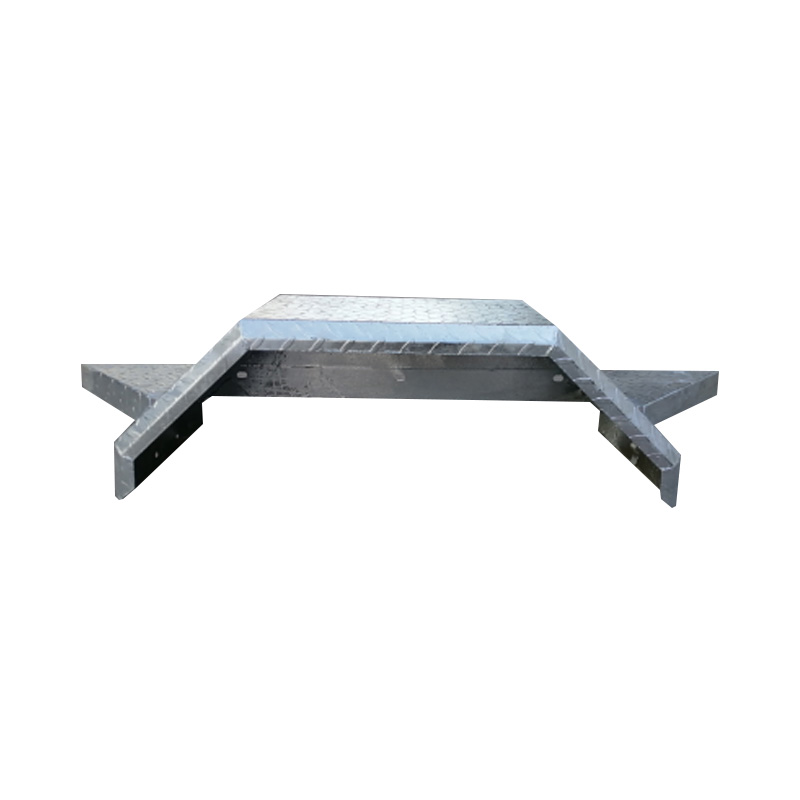
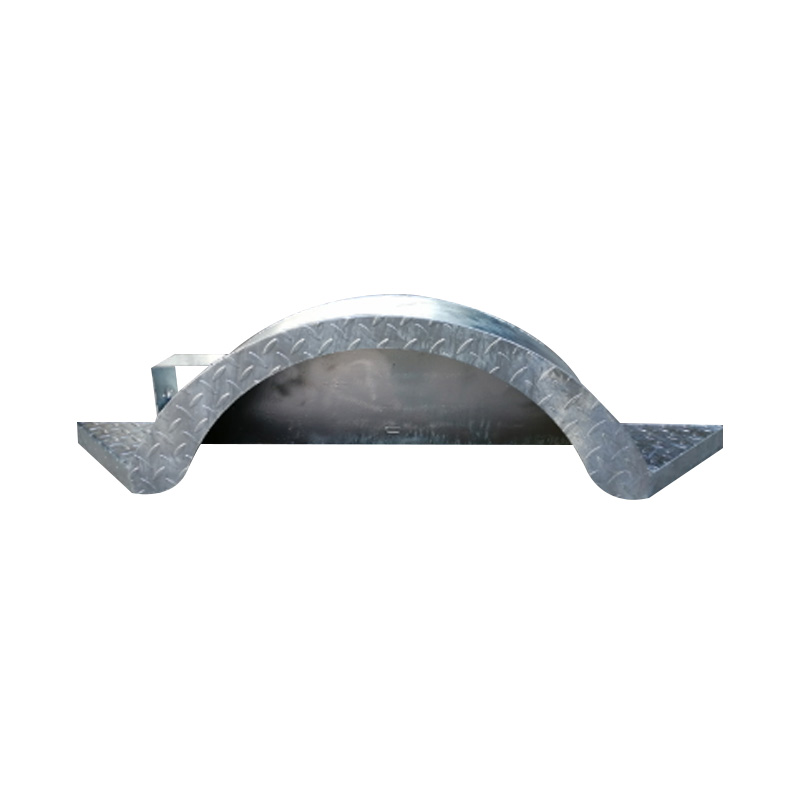
Trailer Mudguard
A trailer mudguard—or fender—is an essential protective cover mounted above the wheels to shield the trailer chassis, cargo, other vehicles, and pedestrians from debris, water, and stones expelled by rotating tires. Often made from durable galvanized steel or aluminum materials, mudguards need to resist impacts, corrosion, and ultraviolet decay. Metal versions offer robust protection and can be shaped to specific designs—single‑wheel or tandem configurations. Mudguards are engineered to comply with legal standards that dictate coverage depth and proximity to the tire to minimize spray and projection of road particles. Beyond legal compliance, they help preserve under‑carriage components by diverting salty water and gravel away from suspension parts and braking surfaces. -
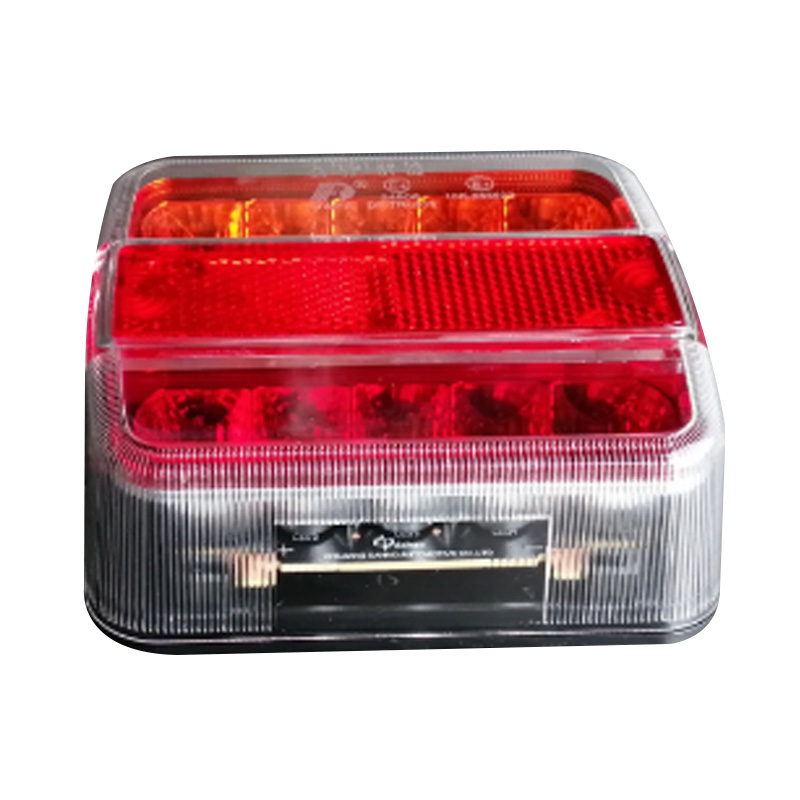
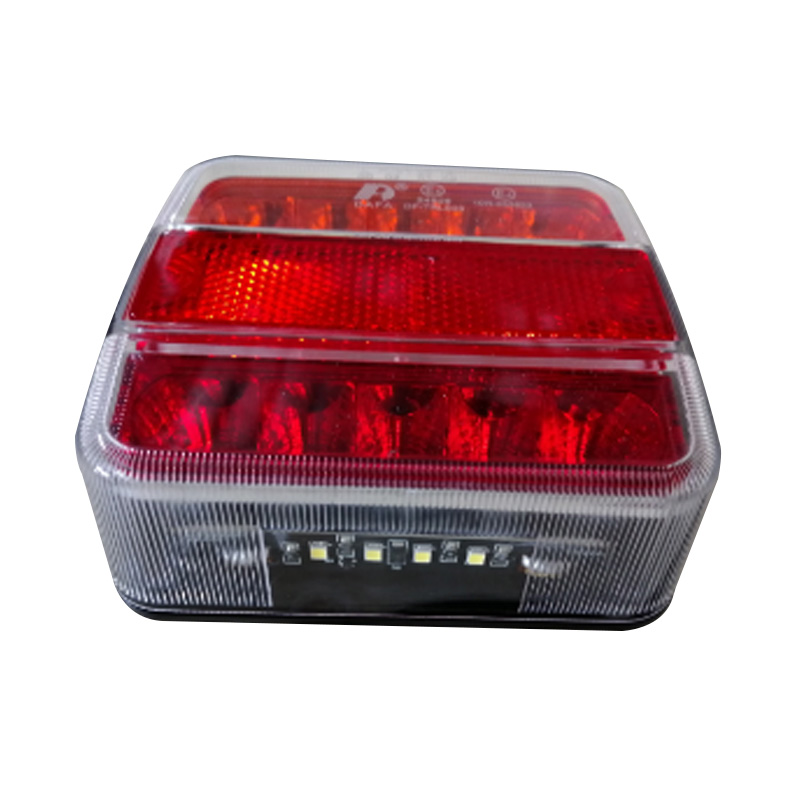
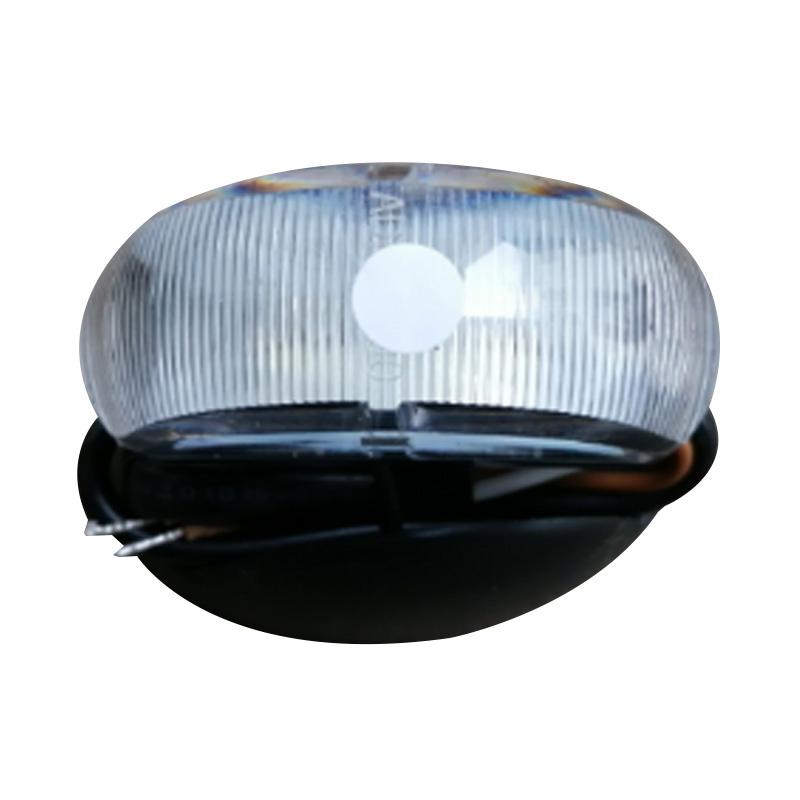
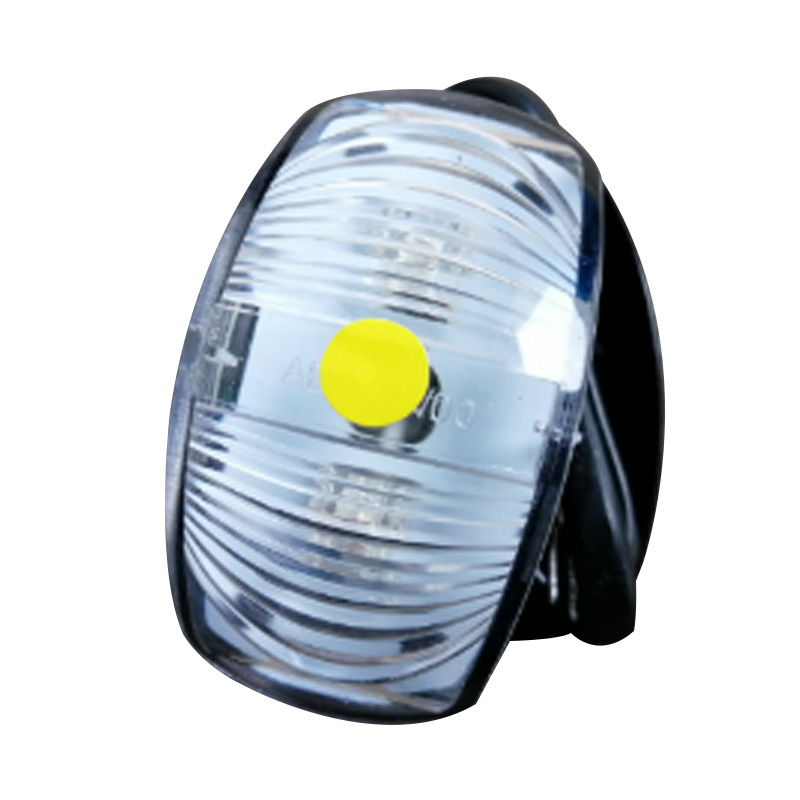
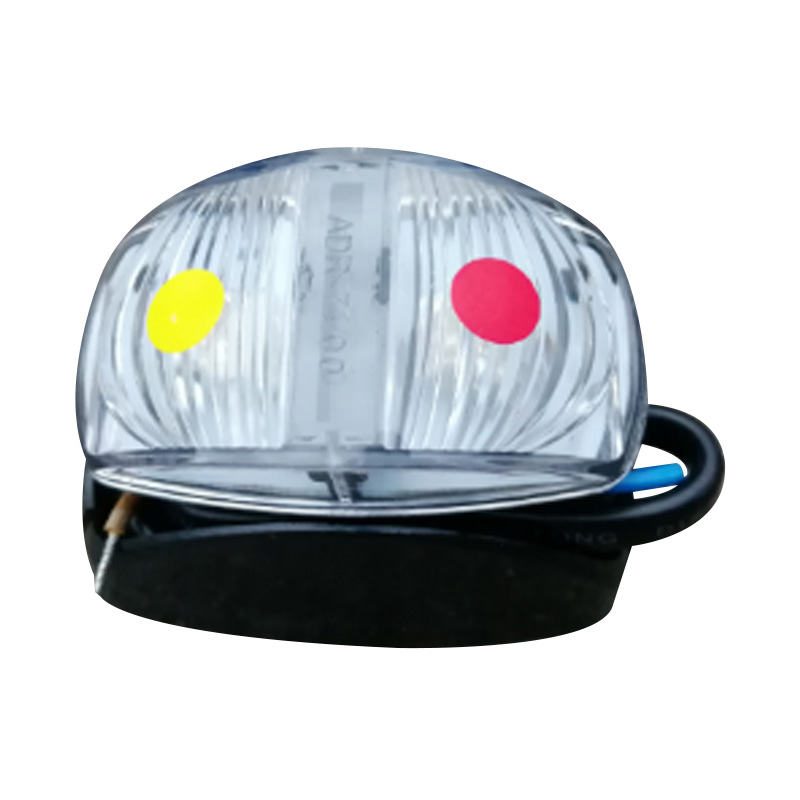
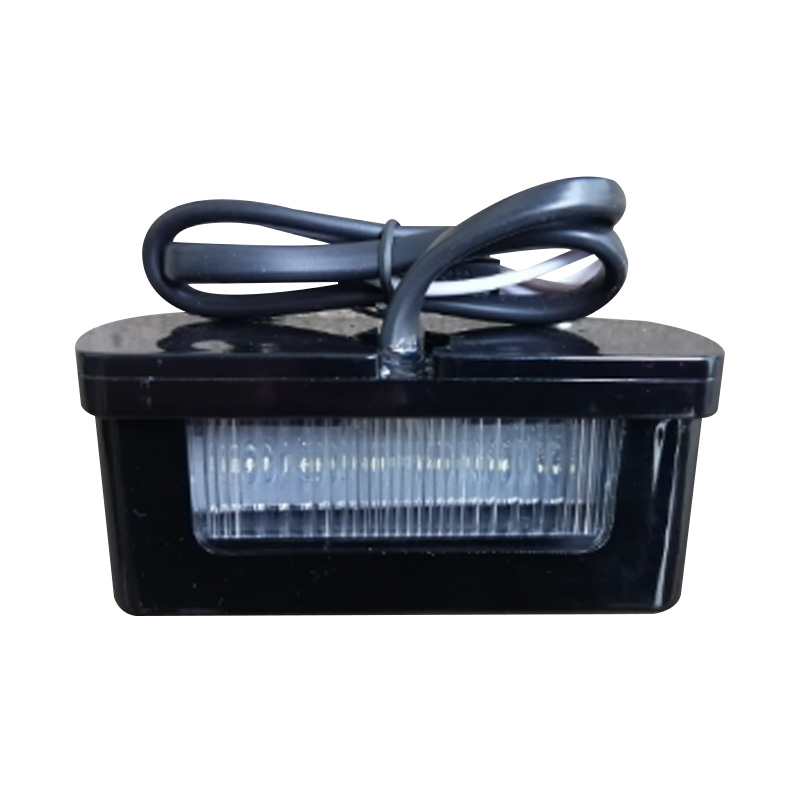
Trailer Light
Trailer lights are engineered to ensure a trailer is visible, communicative, and compliant on public roads, integrating multiple lighting functions—tail lights, stop lights, turn signals, side markers, clearance lamps, license plate illumination, and reflectors—into a single unit or modular kit. Designs vary according to trailer type and dimensions: for example, trailers under 80 inches wide and 30 feet long typically require rear stop, tail, and turn lights plus reflectors and a license plate lamp, while wider or heavier trailers must also include clearance lights and conspicuity strips. Critical technical considerations include proper grounding (white wire to chassis), system voltage (DC), and connector type (4-, 5-, 6-, or 7-way) to ensure synchronised operation with the tow vehicle. -
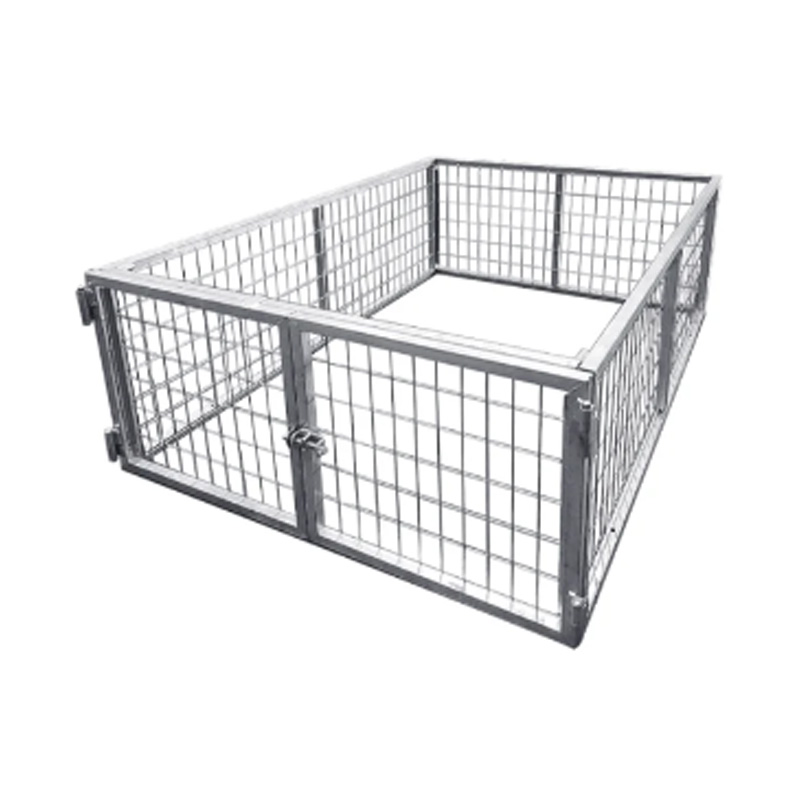
Trailer Cage
A trailer cage is an add-on steel framework bolted onto the sides and rear of a flatbed or utility trailer to confine and secure loose or bulky cargo, effectively forming high walls to prevent spillage and enhance load versatility. These structures typically consist of side panels, a front panel, and a hinged or swing rear gate with locking provisions, and are built from structural hollow sections or mesh grids (e.g., 40 × 40 mm RHS frames with 100 × 50 × 4 mm mesh) that offer clear visibility while maintaining strength. Cage kits are often hot-dip galvanized to resist corrosion and rugged enough for regular commercial use, and can be installed or removed in minutes to adapt to different haul scenarios. -
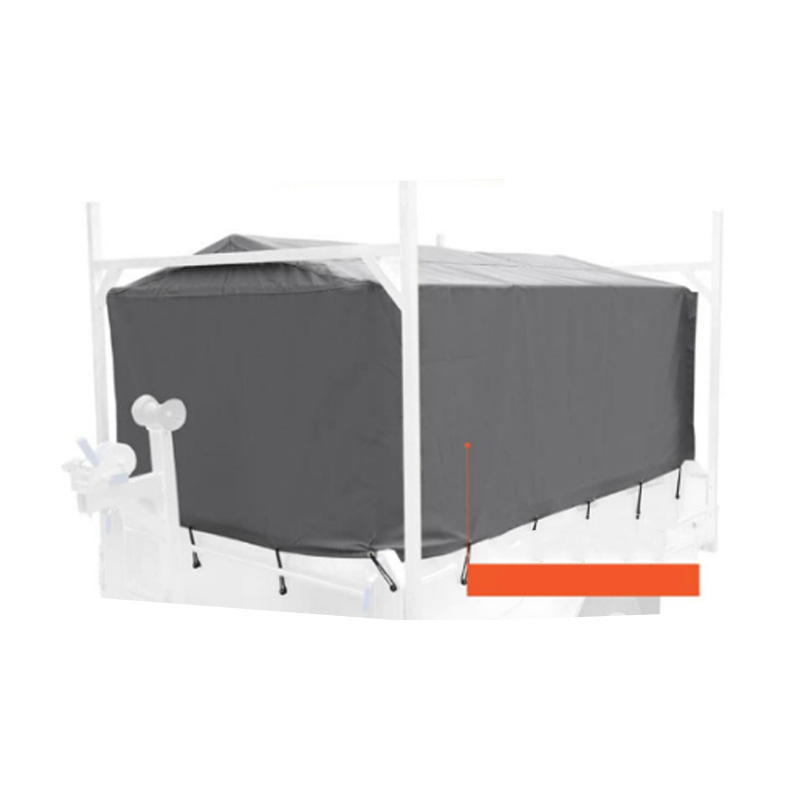
Trailer Canvas Cover
A trailer canvas cover is an important accessory used to protect cargo from outdoor elements such as rain, dust, and UV rays during transport. Typically made from durable materials like PVC-coated polyester, ripstop canvas, or heavy-duty polyethylene, these covers offer varying degrees of water resistance, breathability, and abrasion resistance. Canvas covers are particularly beneficial for loads sensitive to moisture or debris, such as garden equipment, construction materials, or livestock feed. They are often equipped with features like reinforced eyelets, adjustable straps, and elastic hems to ensure a secure fit across different trailer sizes and shapes. Some models include UV-resistant coatings to prolong the cover's lifespan and maintain its protective qualities. -
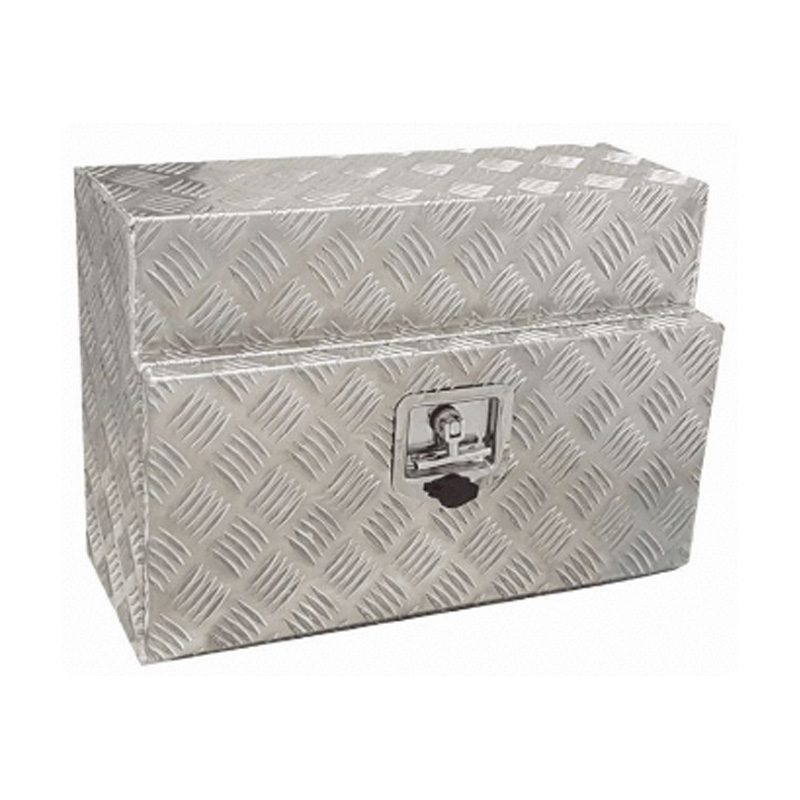
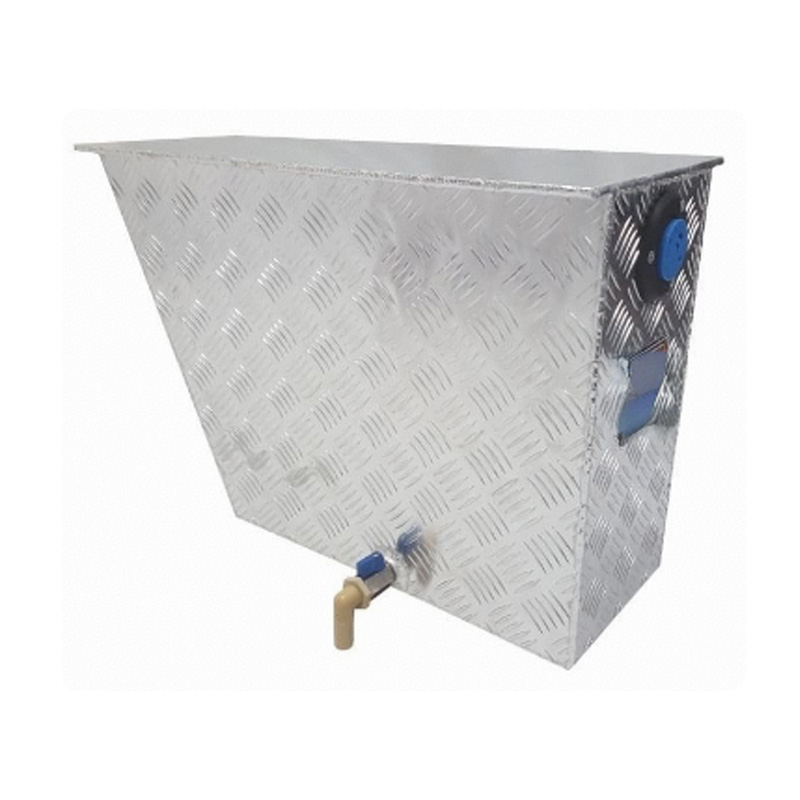
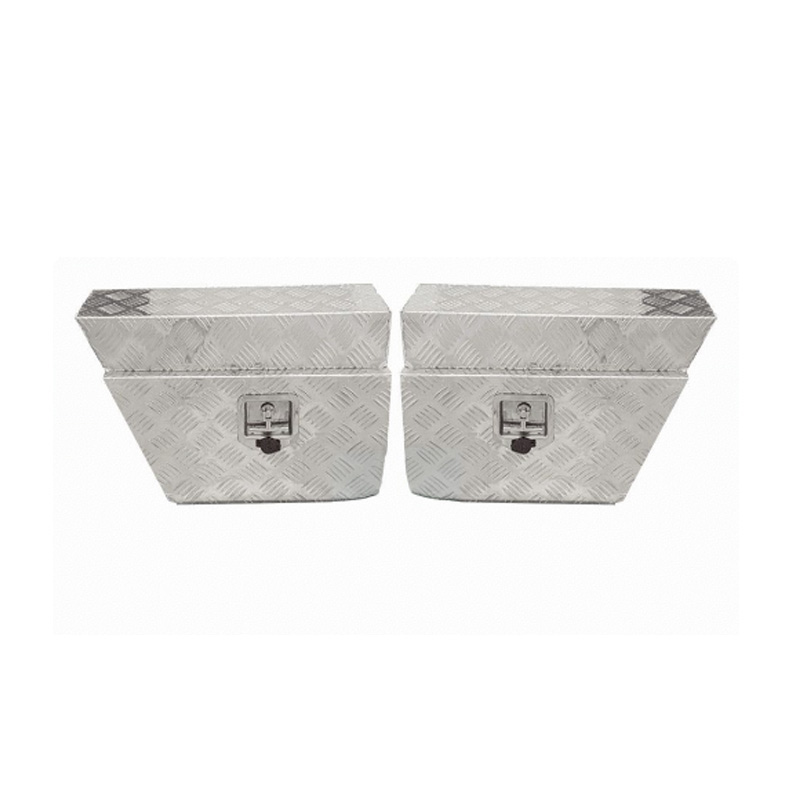
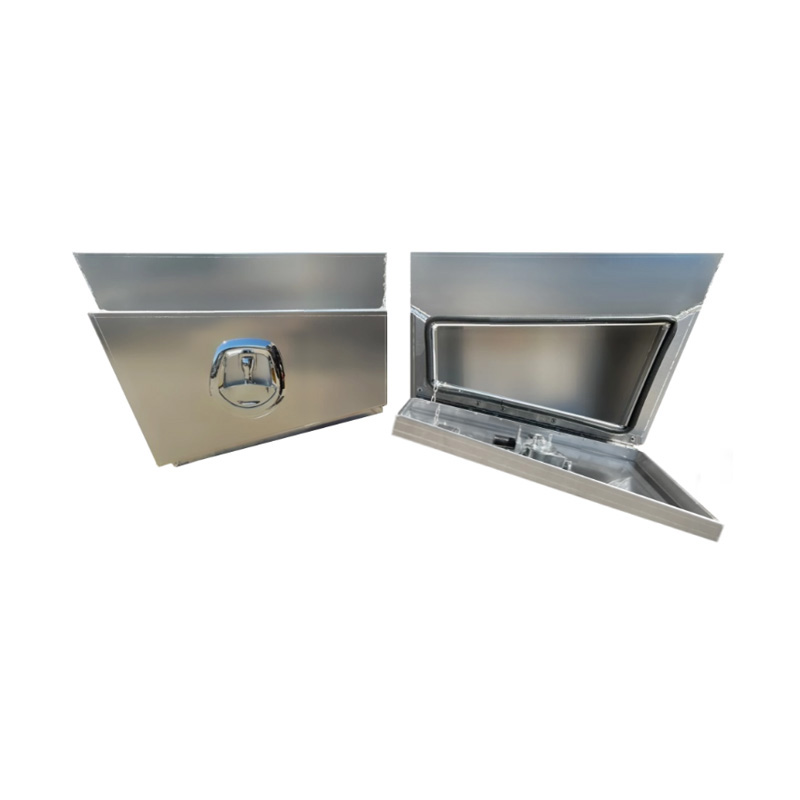
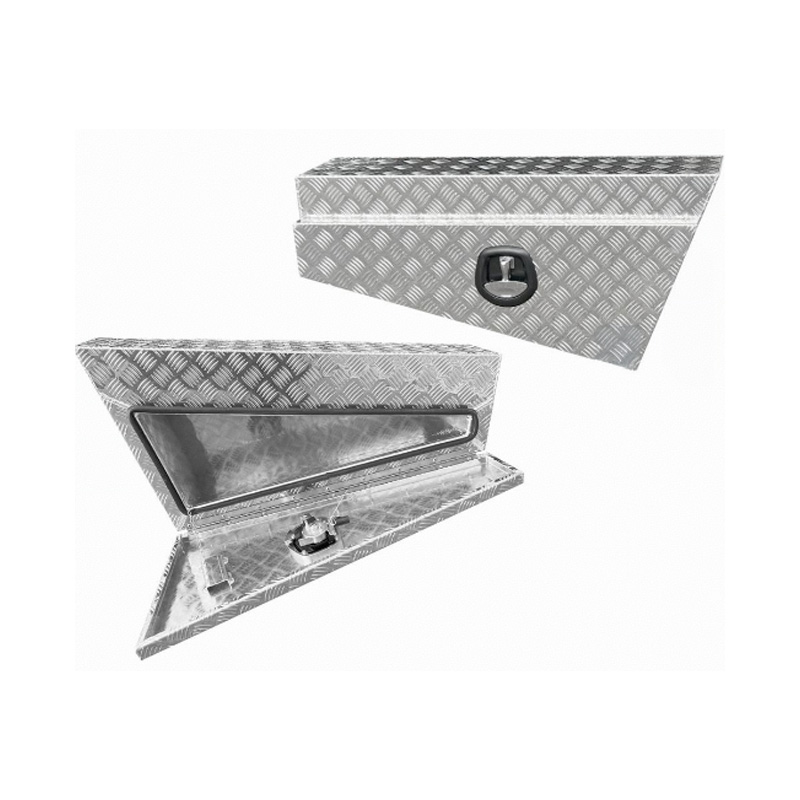
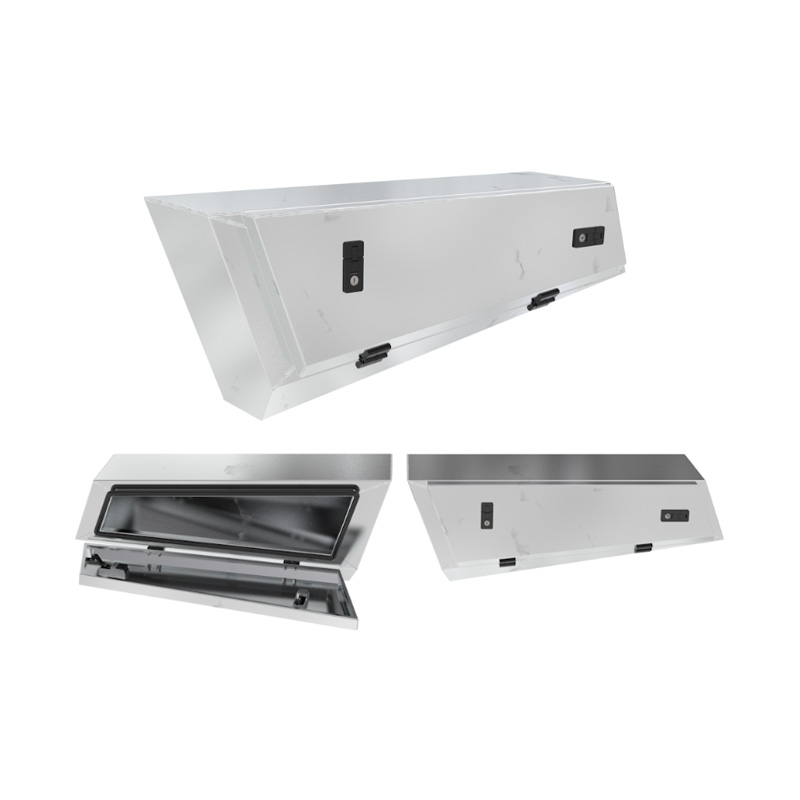
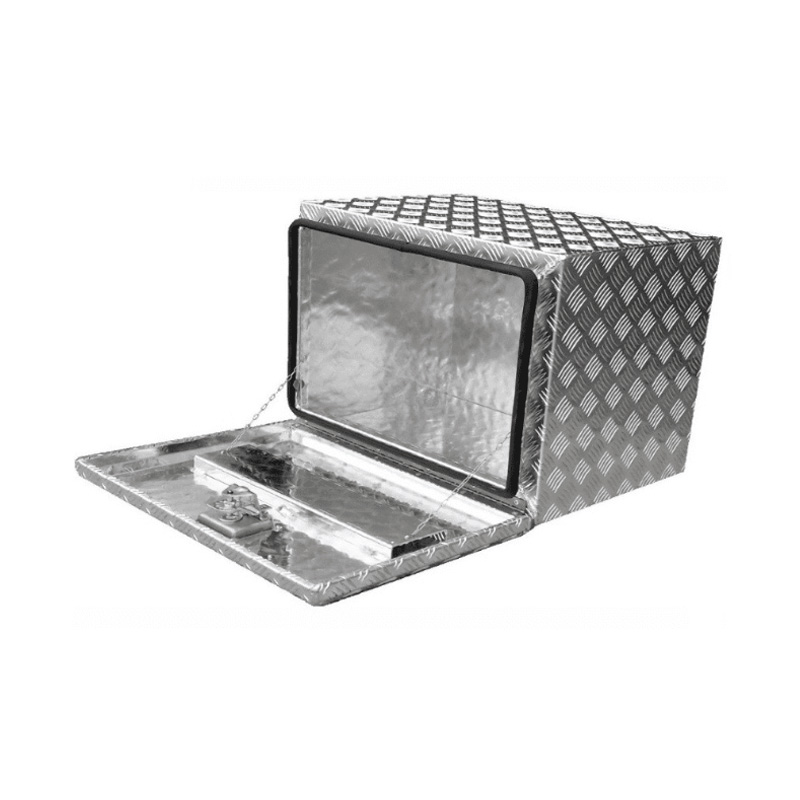
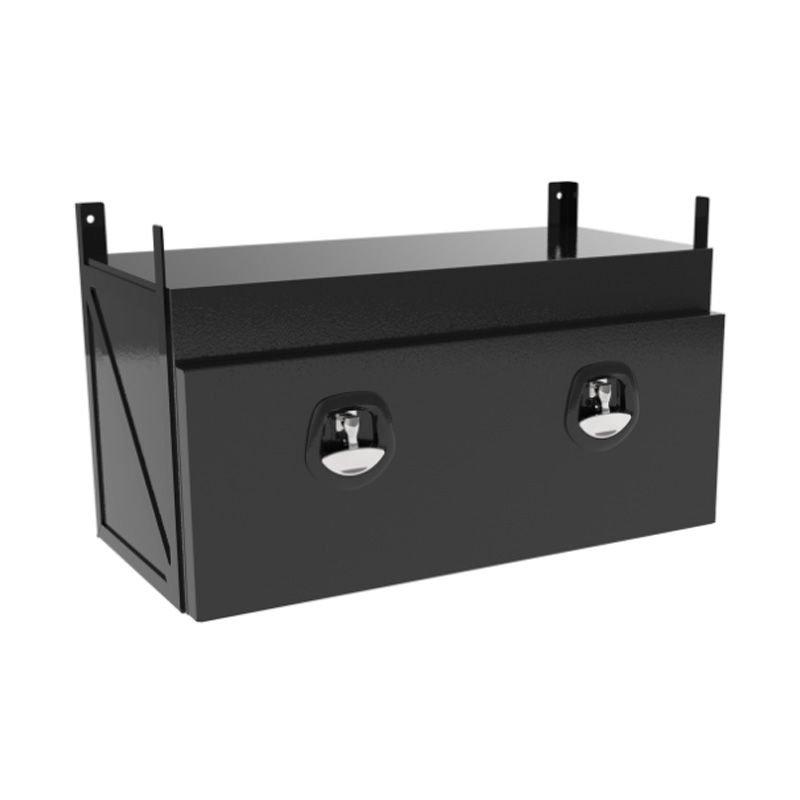
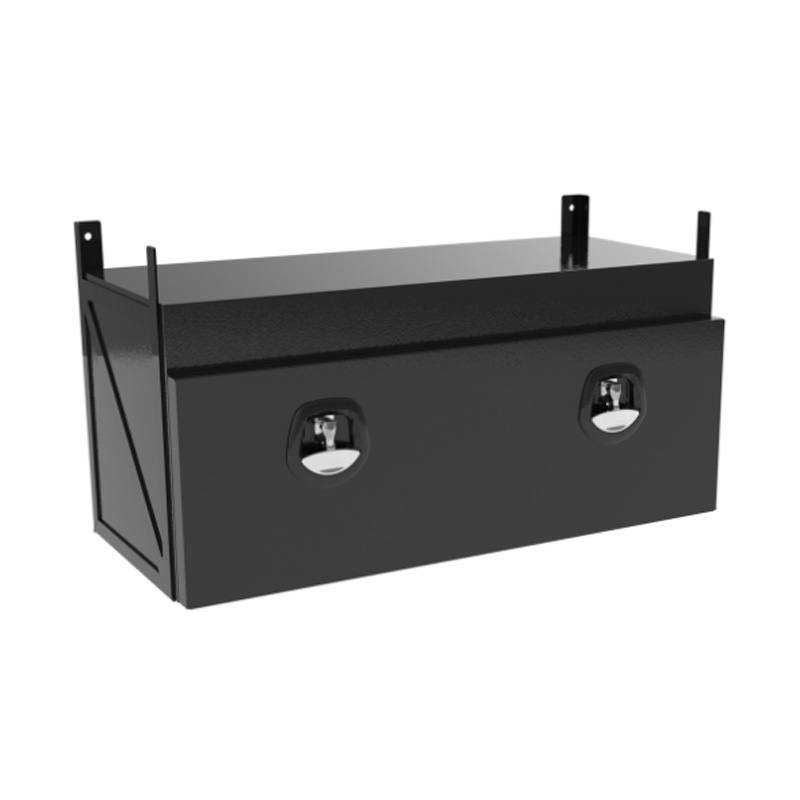
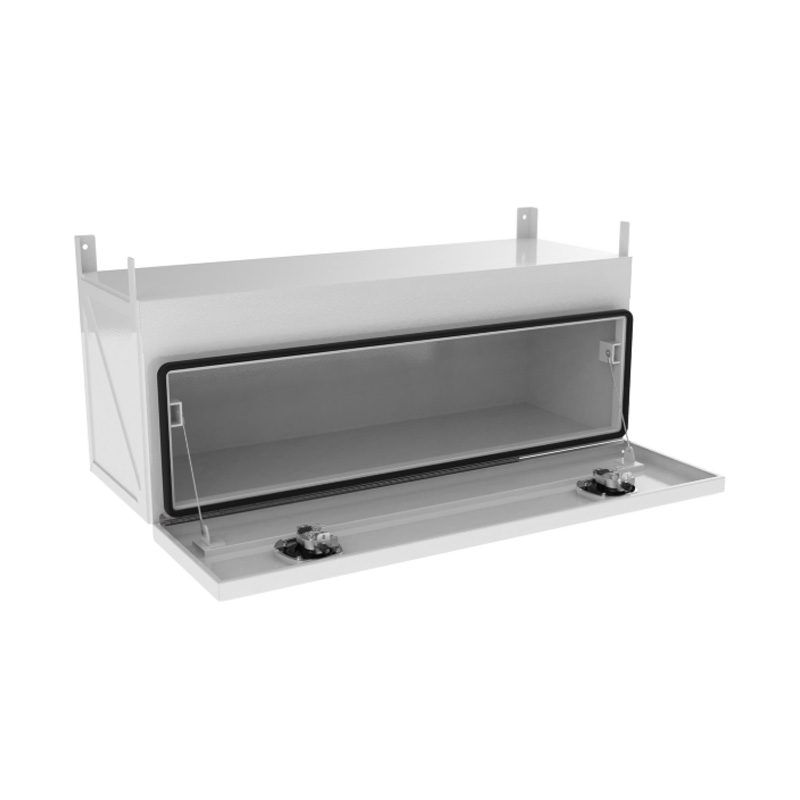
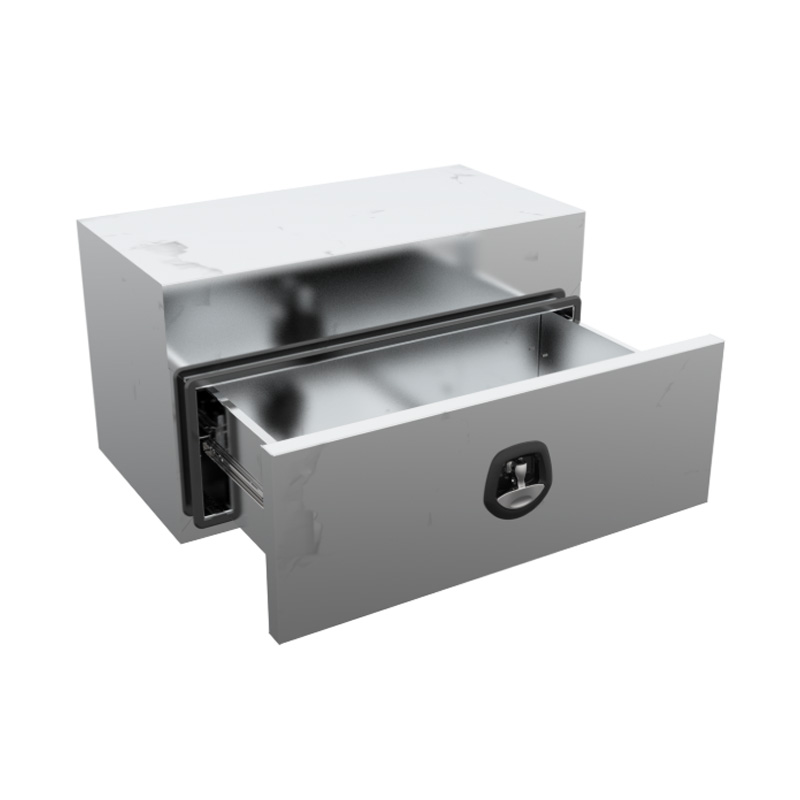
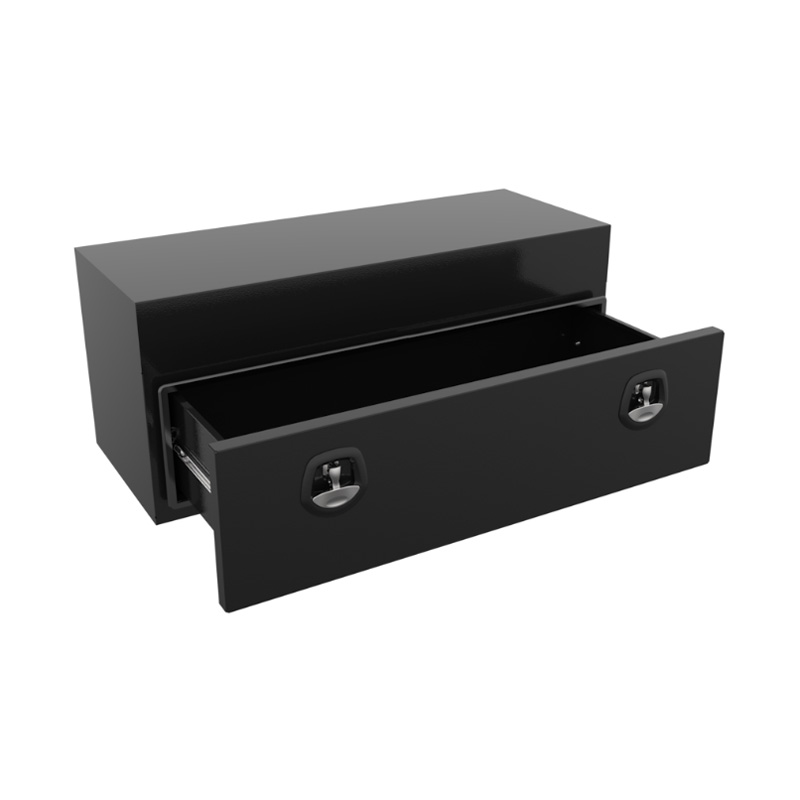
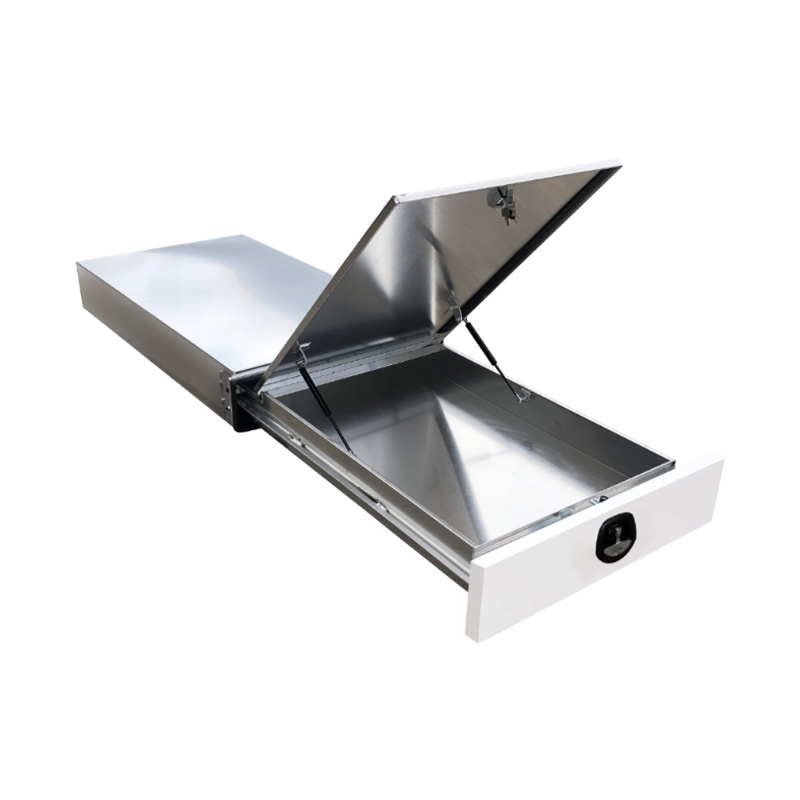
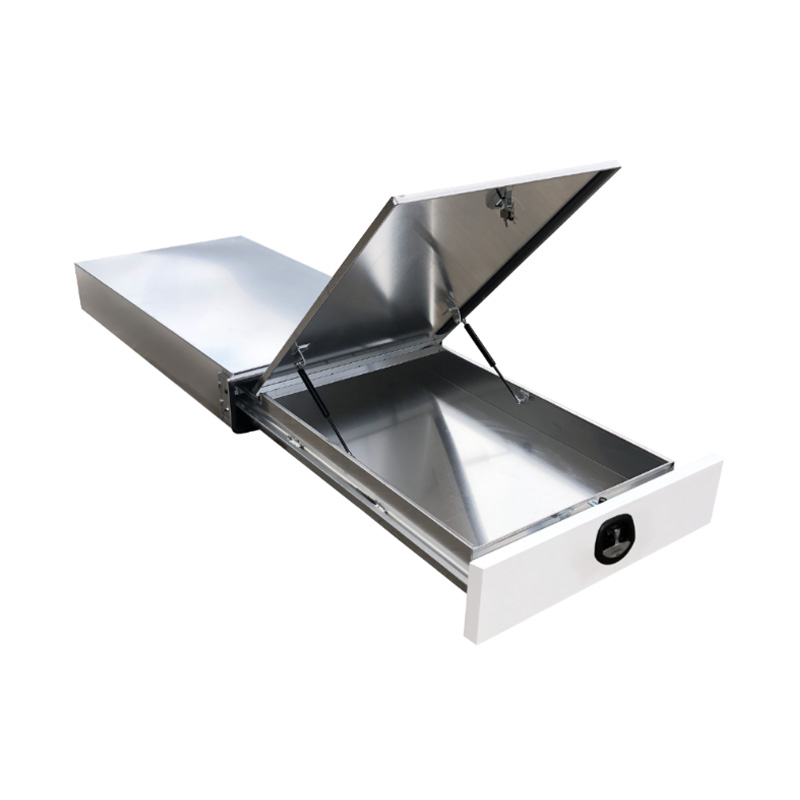
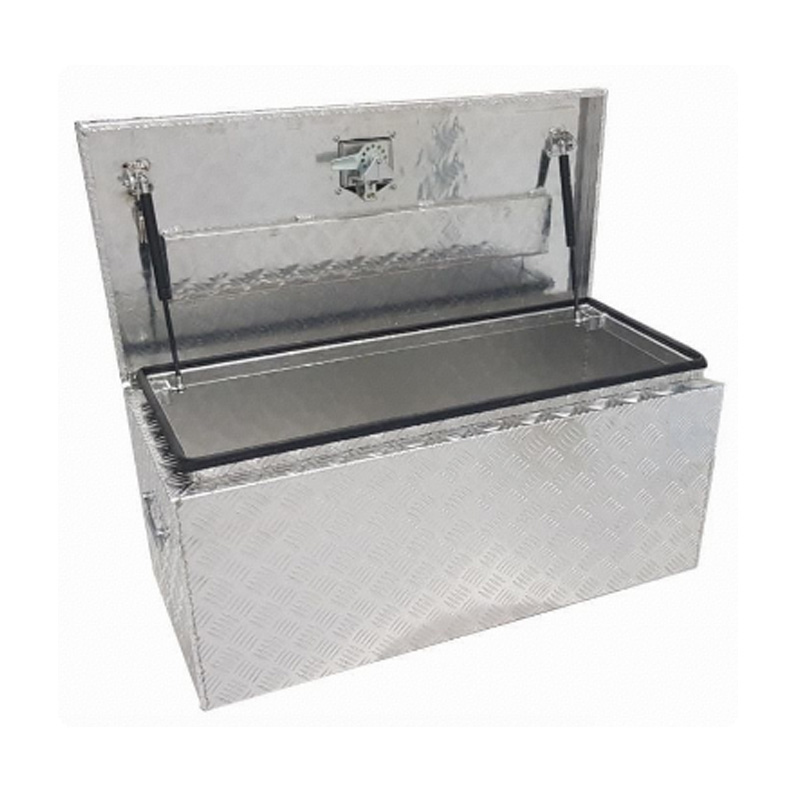
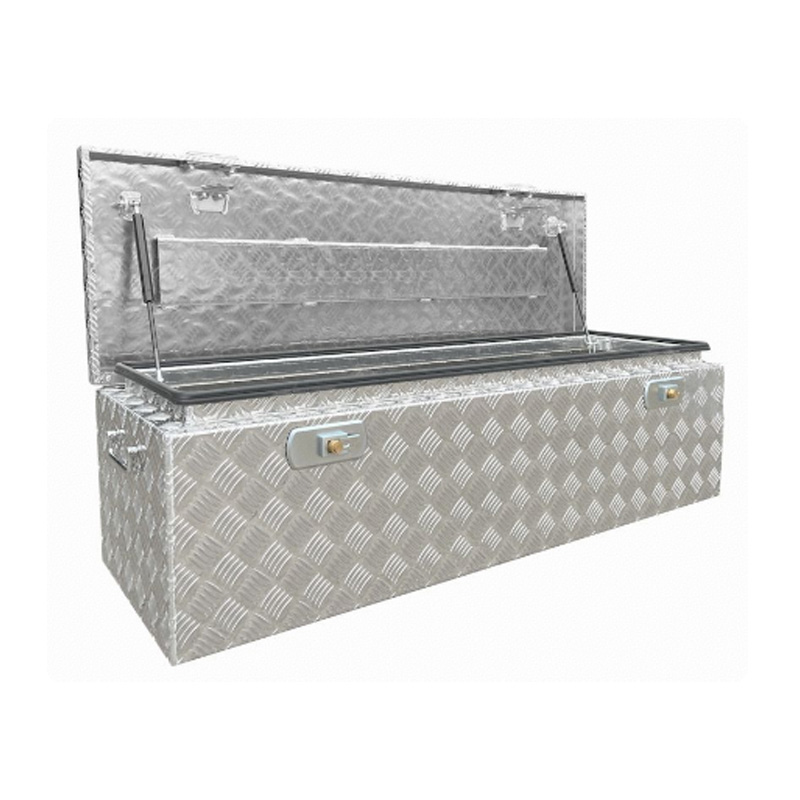
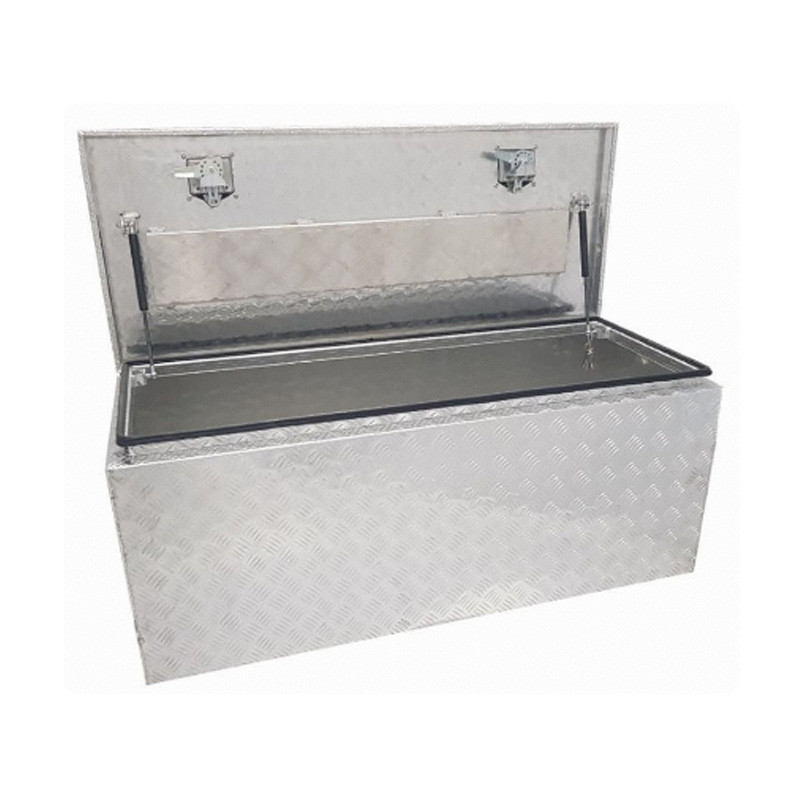
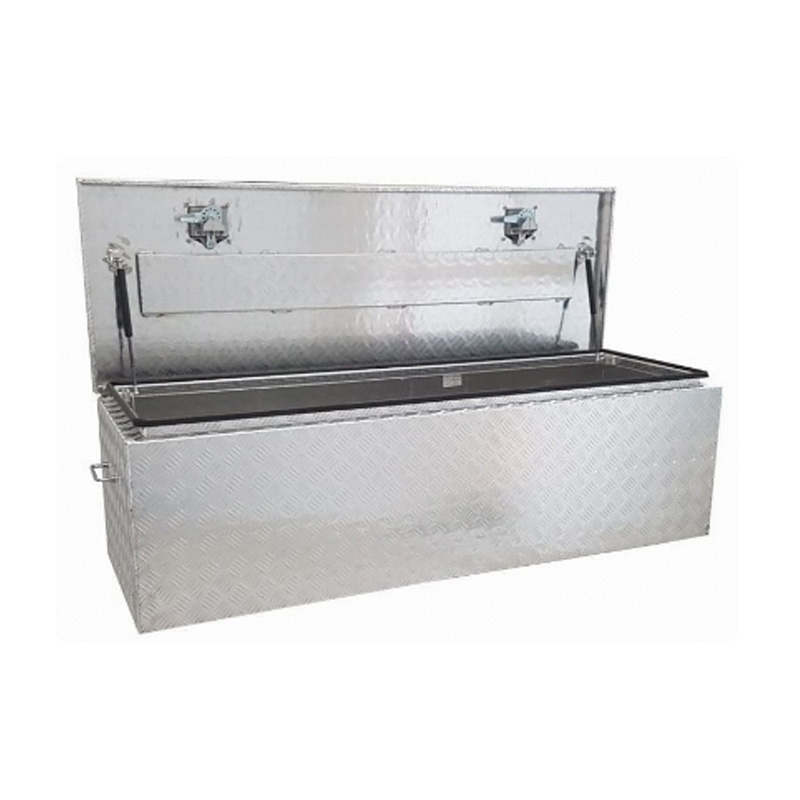
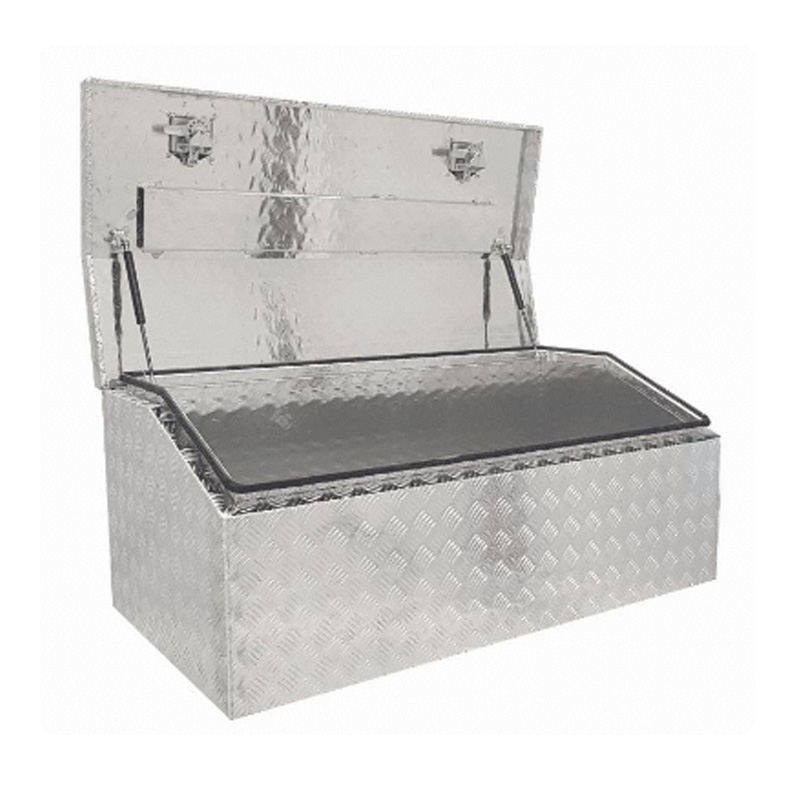
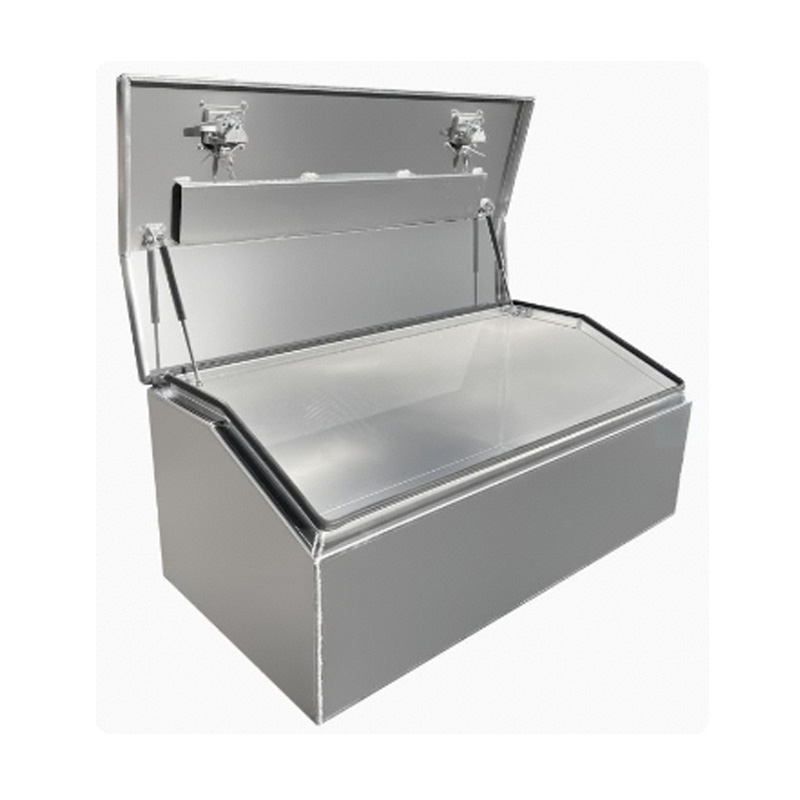
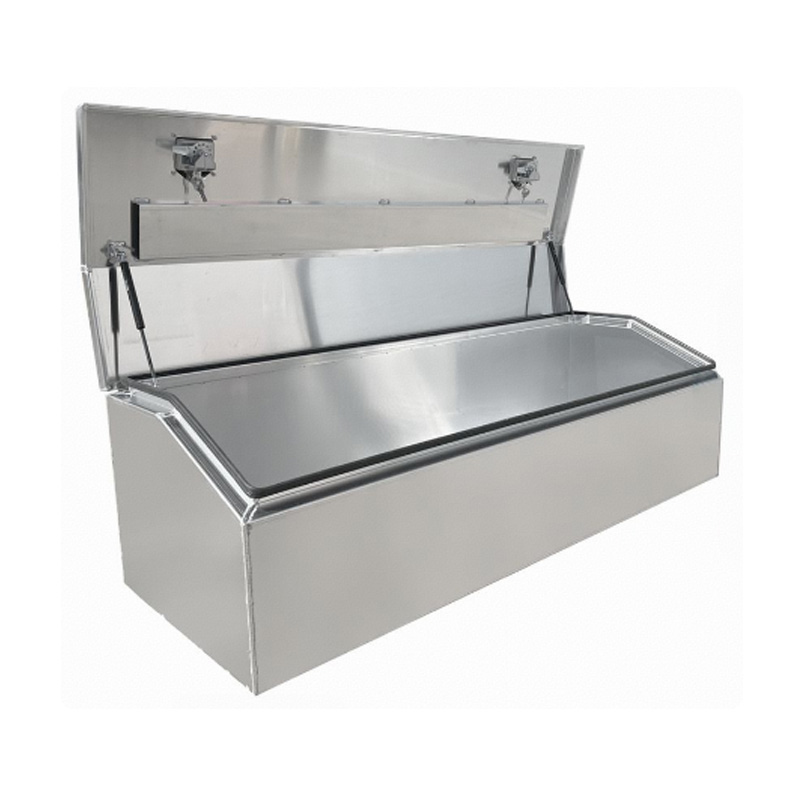
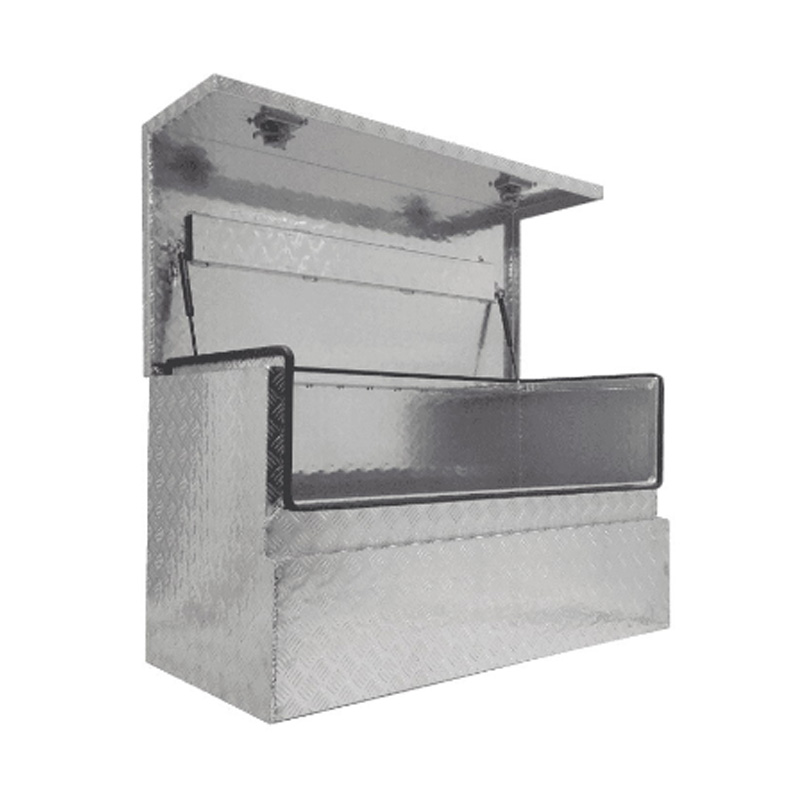
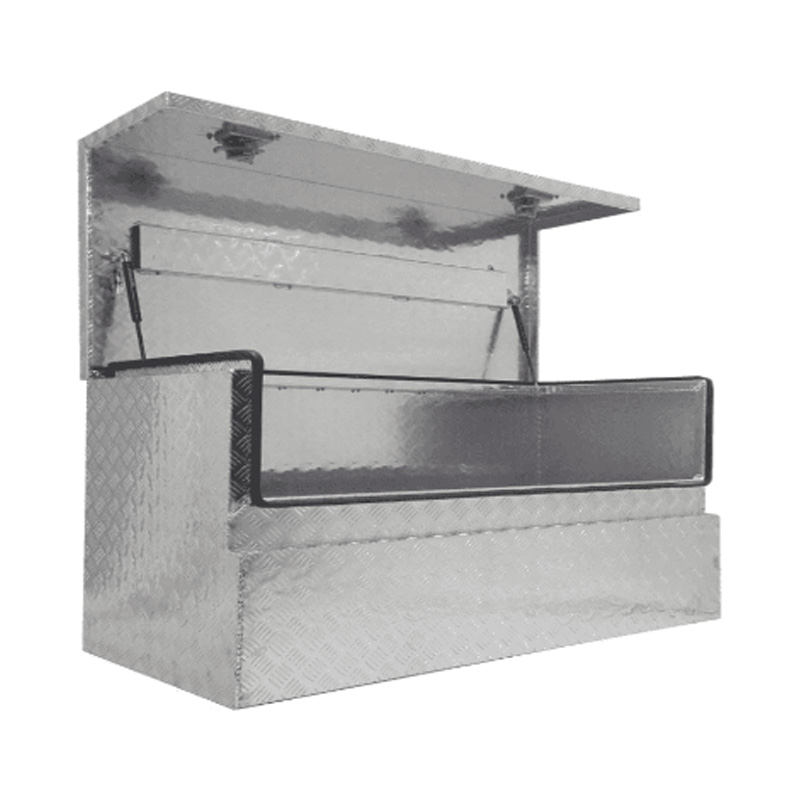
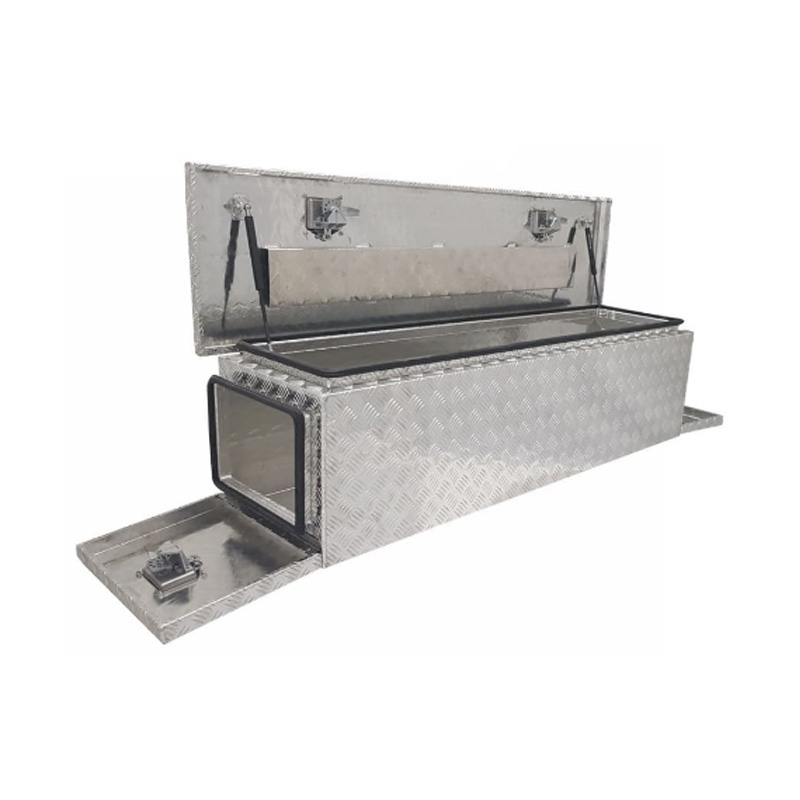
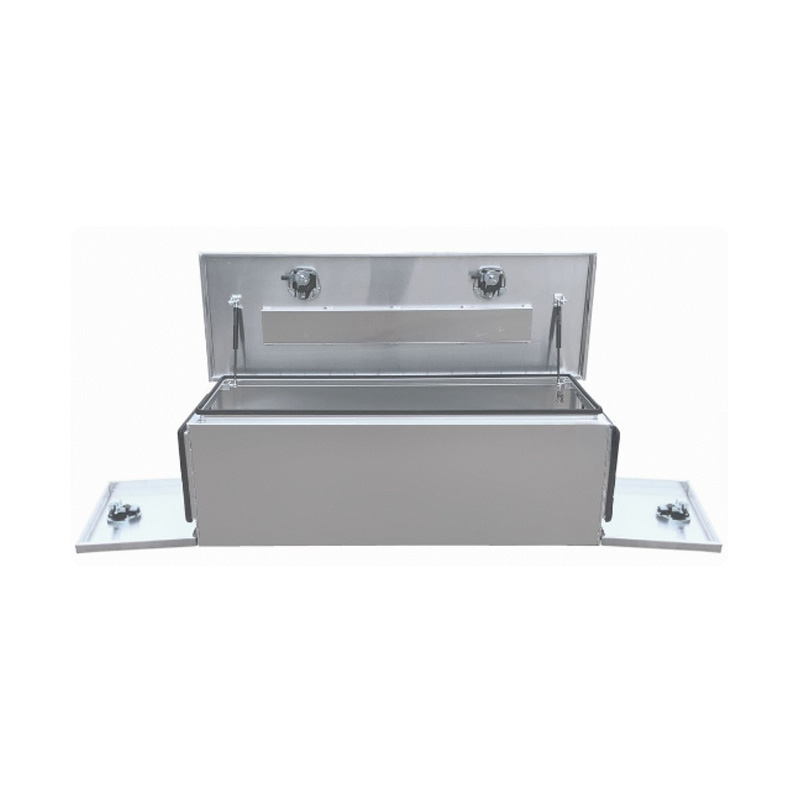
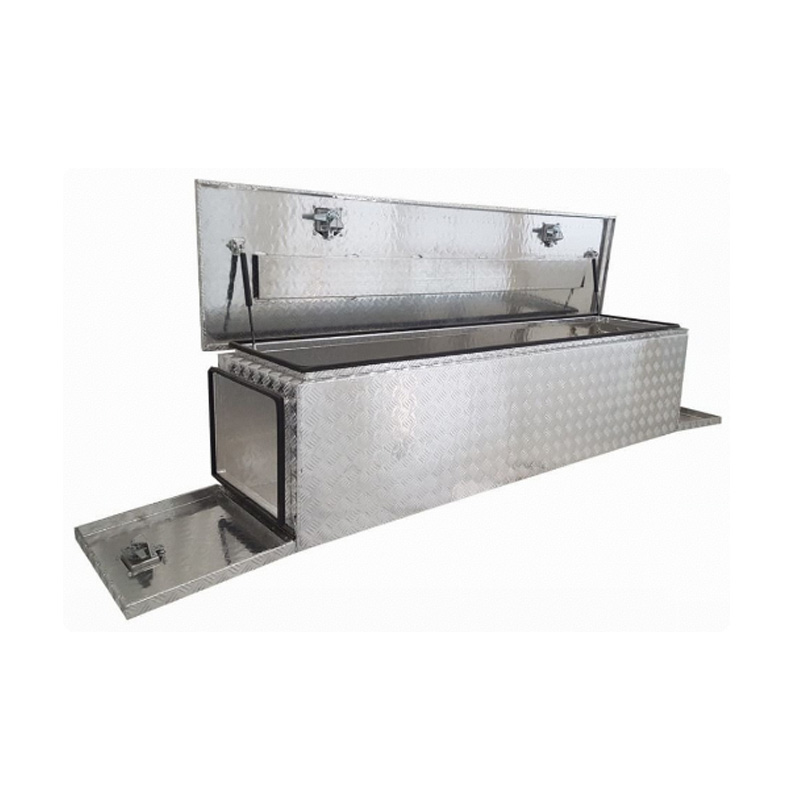
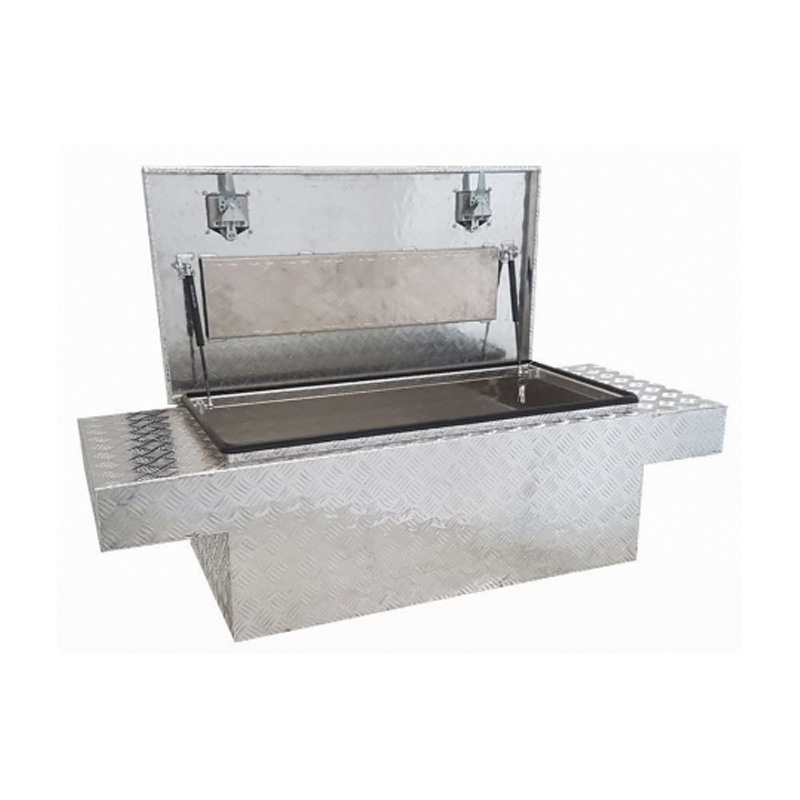
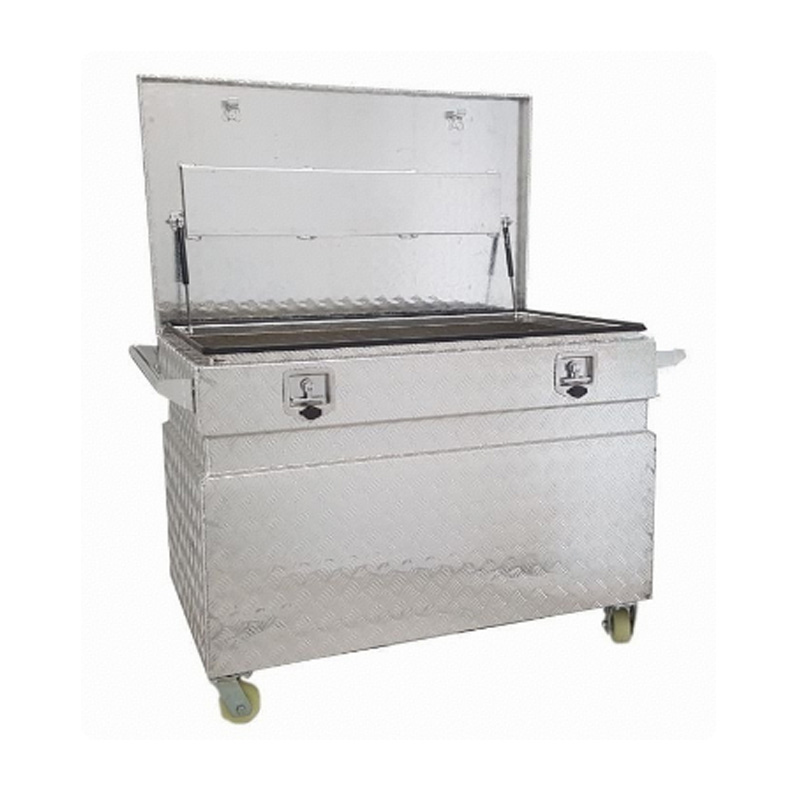
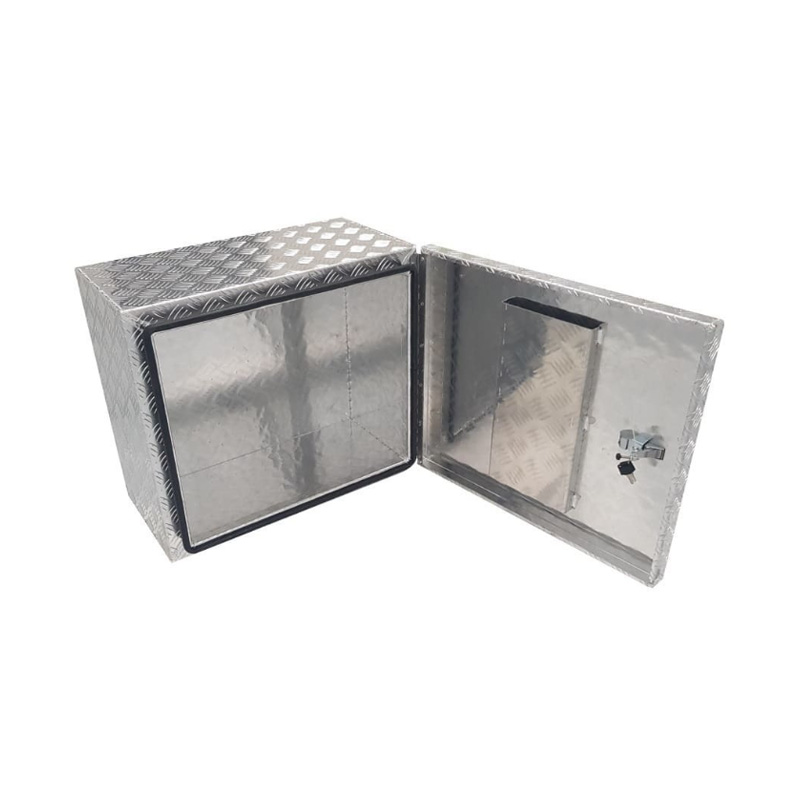
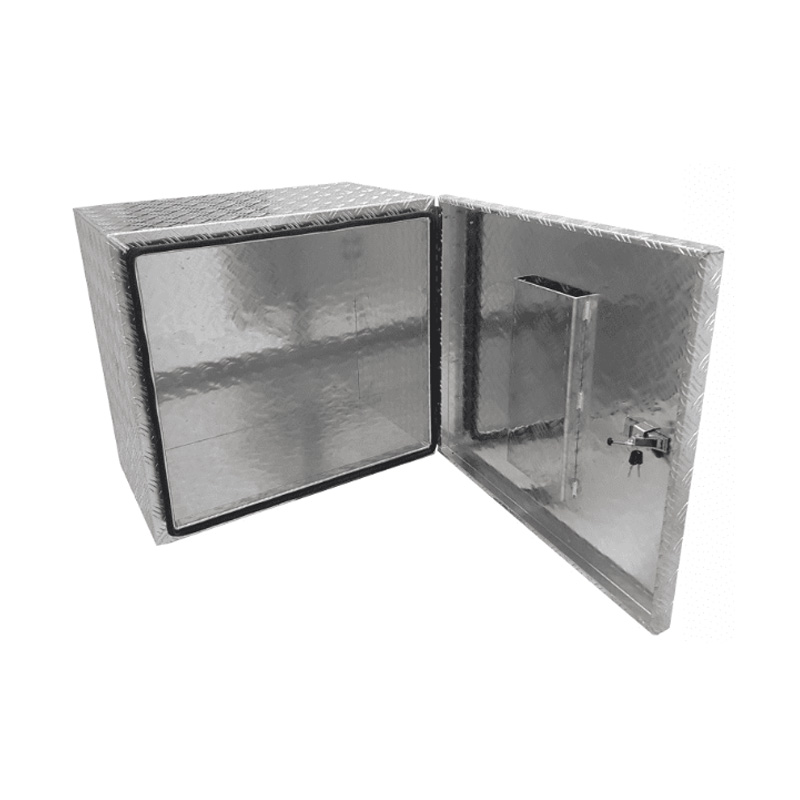
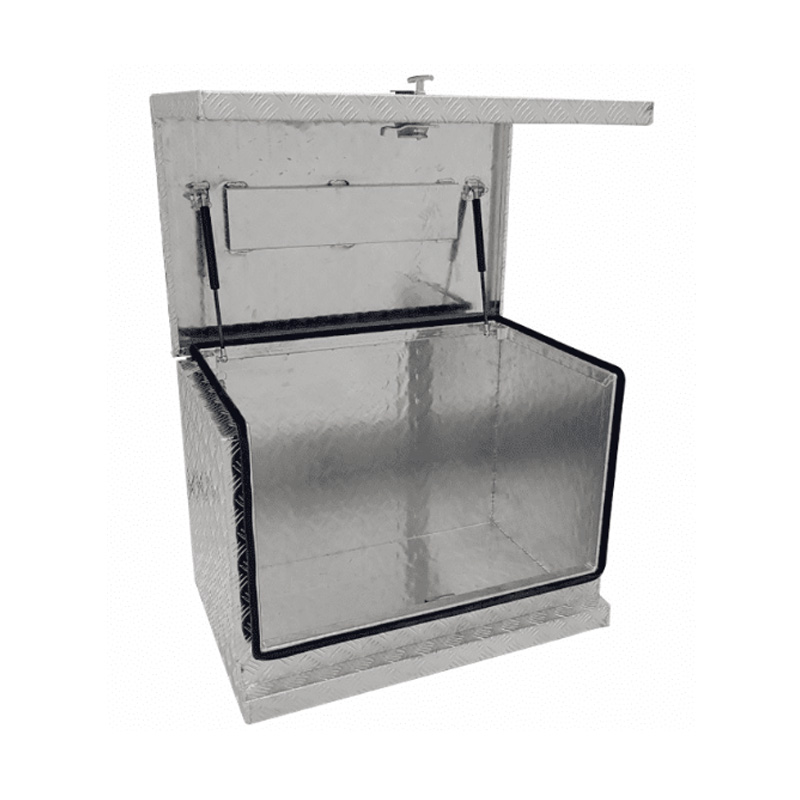
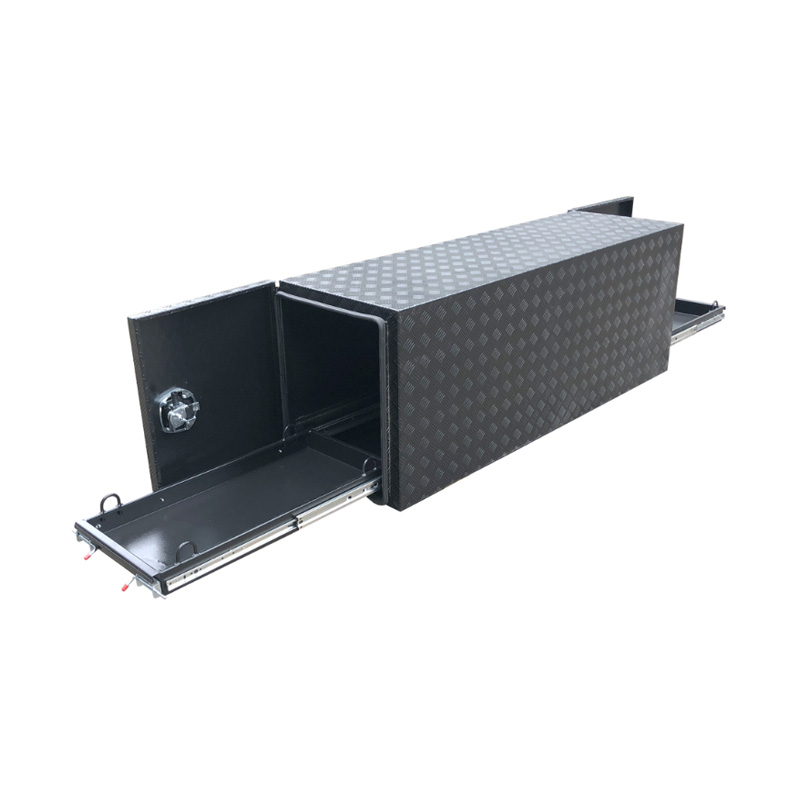
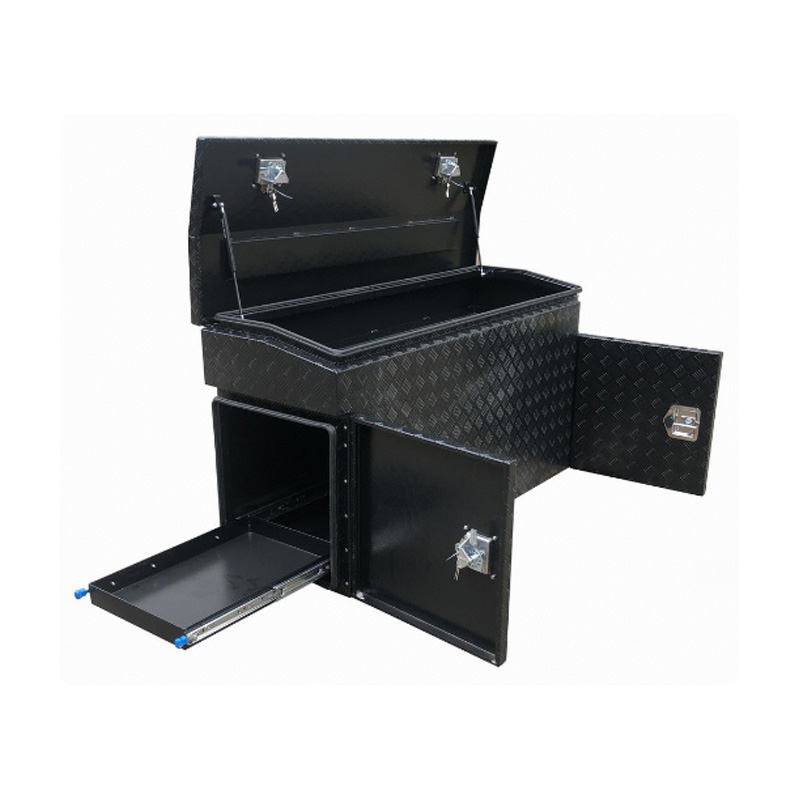
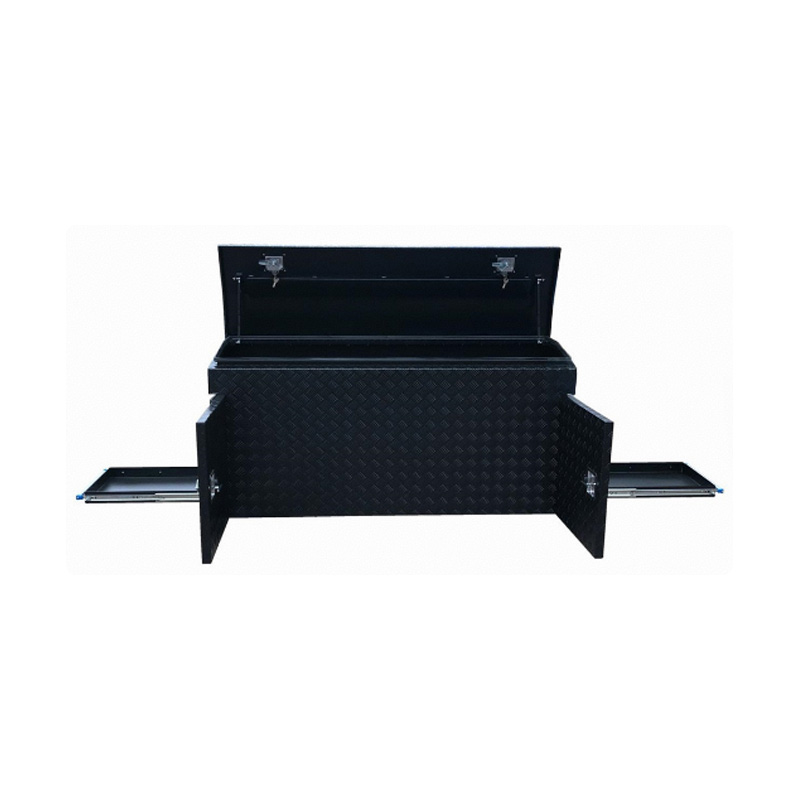
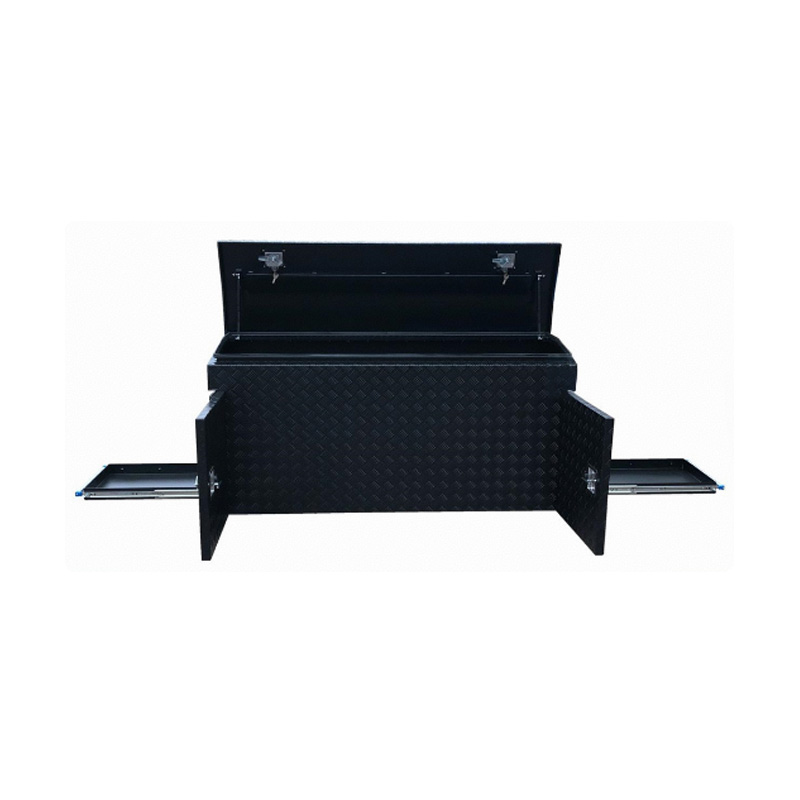
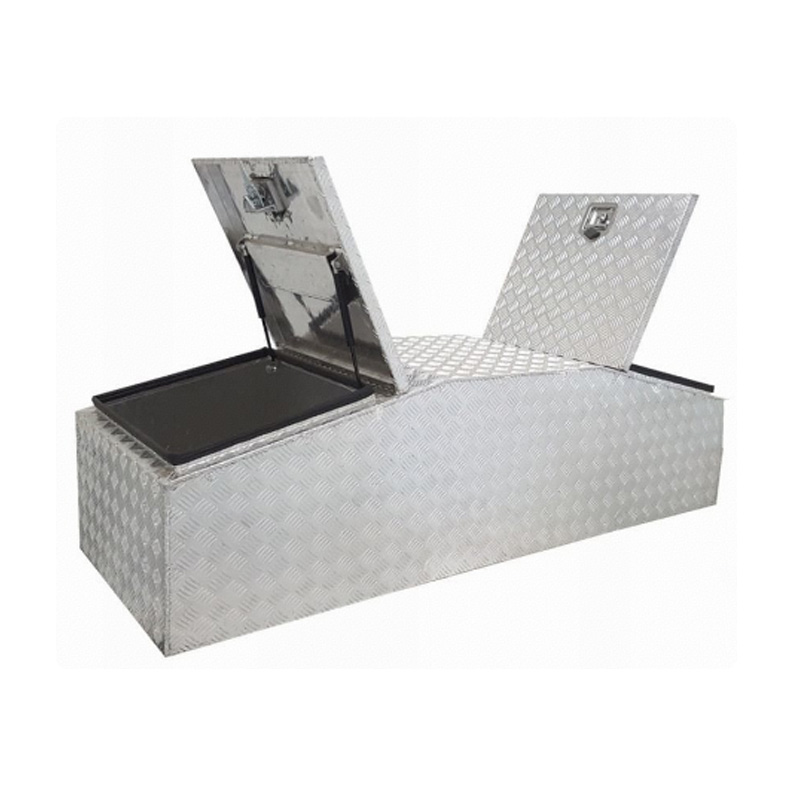
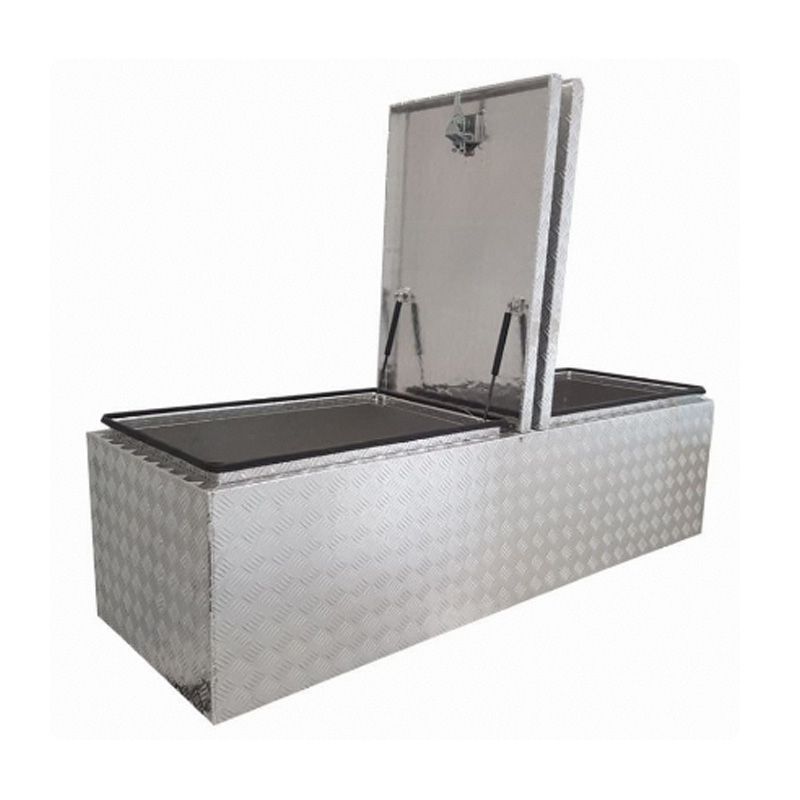
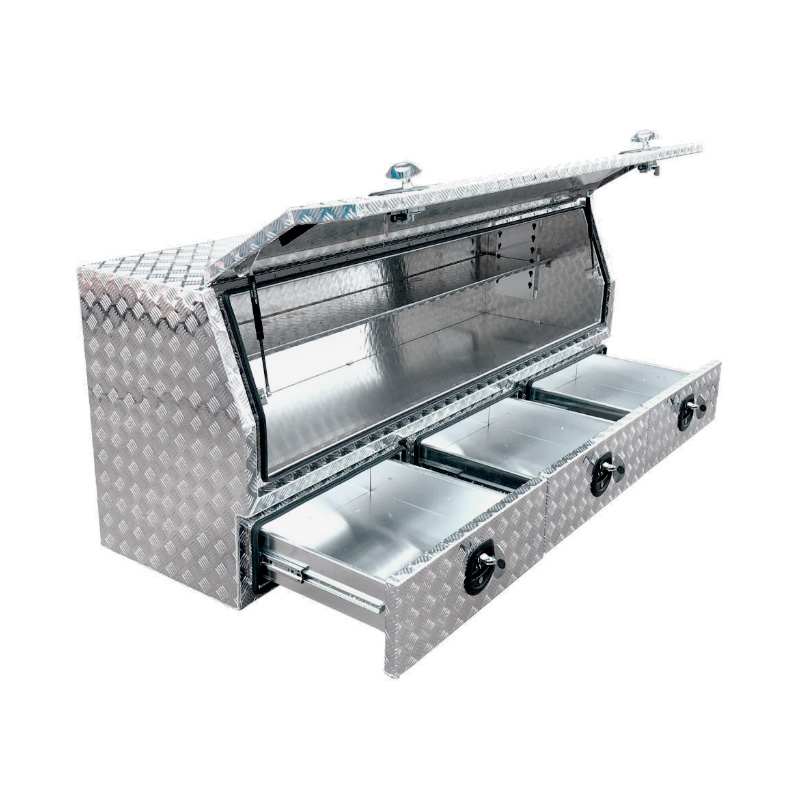
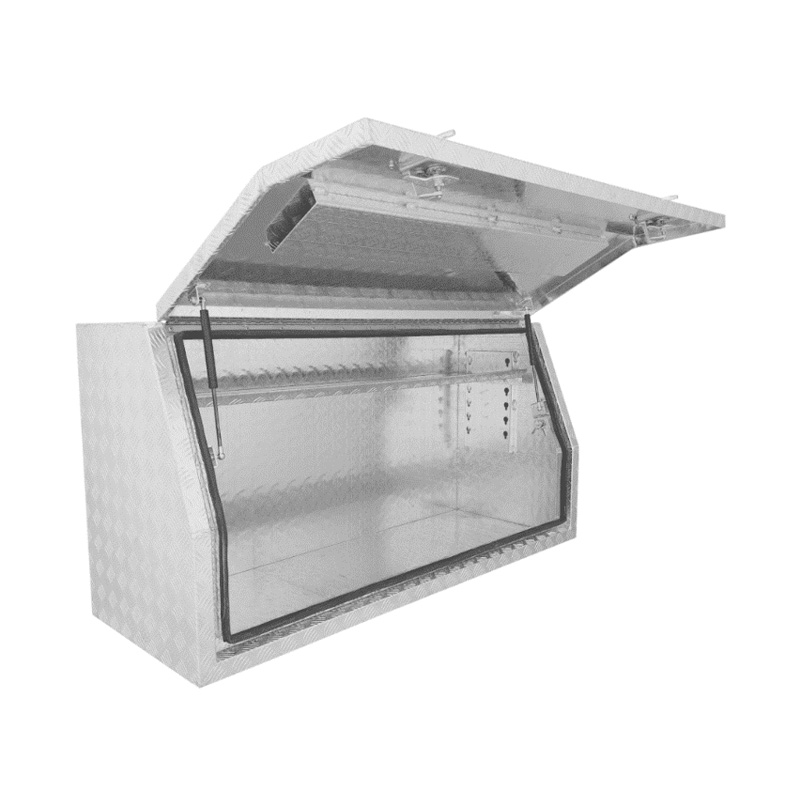
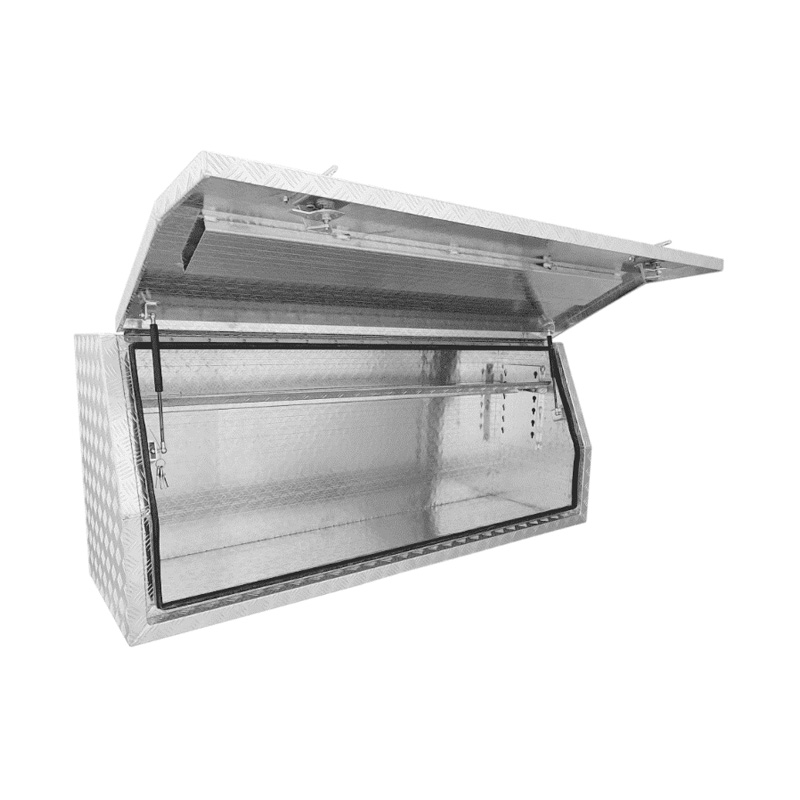
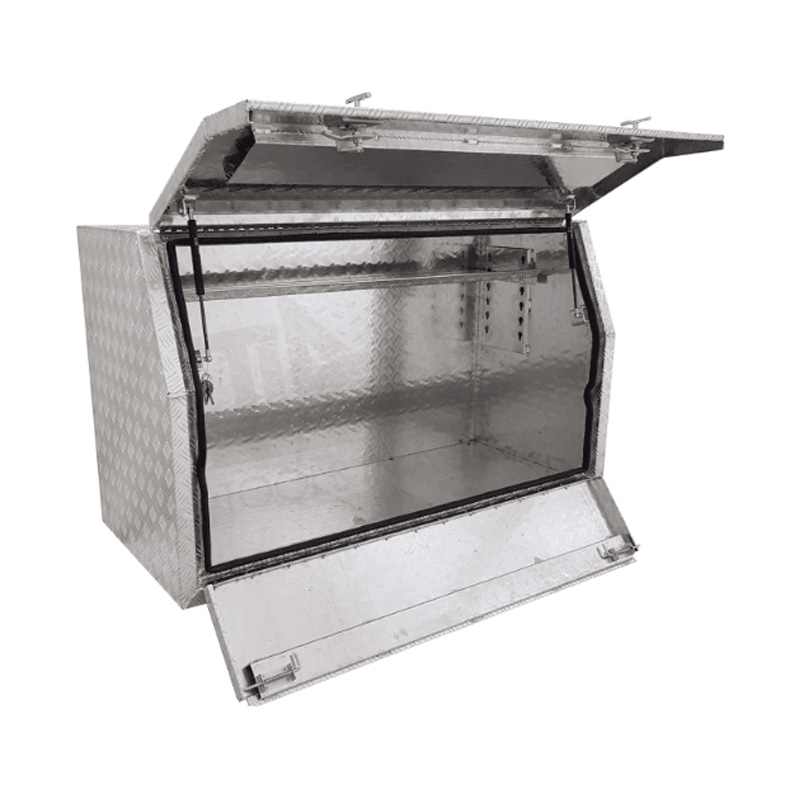
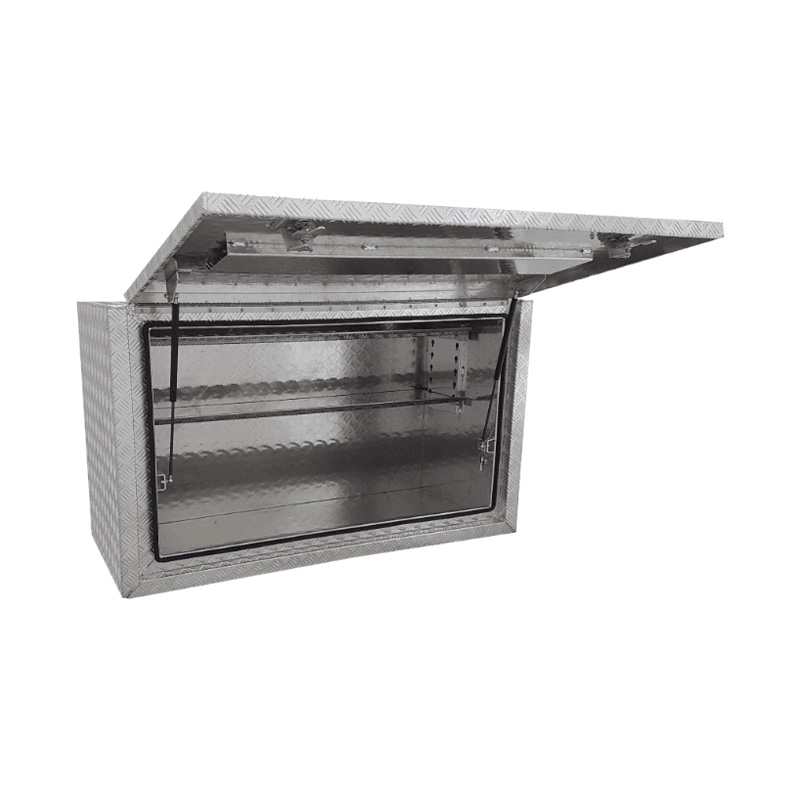
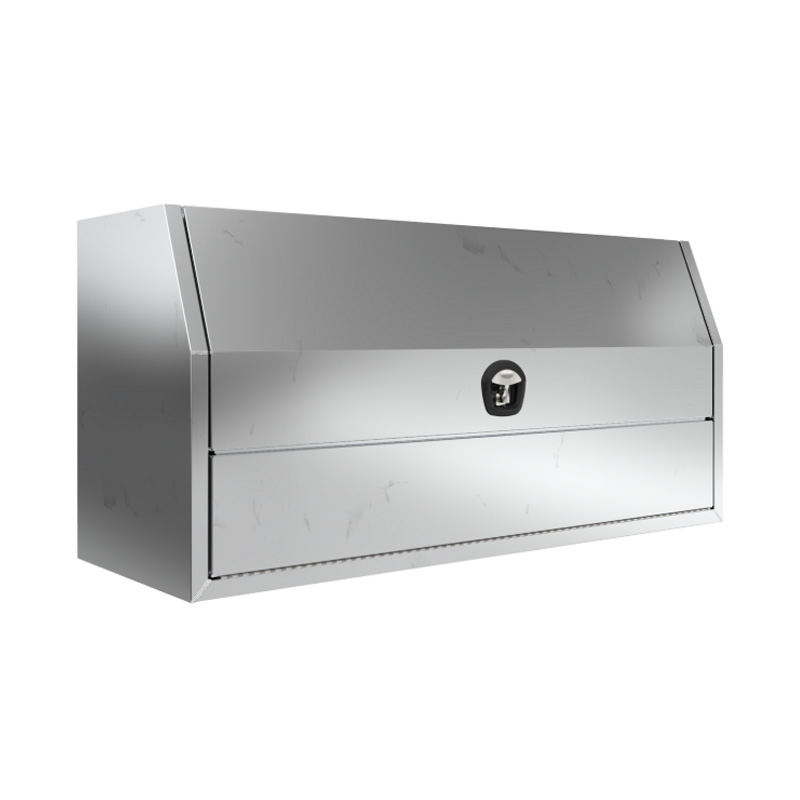
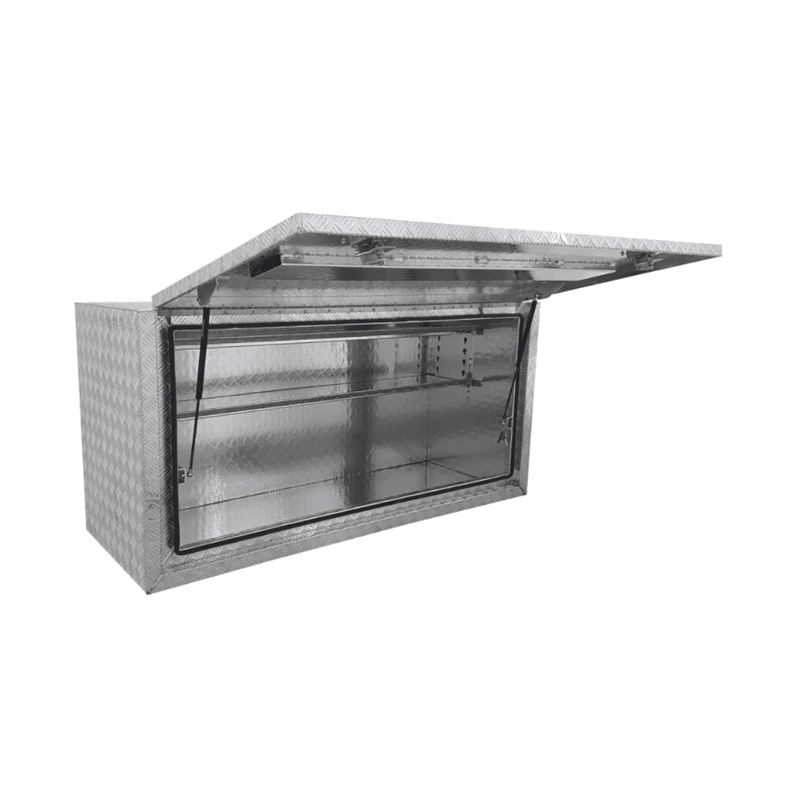
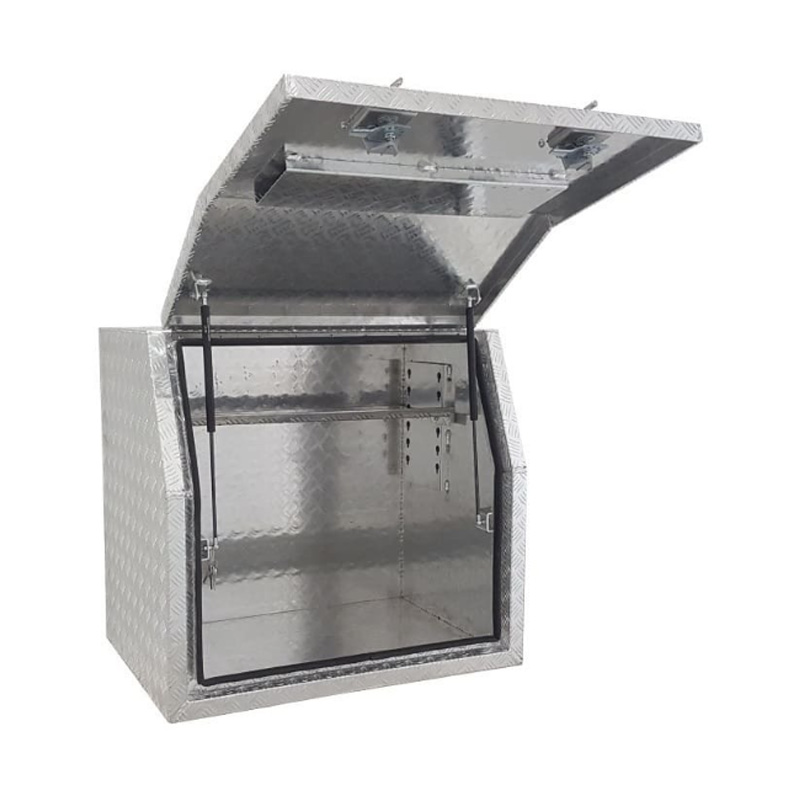
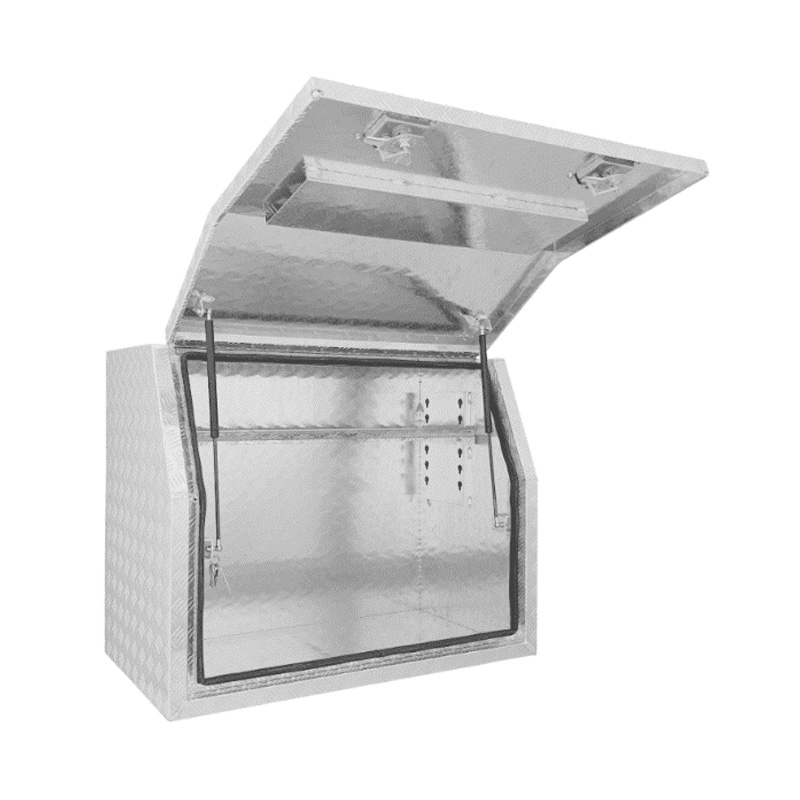
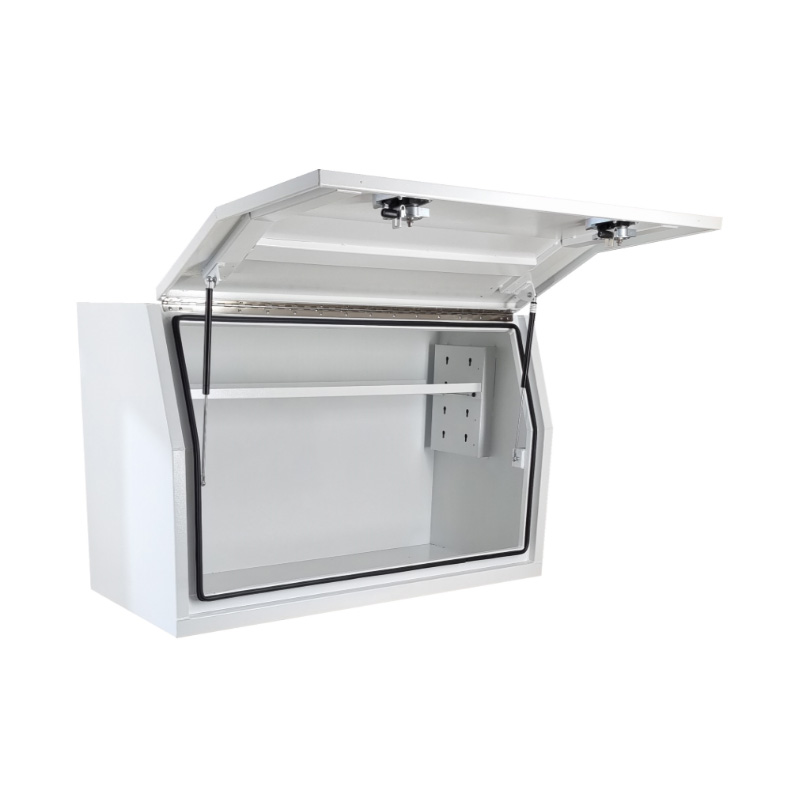
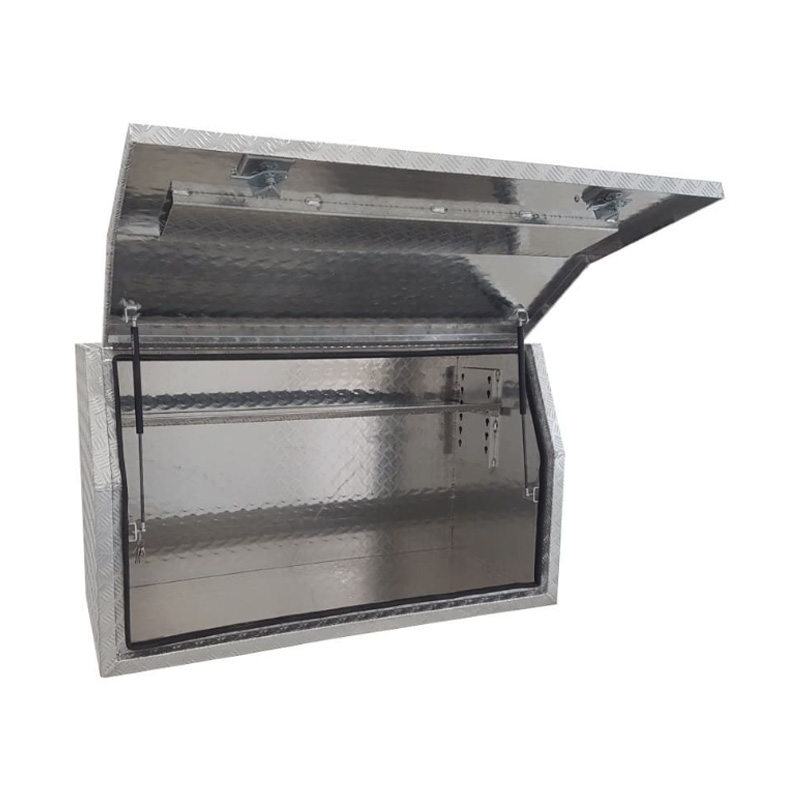
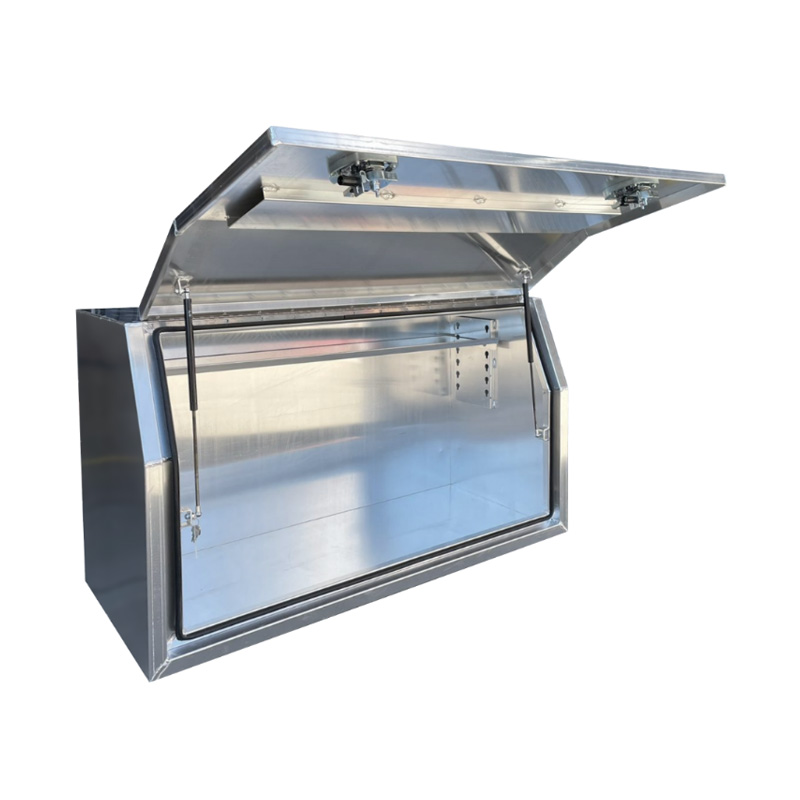
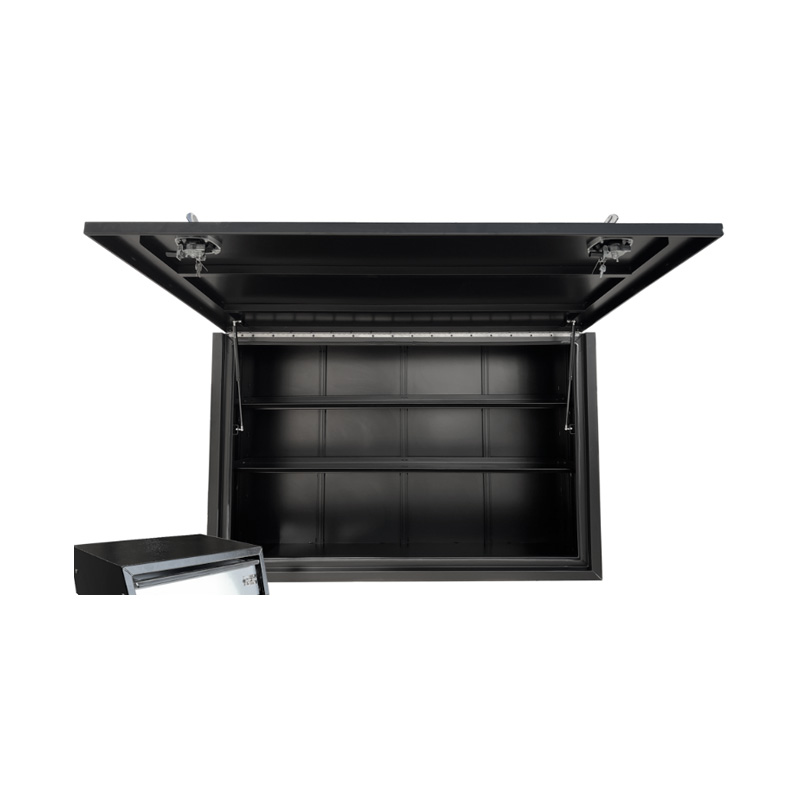
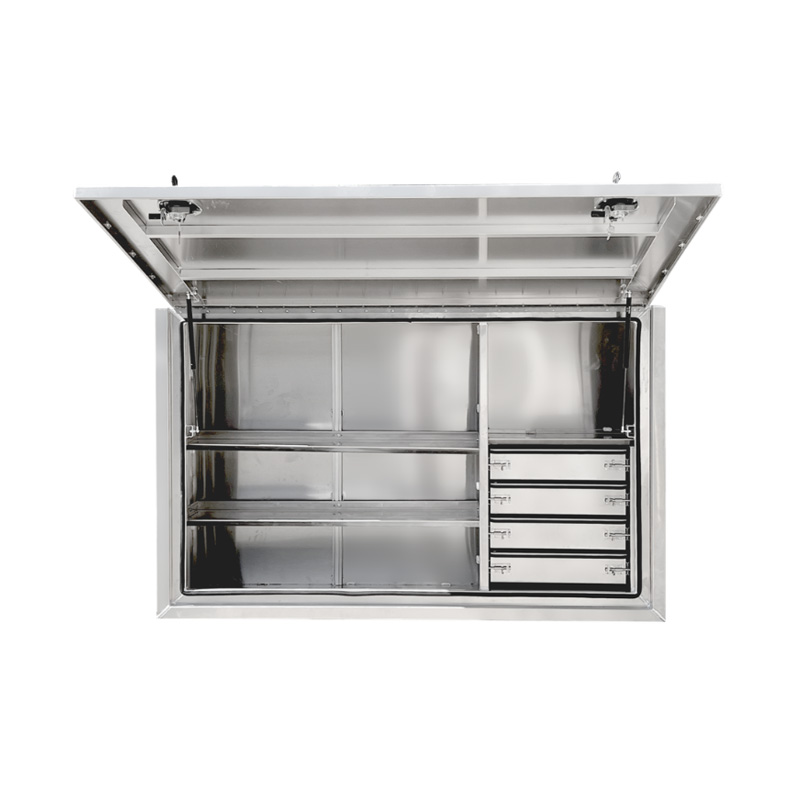
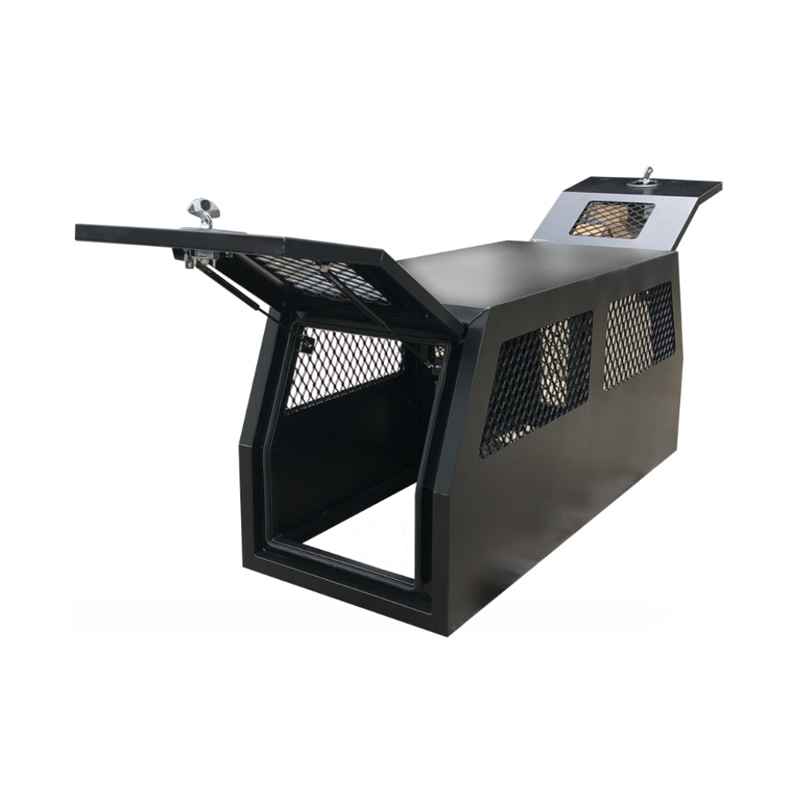
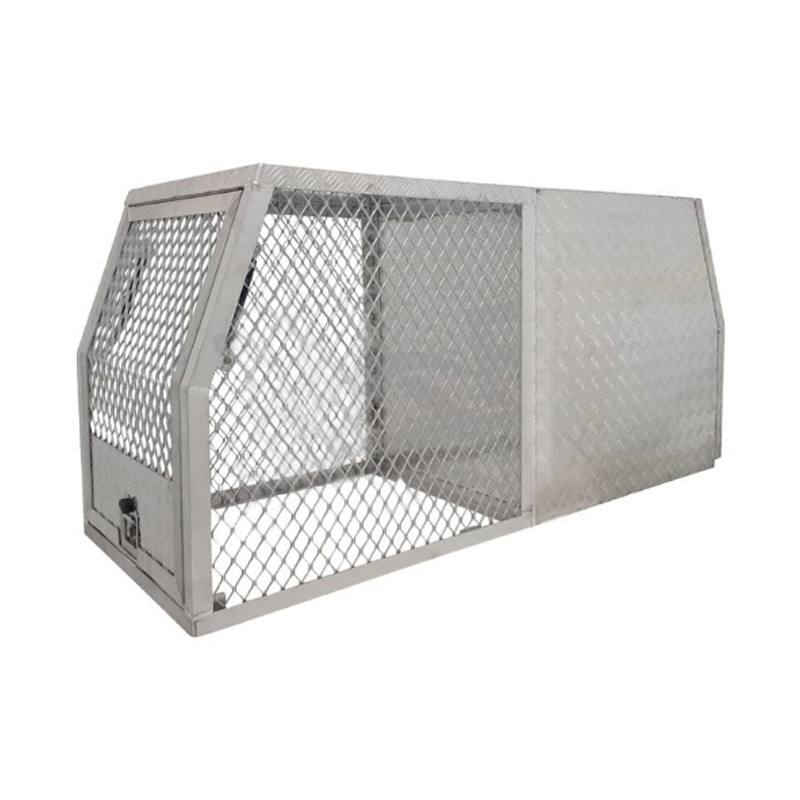
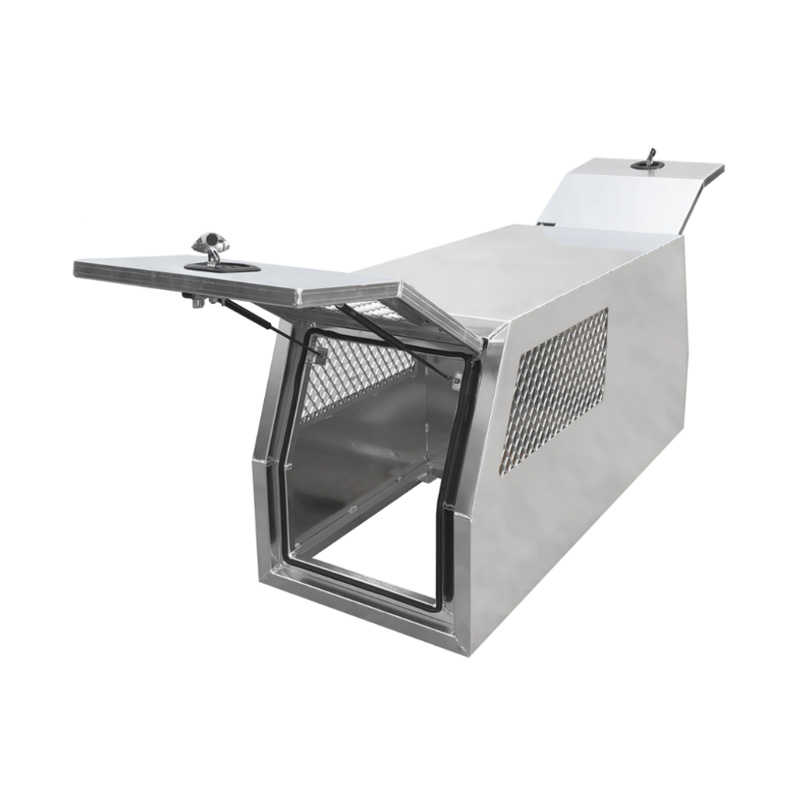
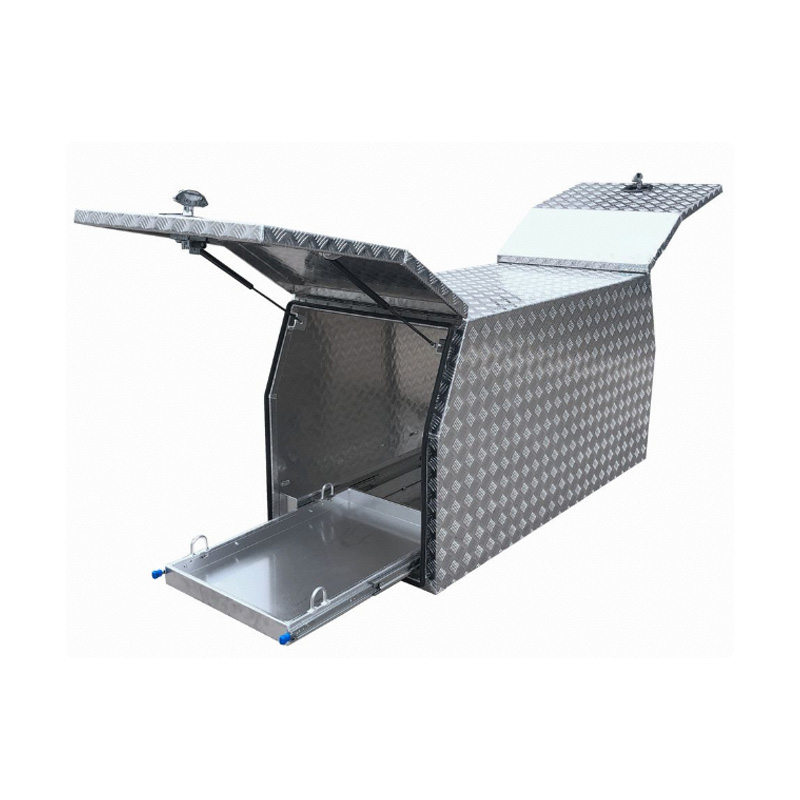
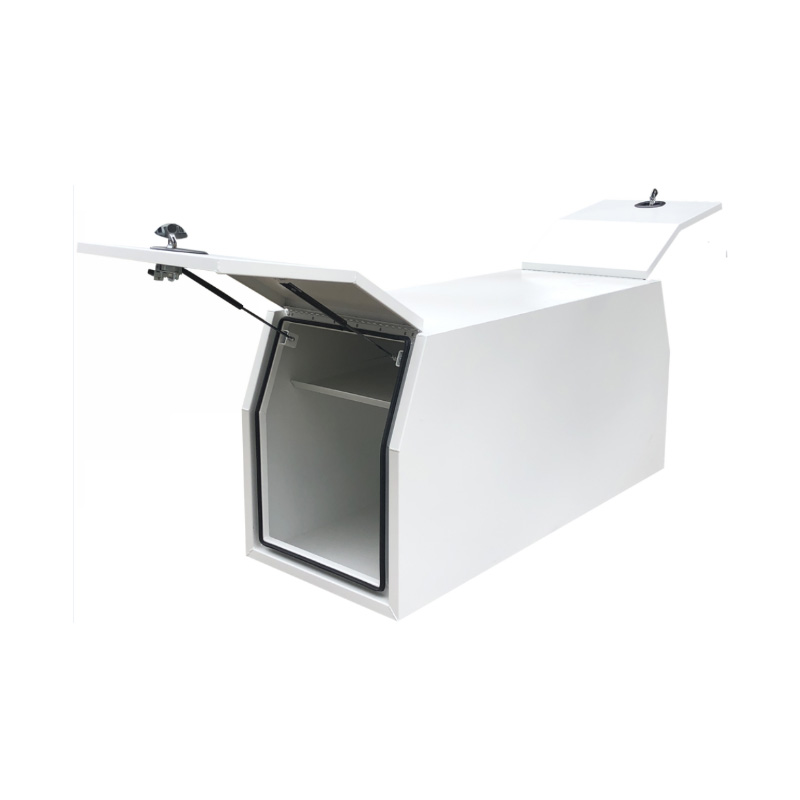
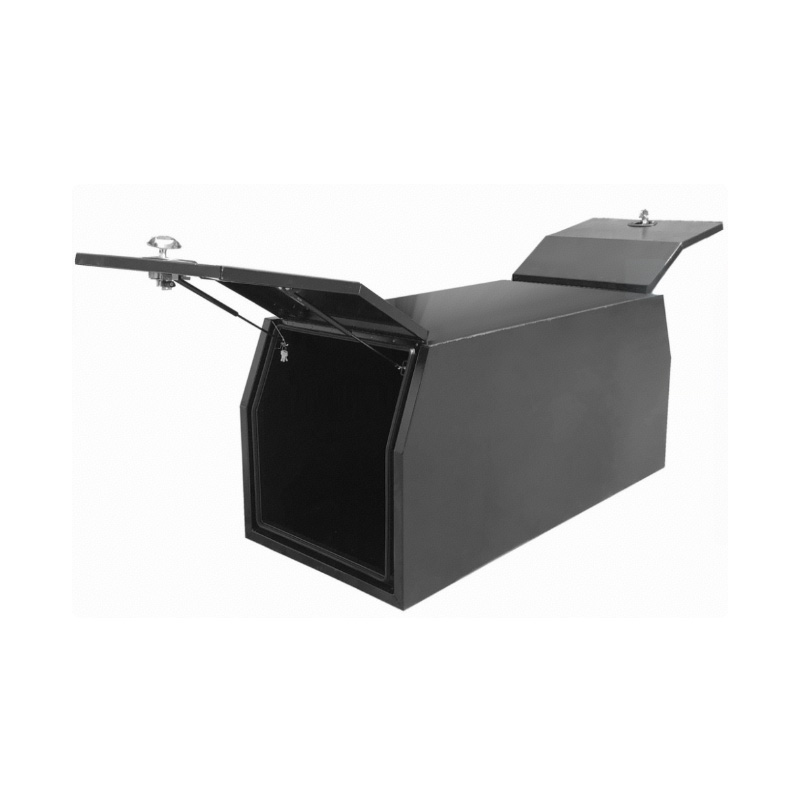
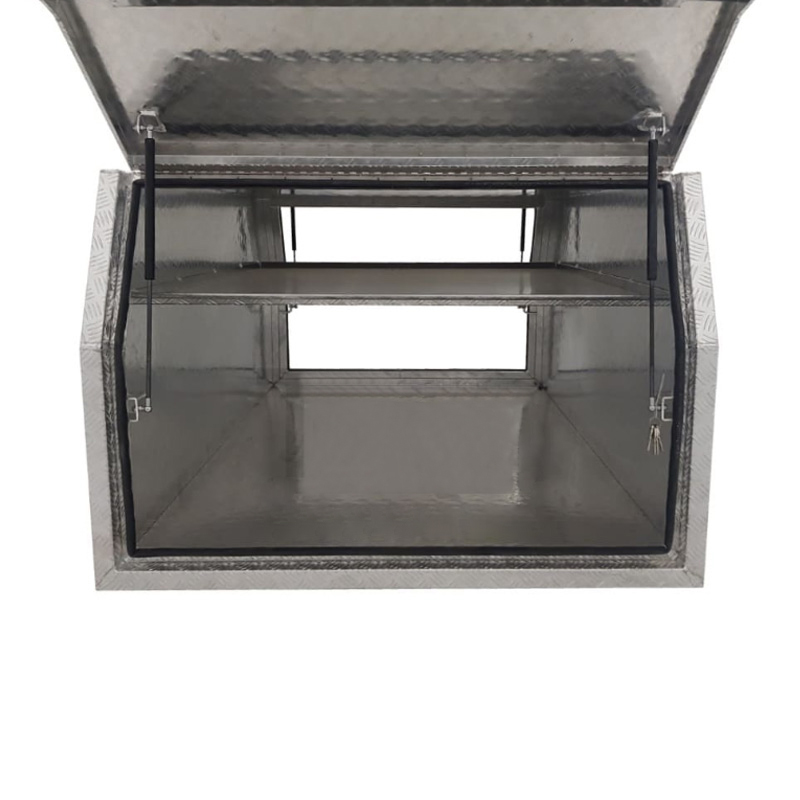
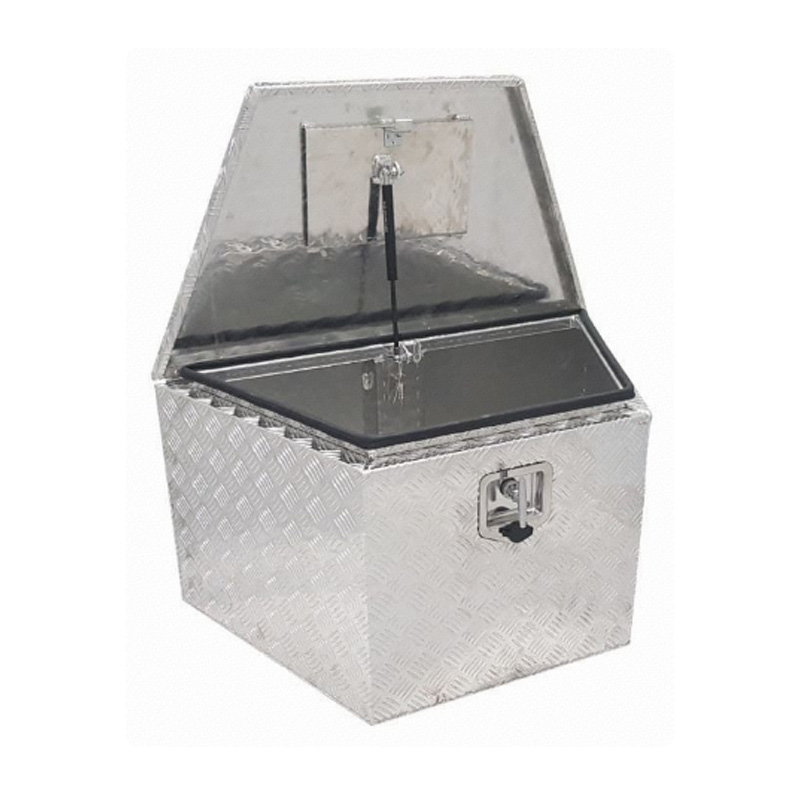
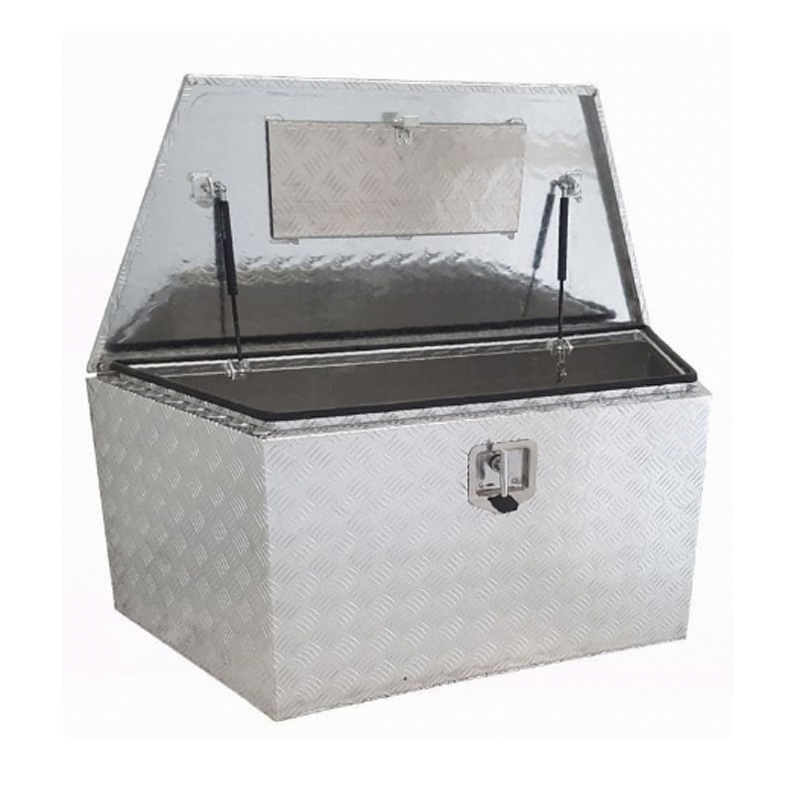
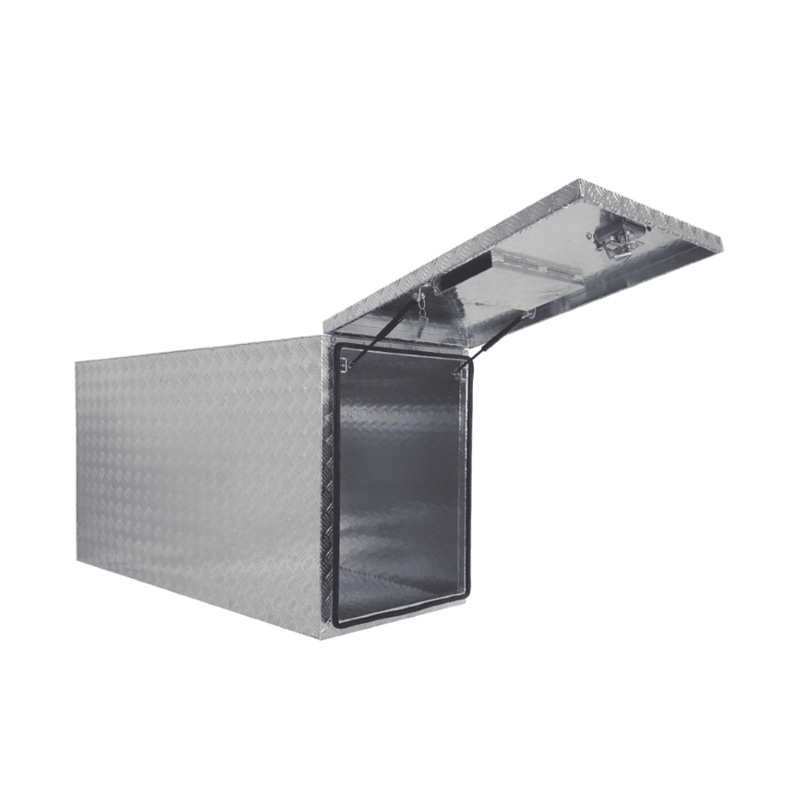
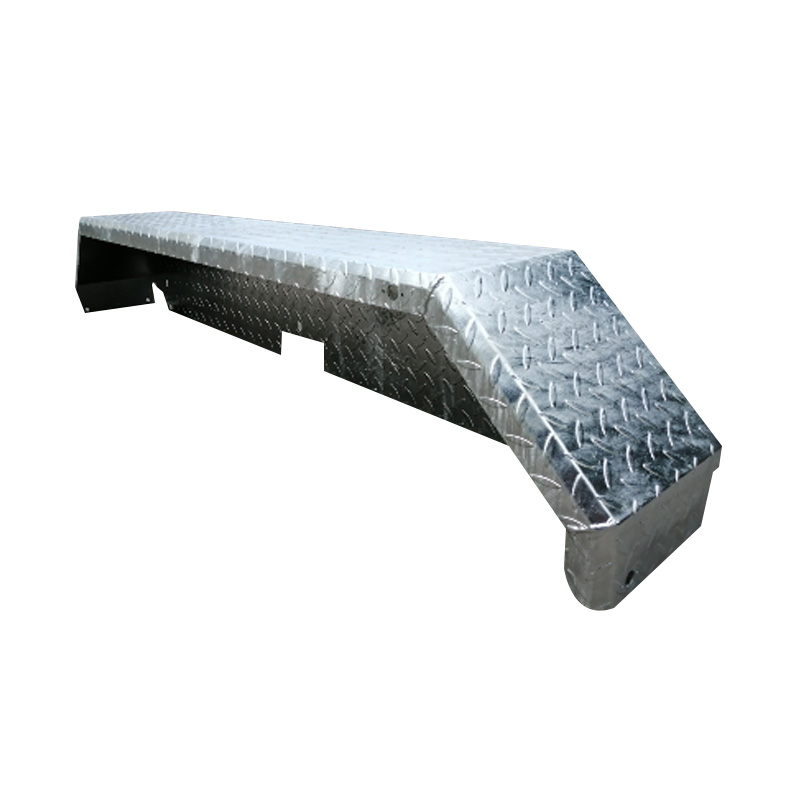
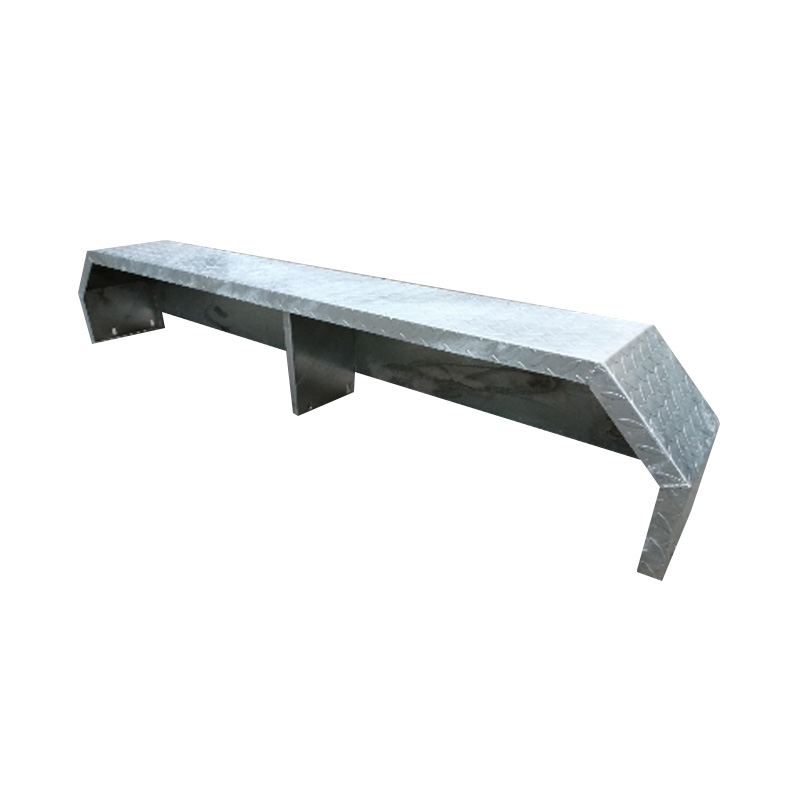
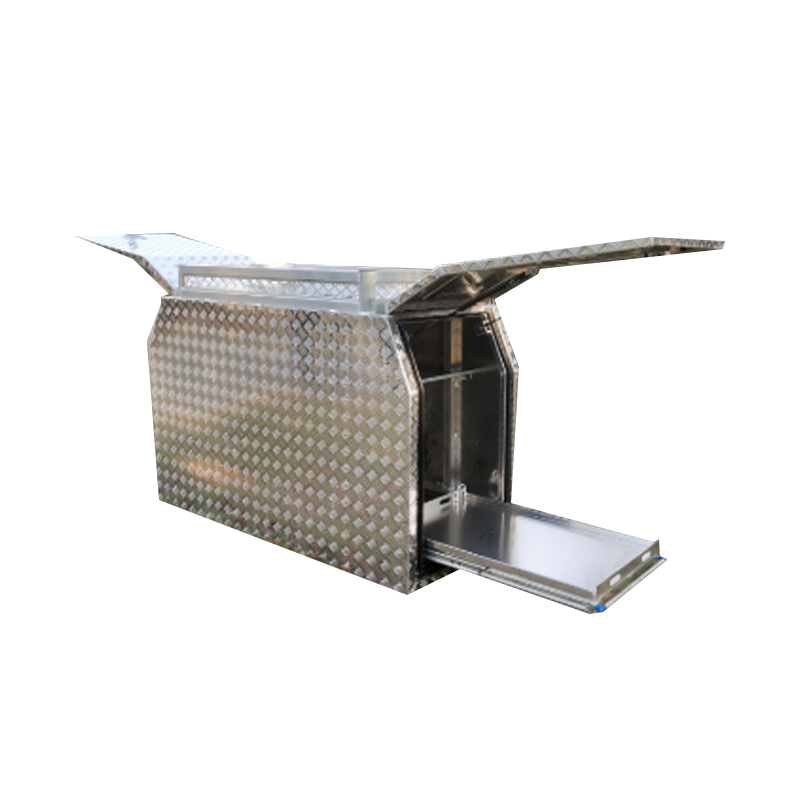
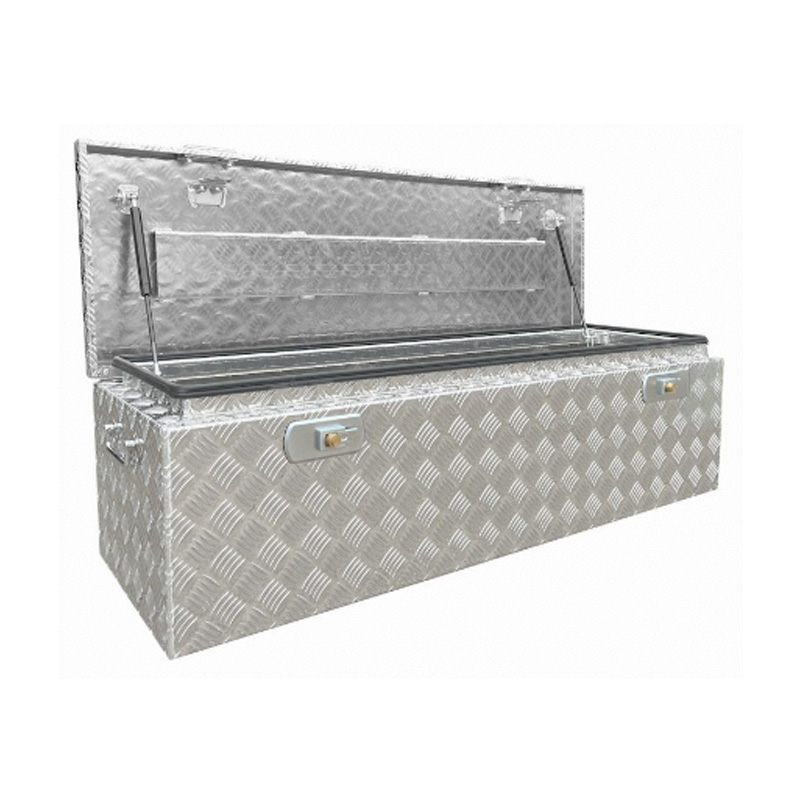
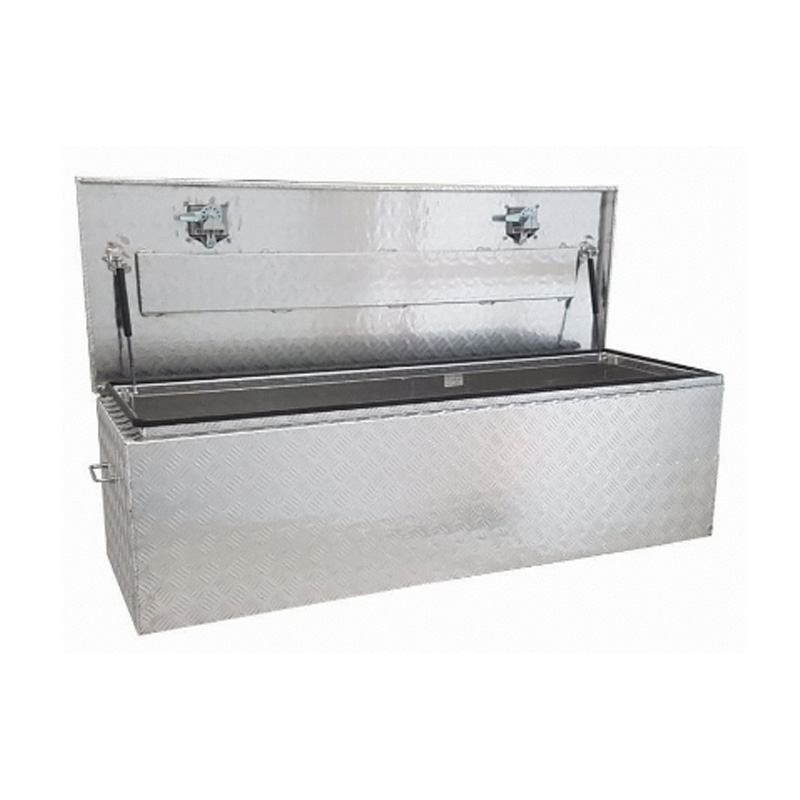
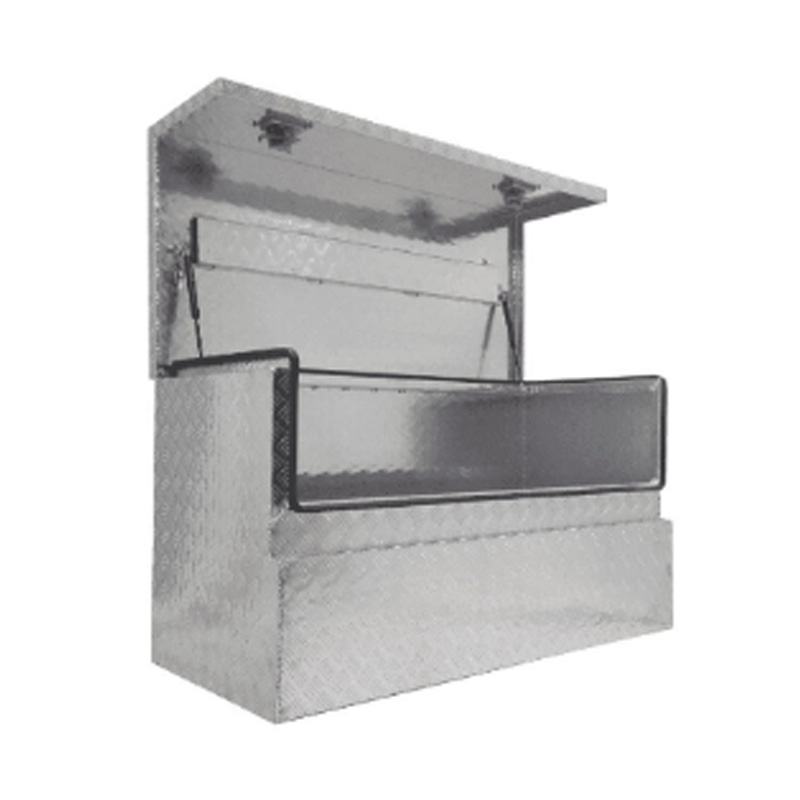
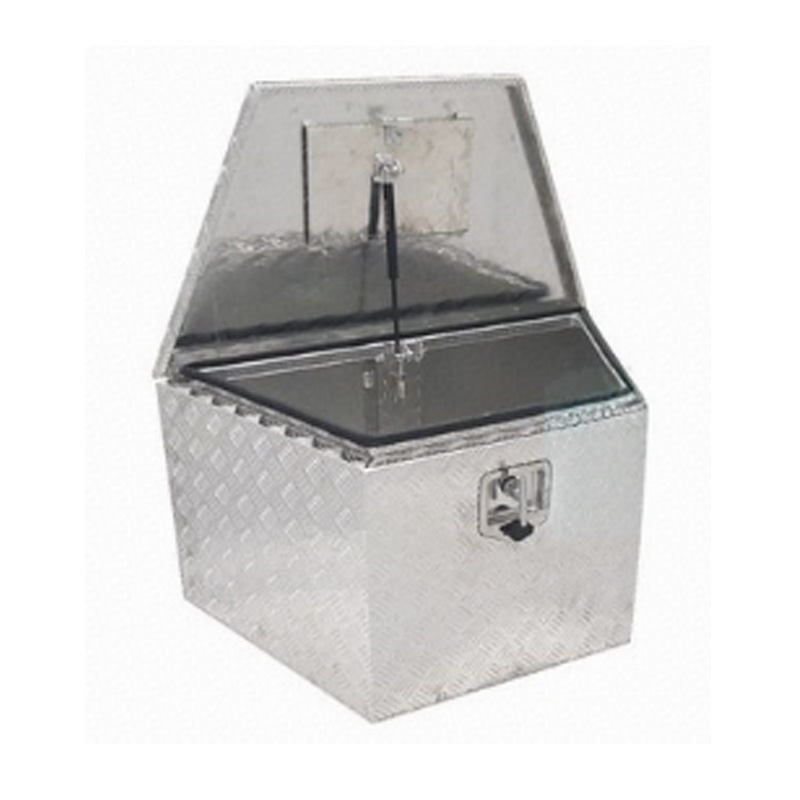
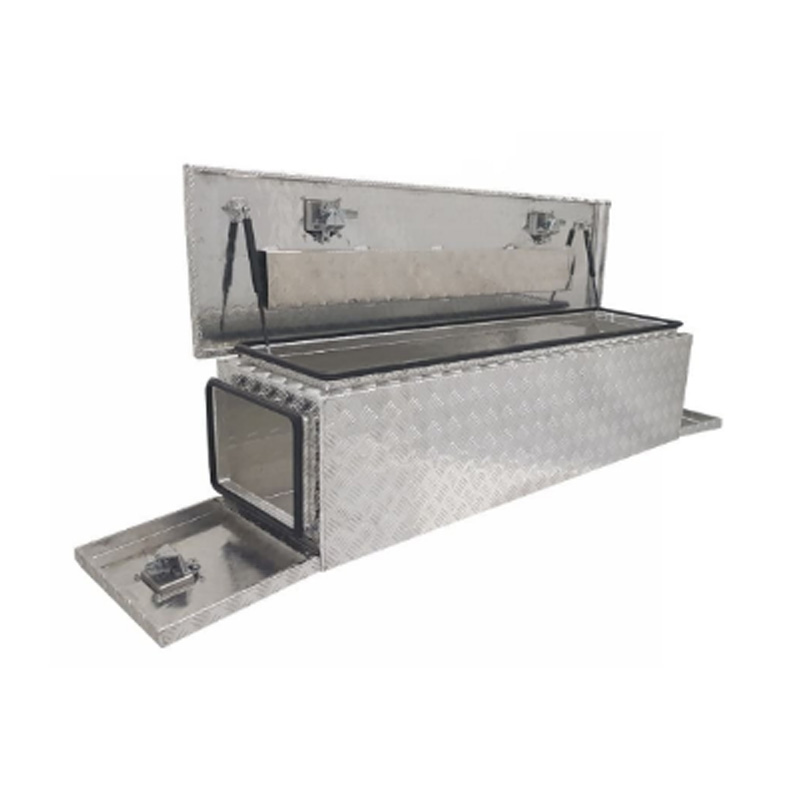
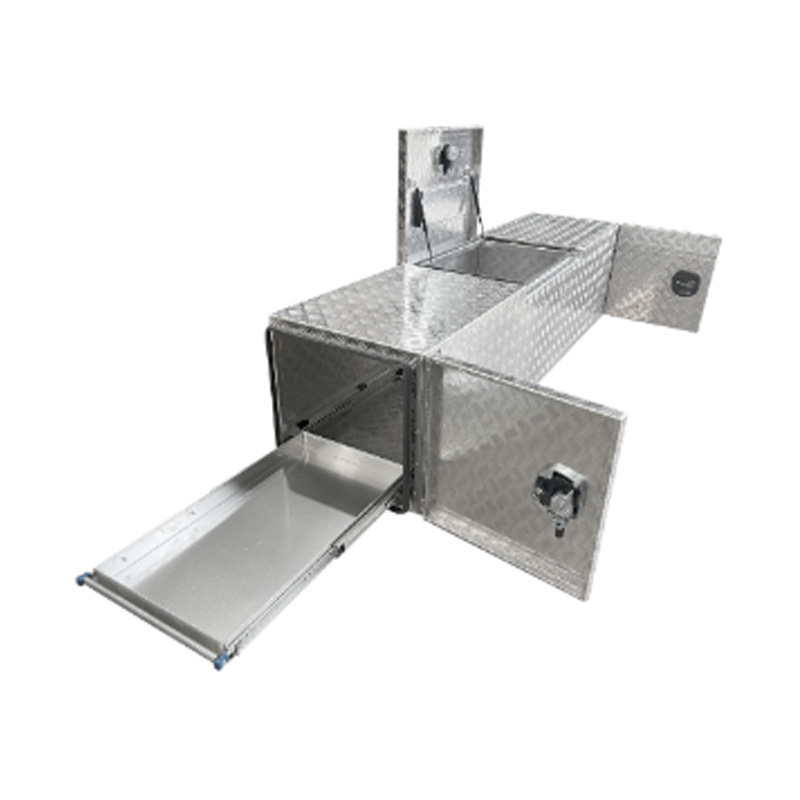
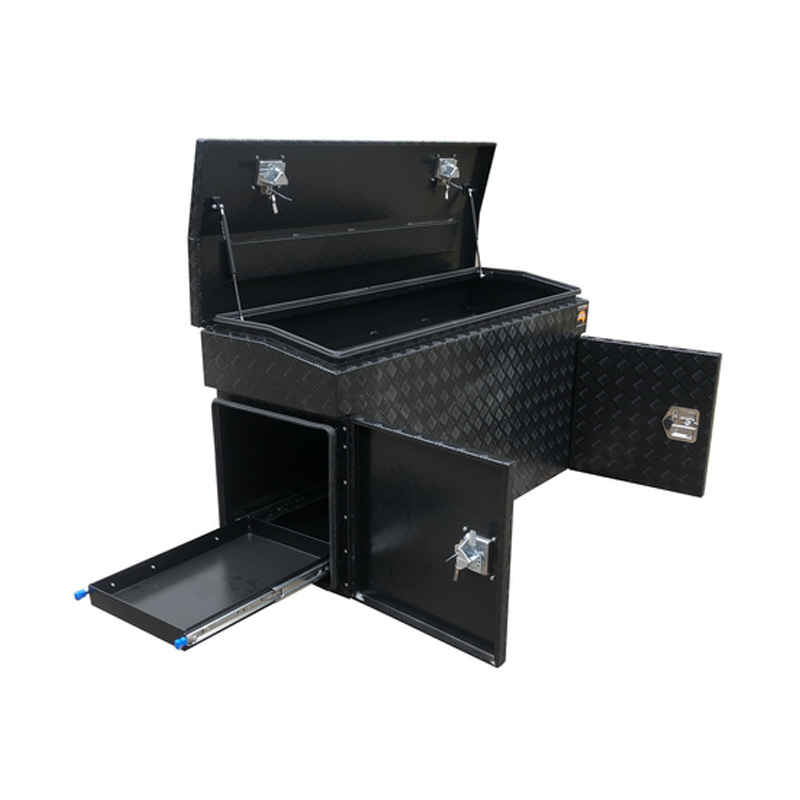
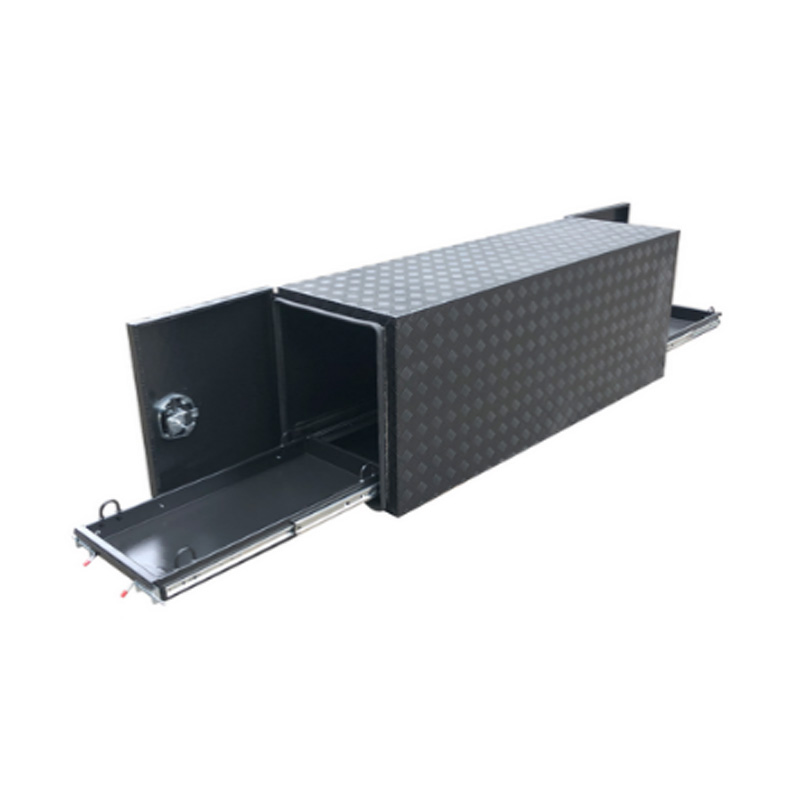
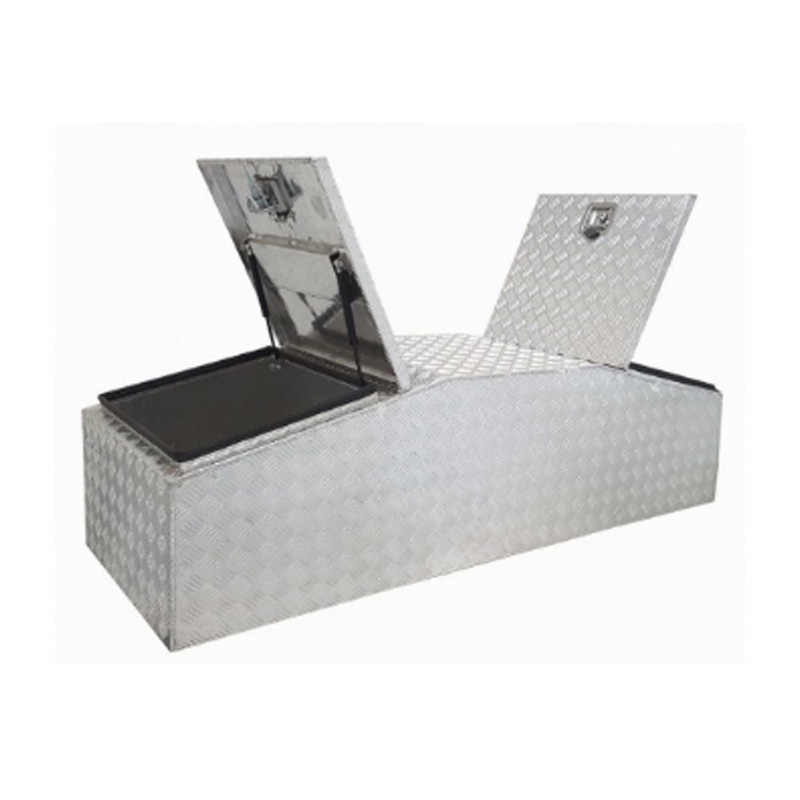
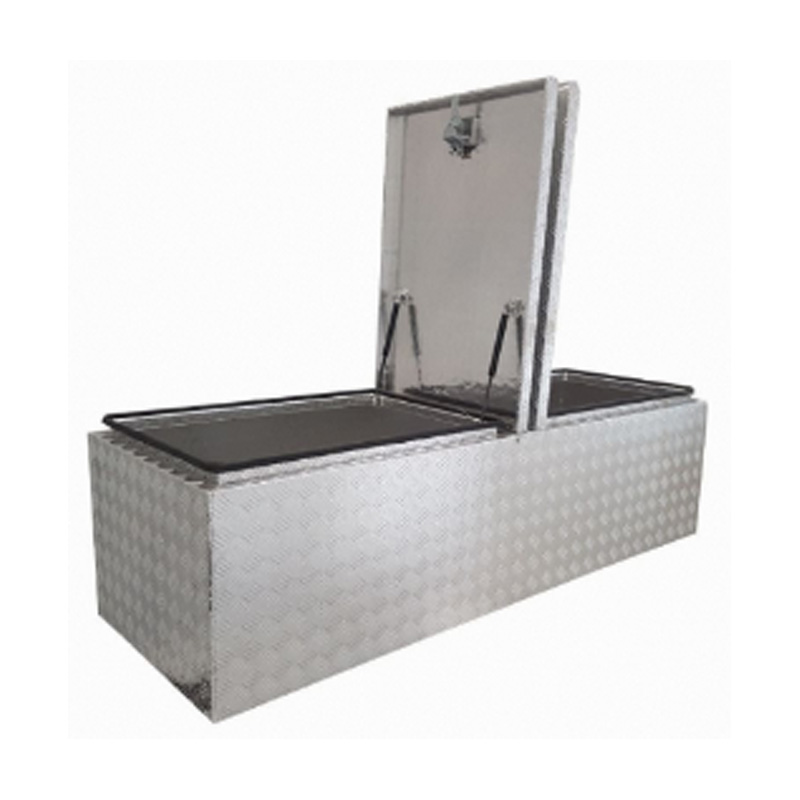
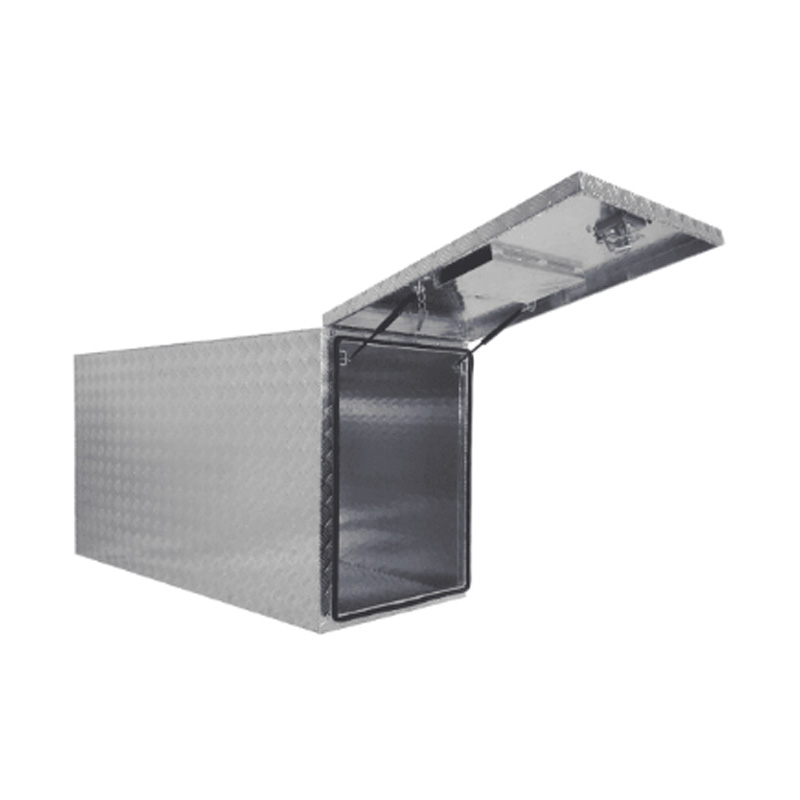
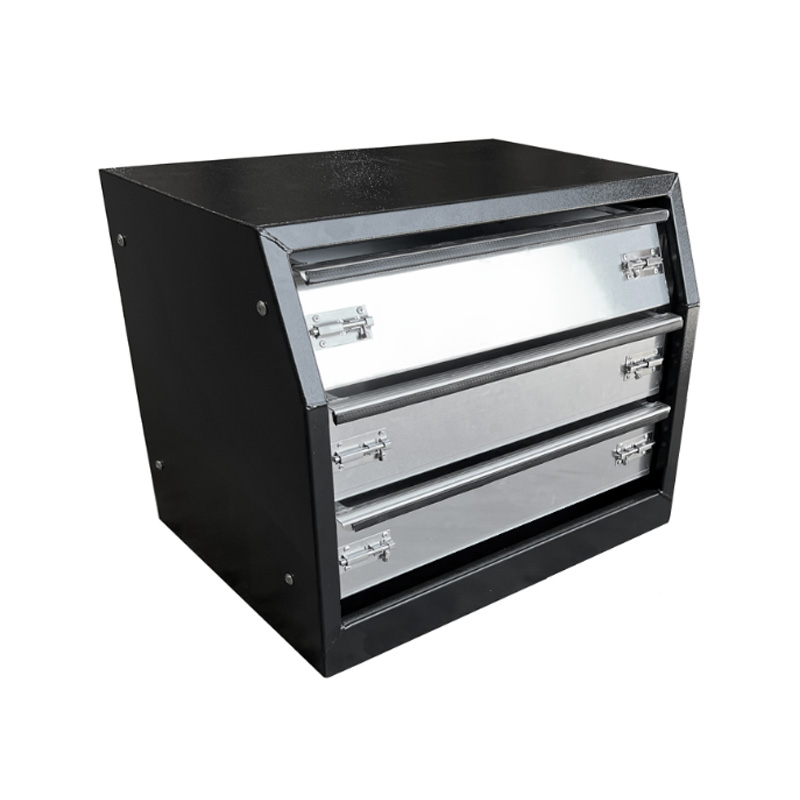
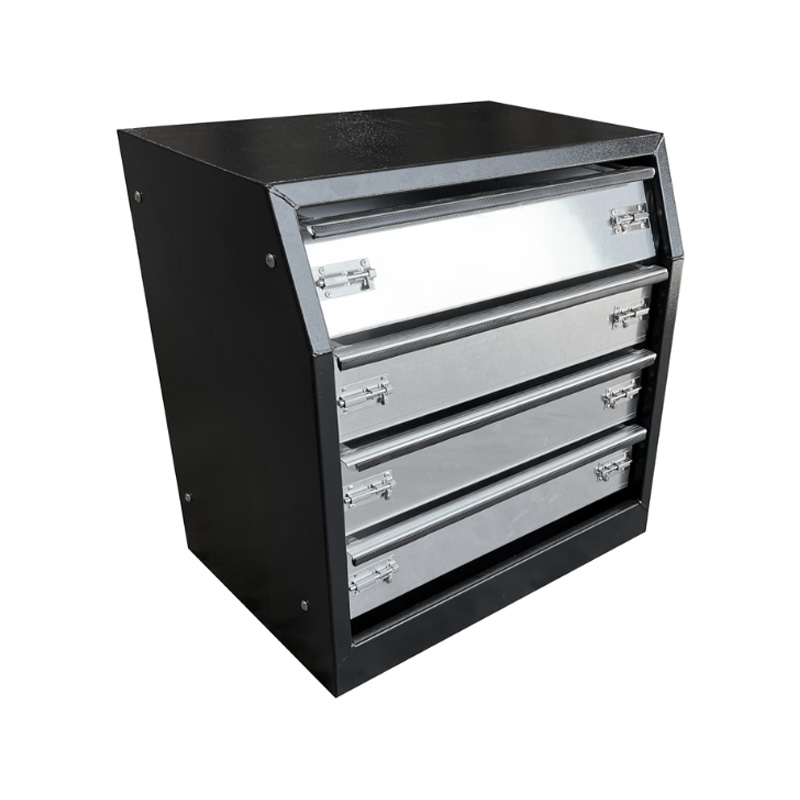
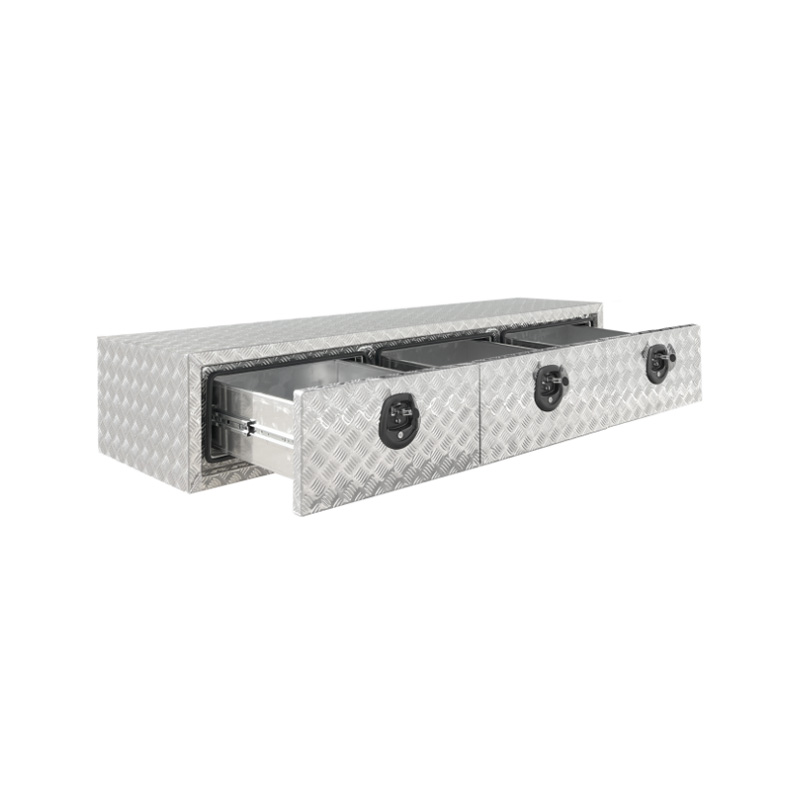
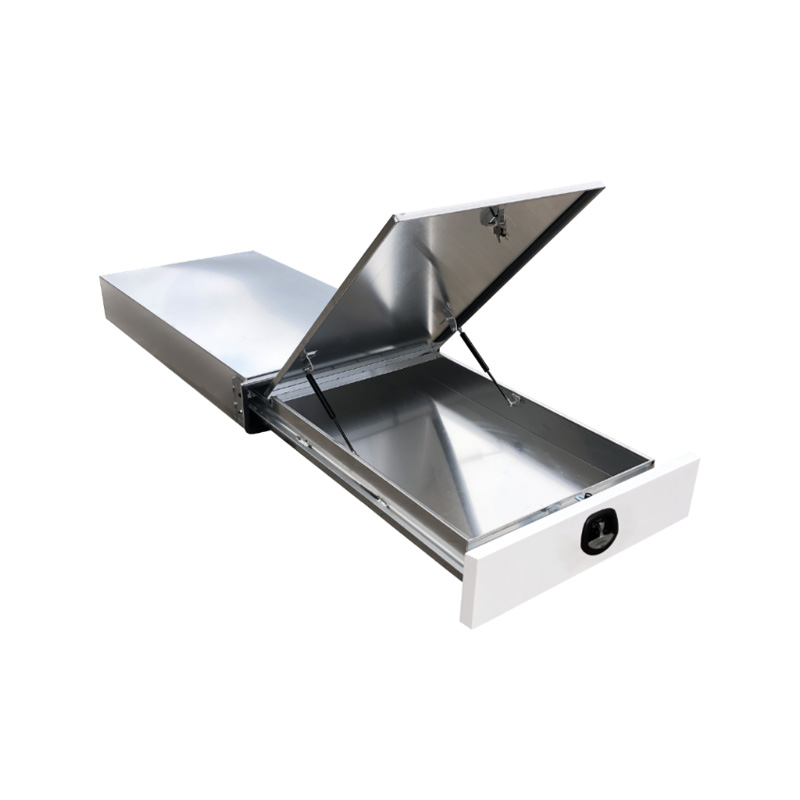
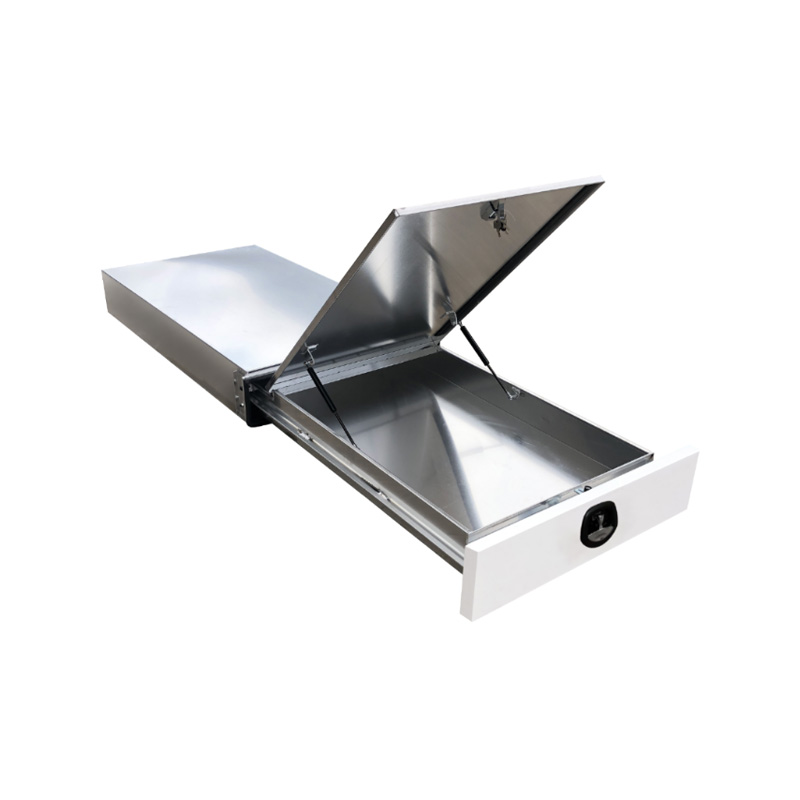
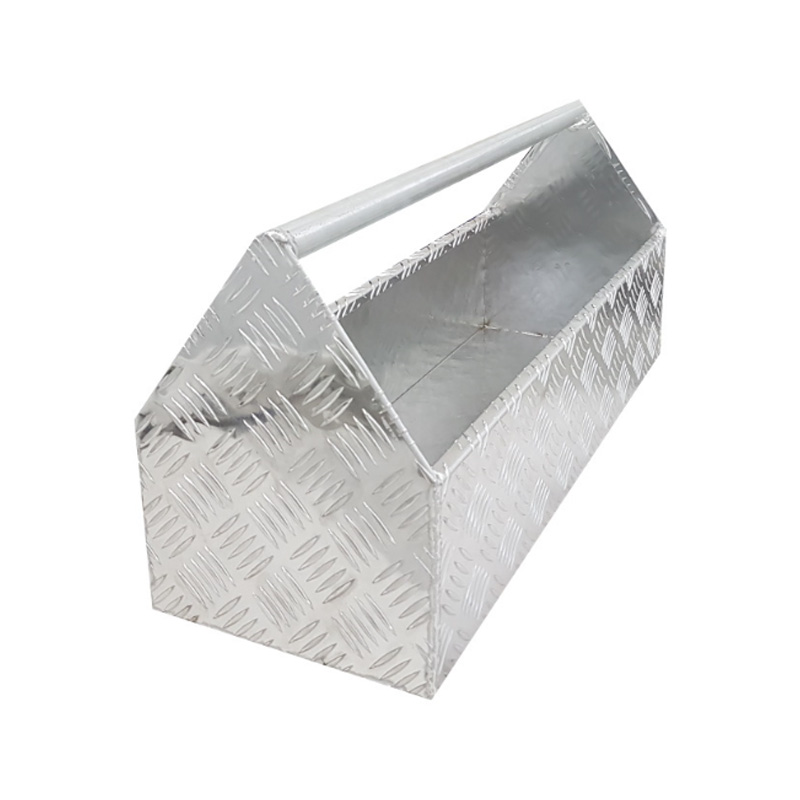
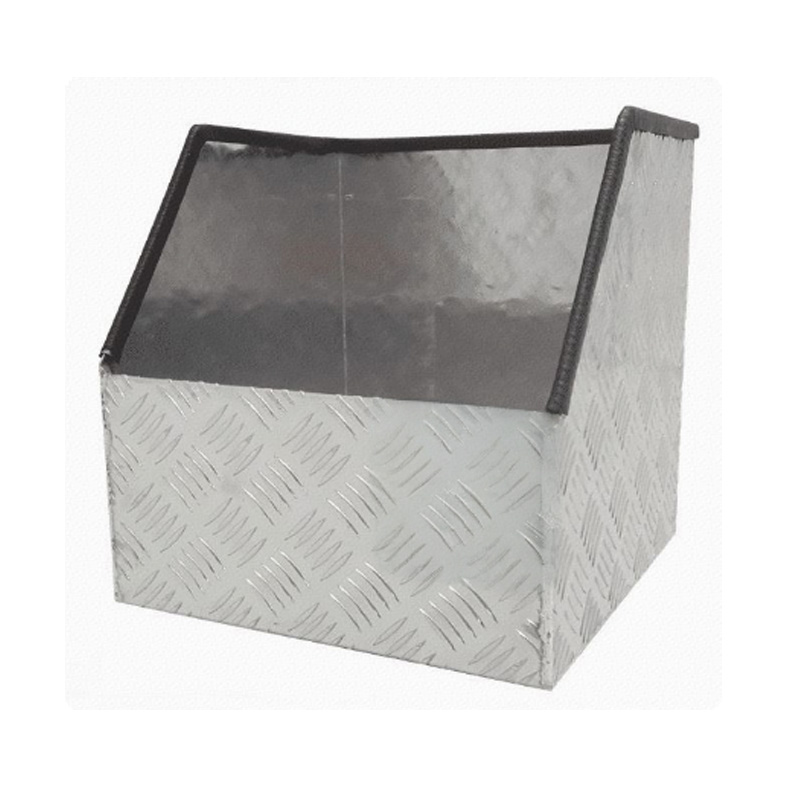
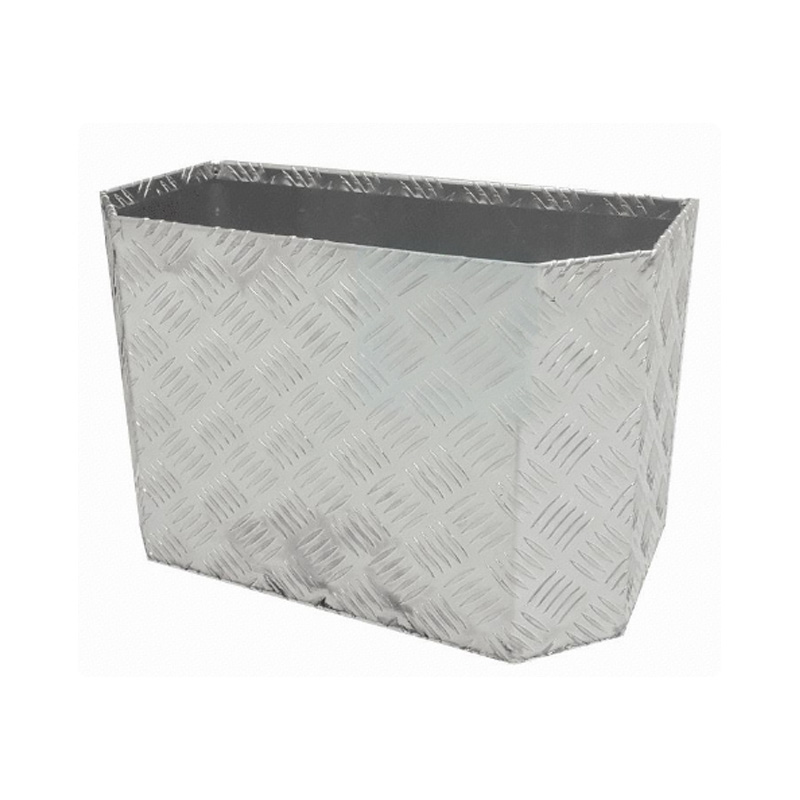
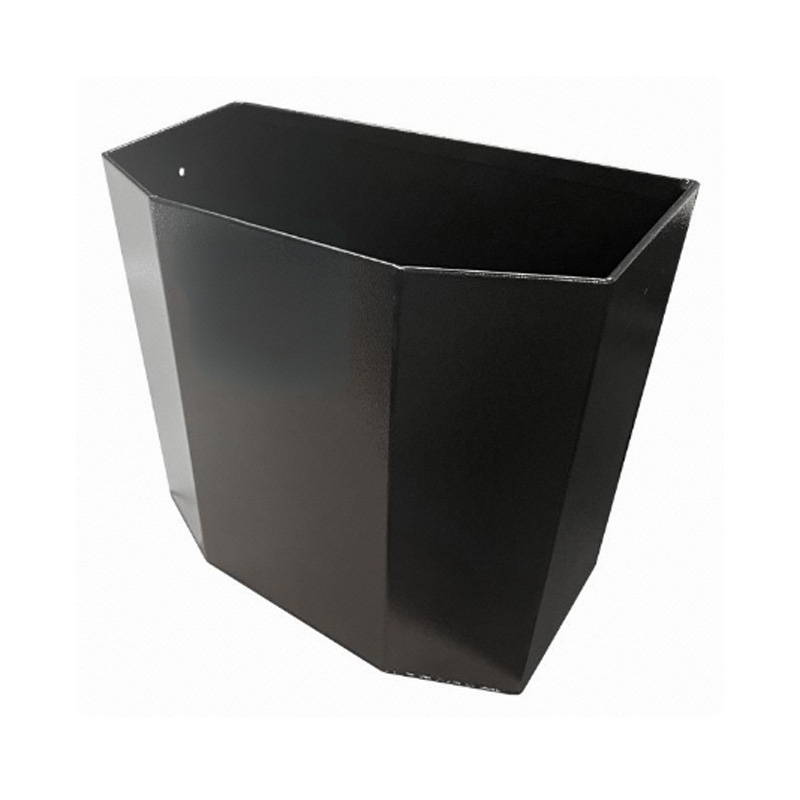
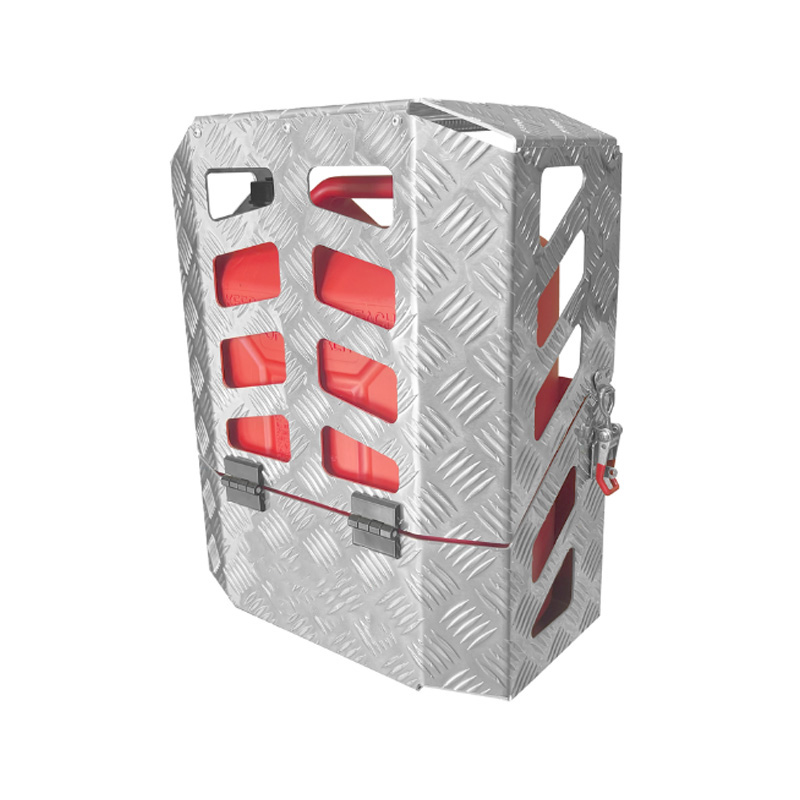
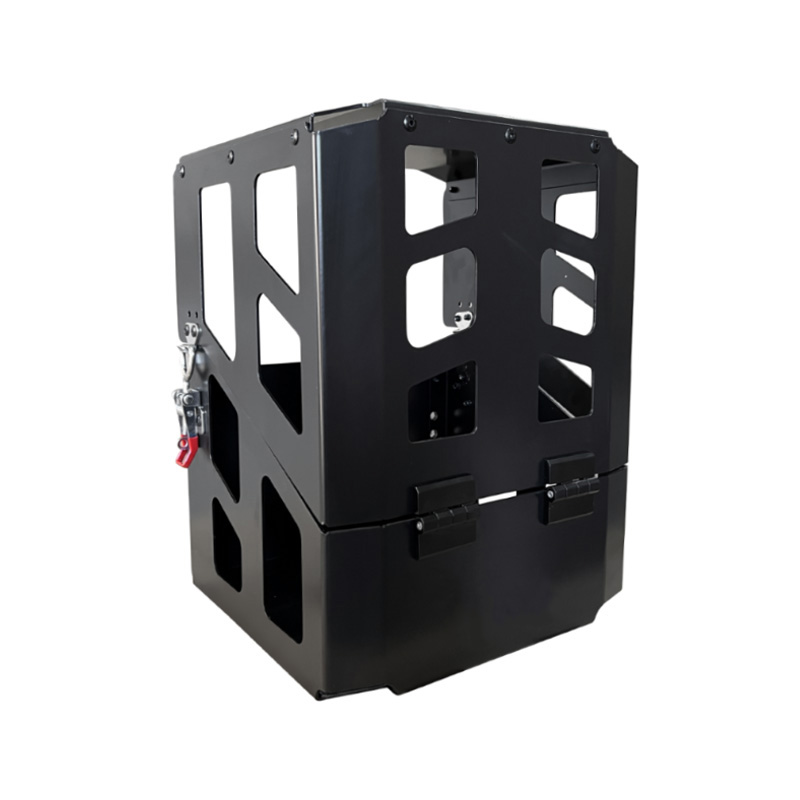
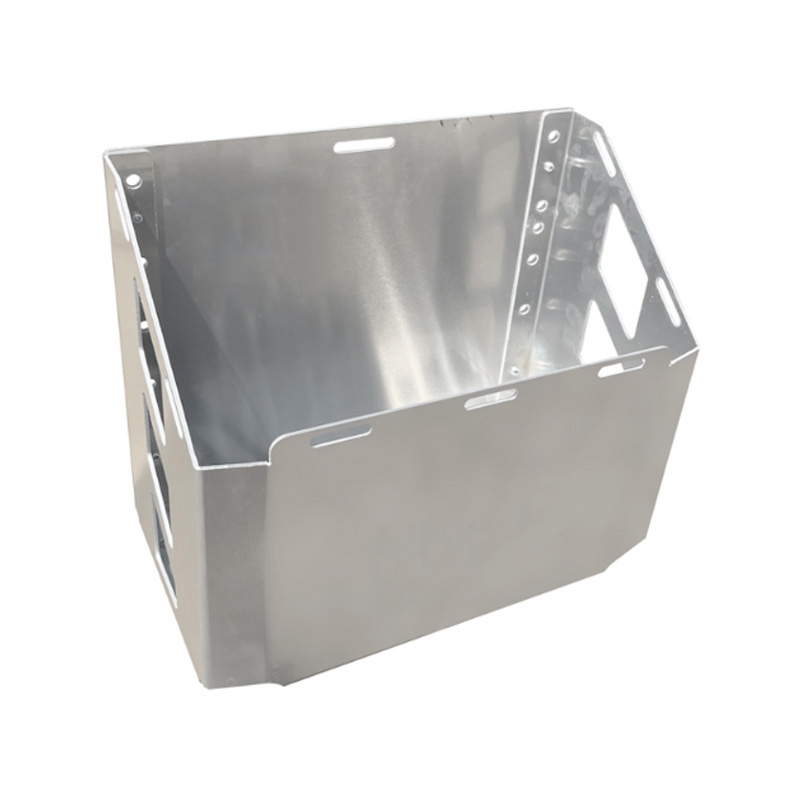
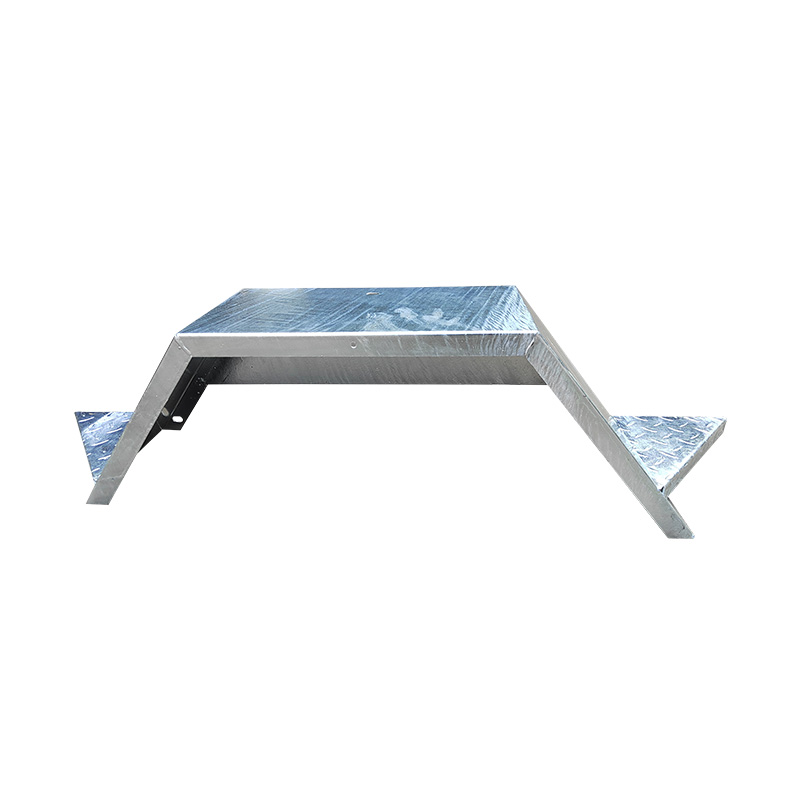
Trailer Drawbar Toolbox
A trailer drawbar toolbox is a storage solution mounted on the front drawbar of a trailer, providing secure and weather-resistant space for tools and equipment. Constructed from materials like aluminum checker plate, these toolboxes are designed to withstand harsh outdoor conditions and frequent use. The design often includes compartments or trays for organized storage, allowing for easy access to tools and accessories. Installation is generally straightforward, with options for bolting or welding the toolbox to the trailer frame. When choosing a drawbar toolbox, it's essential to consider factors such as size, weight capacity, and compatibility with the trailer's design to ensure optimal functionality and safety. -
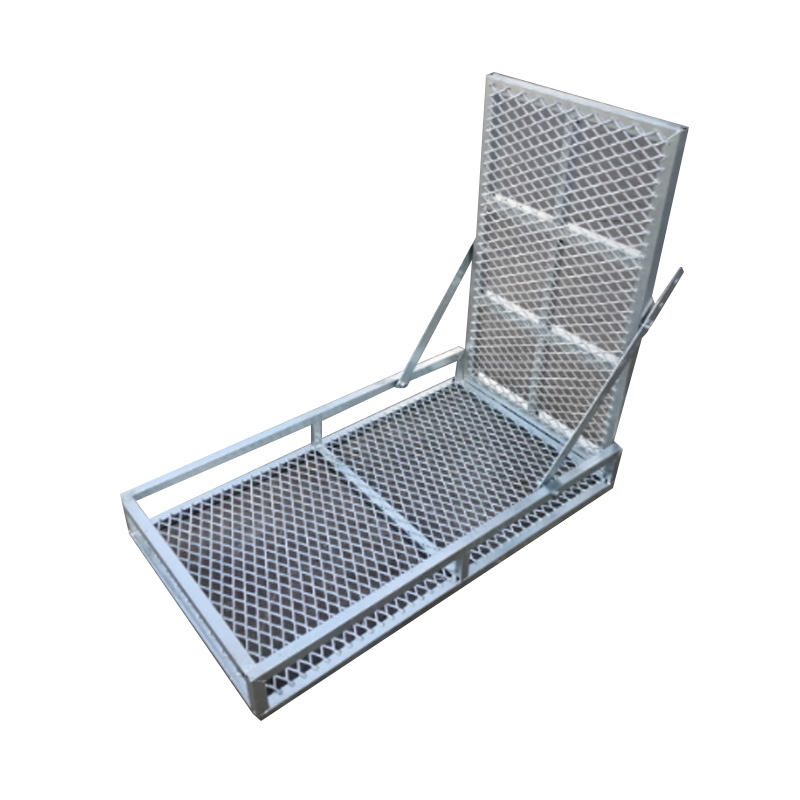
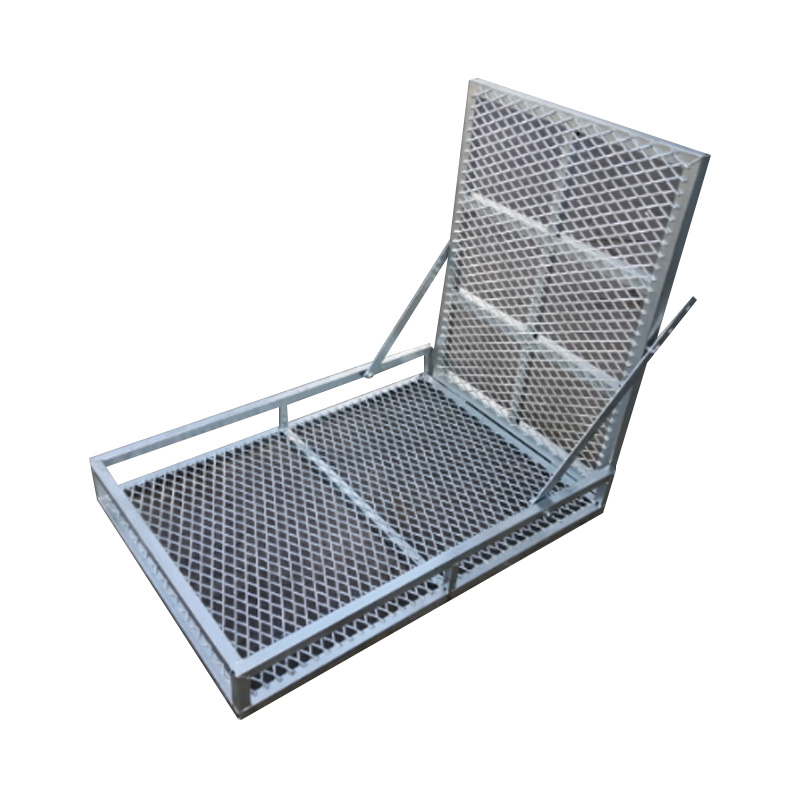
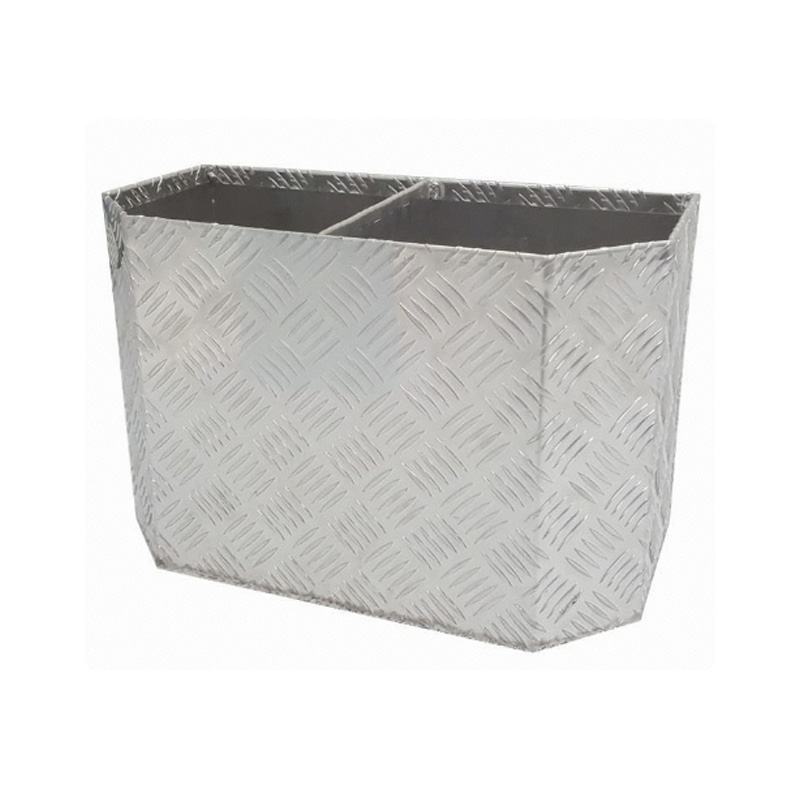
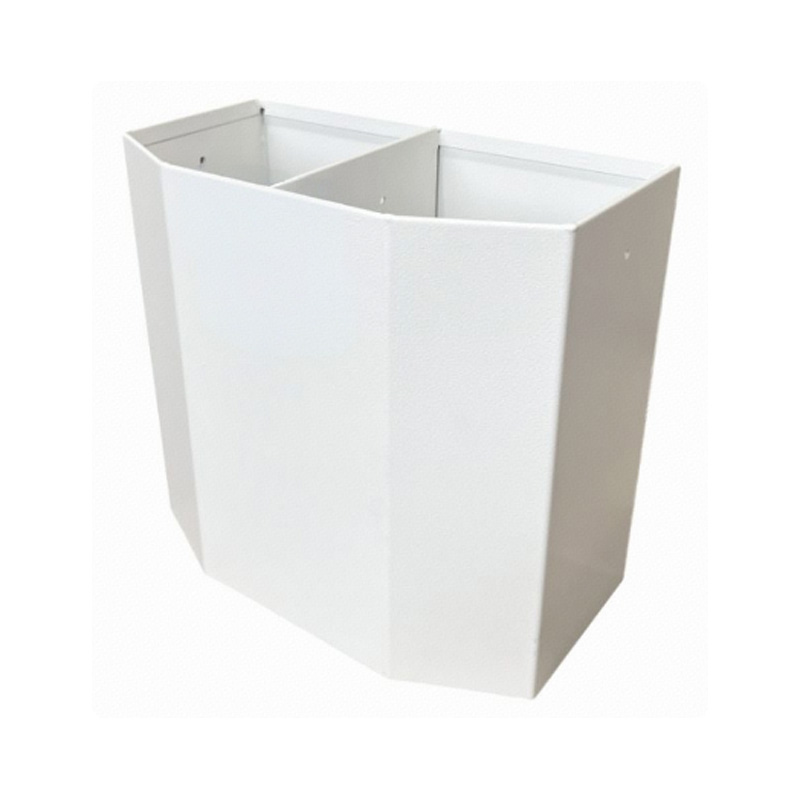
Trailer Mower Box
A trailer mower box is a dedicated, reinforced compartment mounted at the front of a mower trailer designed to securely transport samll mowers. Constructed typically from RHS and mesh grids, it often integrates a rear-loading ramp or swing-down door system engineered to handle the machine's front-end weight during loading and unloading, thereby preserving the trailer’s center of gravity and ensuring safe transit. Properly designed mower boxes enable quick transitions between jobs, reduce wear on the main trailer deck, and keep bulky equipment separate from loose cargo, allowing for improved space utilization. -
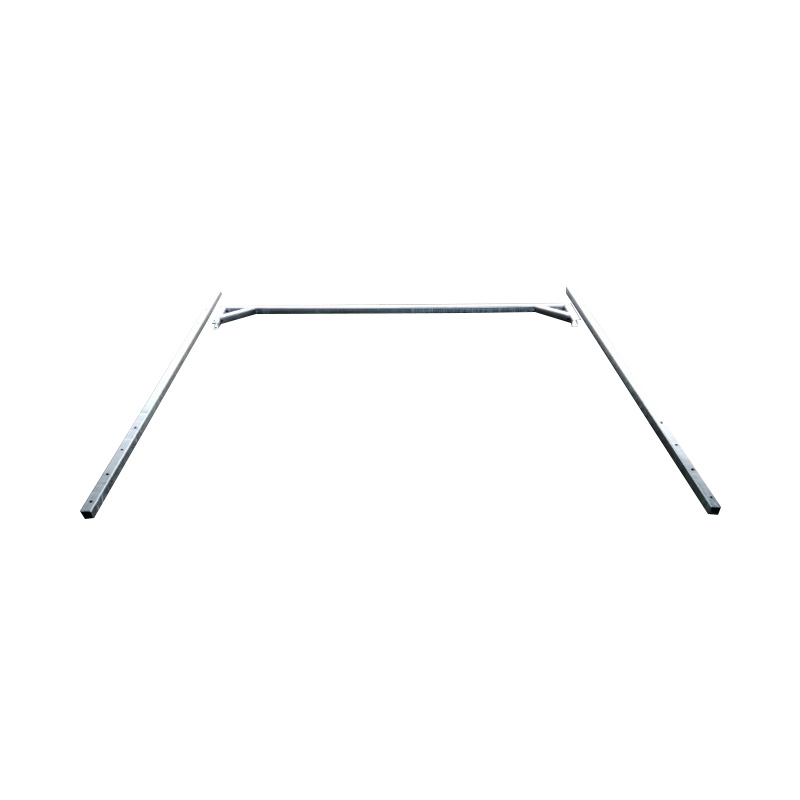
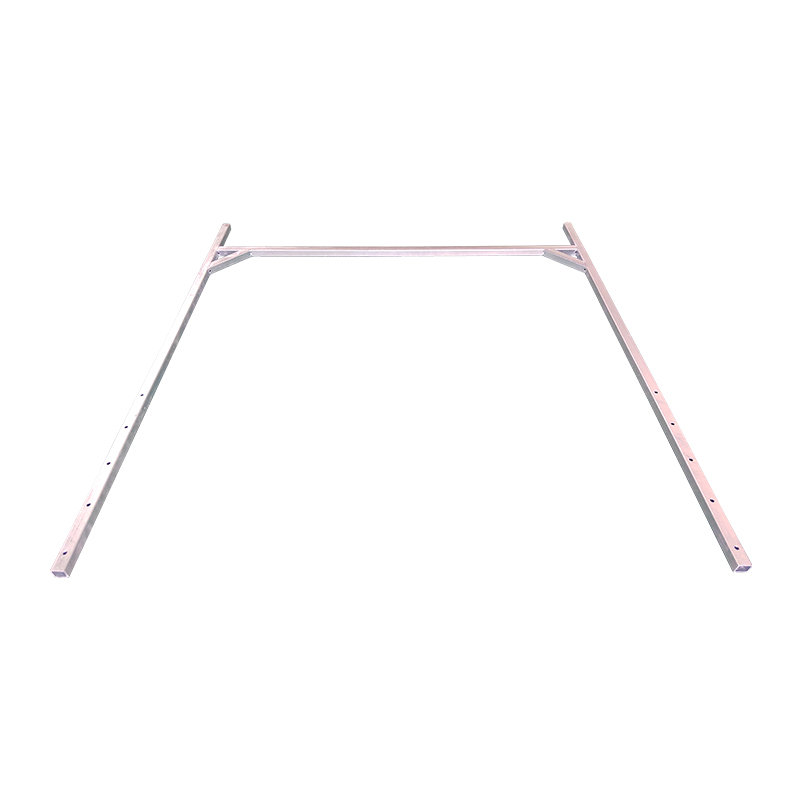
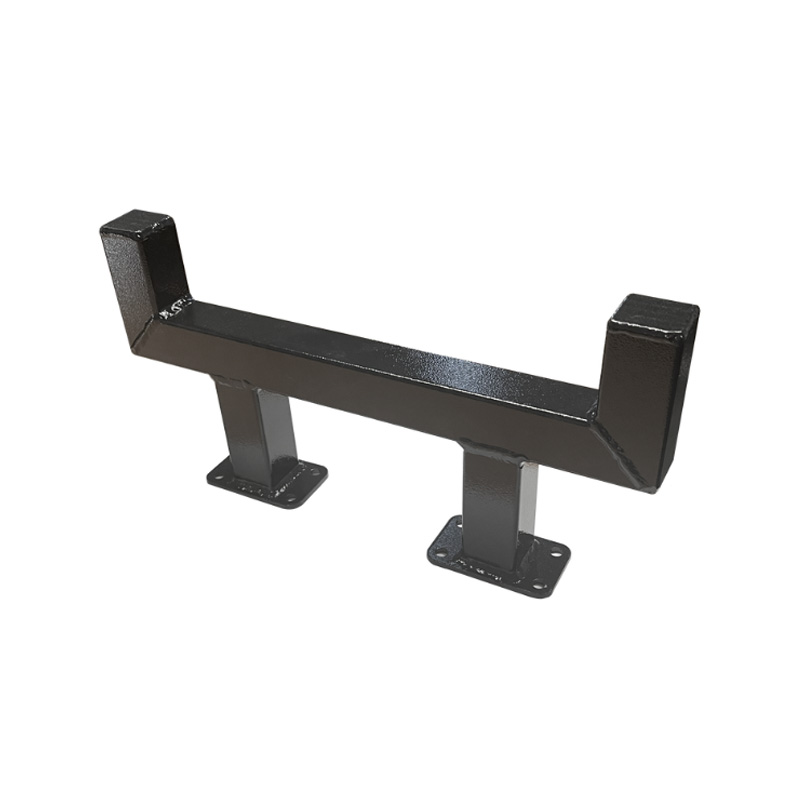
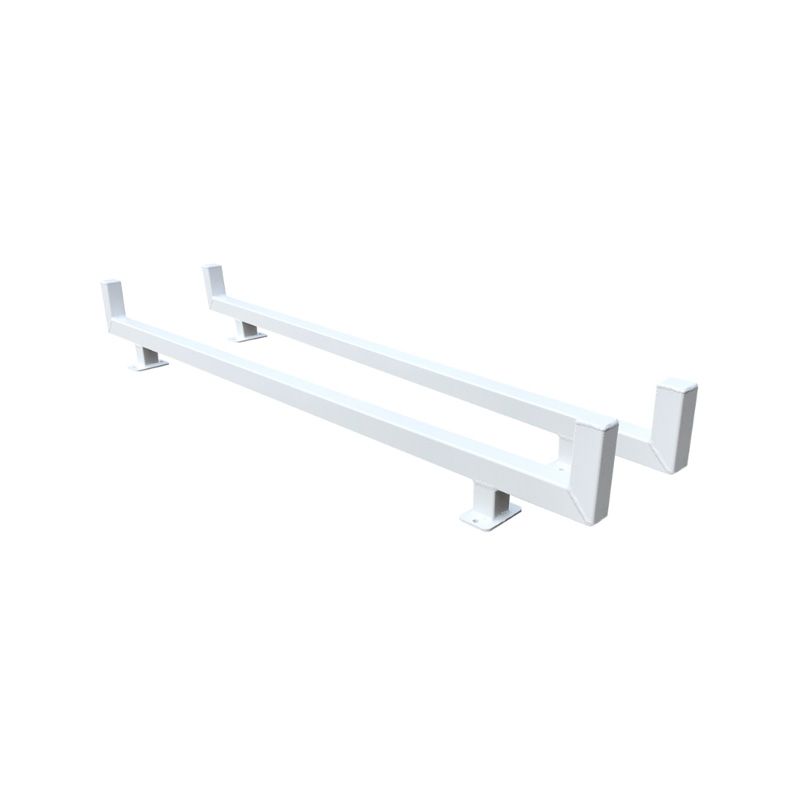
Trailer H Bar
A trailer H bar—also known as a ladder rack, H‑style support bar, or cross‑beam structure—is a robust welded assembly mounted above the trailer bed to support long materials such as ladders, pipes, conduit, and timber. Shaped like the letter "H", these bars consist of parallel uprights connected by a horizontal crossbar, typically fabricated from high-tensile steel, and finished with galvanizing to withstand outdoor exposure. By raising long items above the trailer floor, the H-bar improves payload packaging, reduces load-induced swaying, and aids access to the trailer bed. Taller configurations can accommodate pipes and timber bundles while maintaining legal clearance, while adjustable-height variants allow decks to remain clear, facilitating loading of wider cargo beneath the bars. -
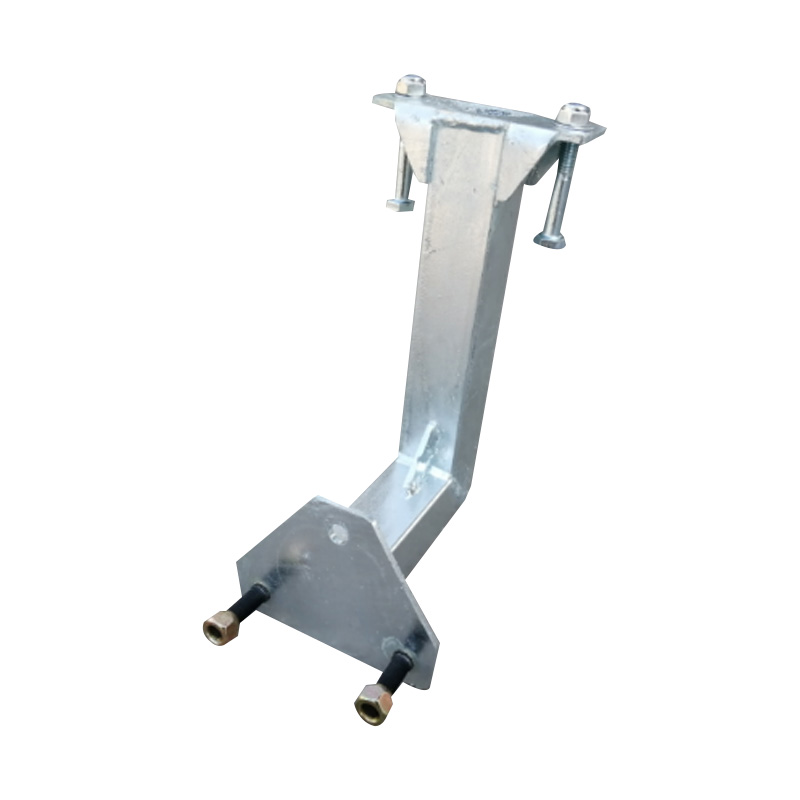
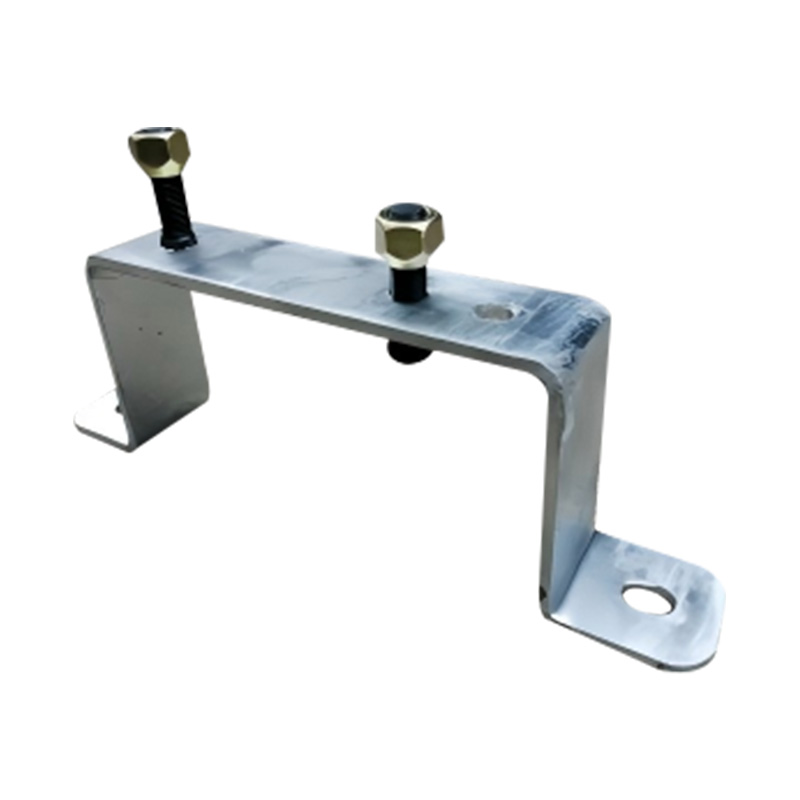
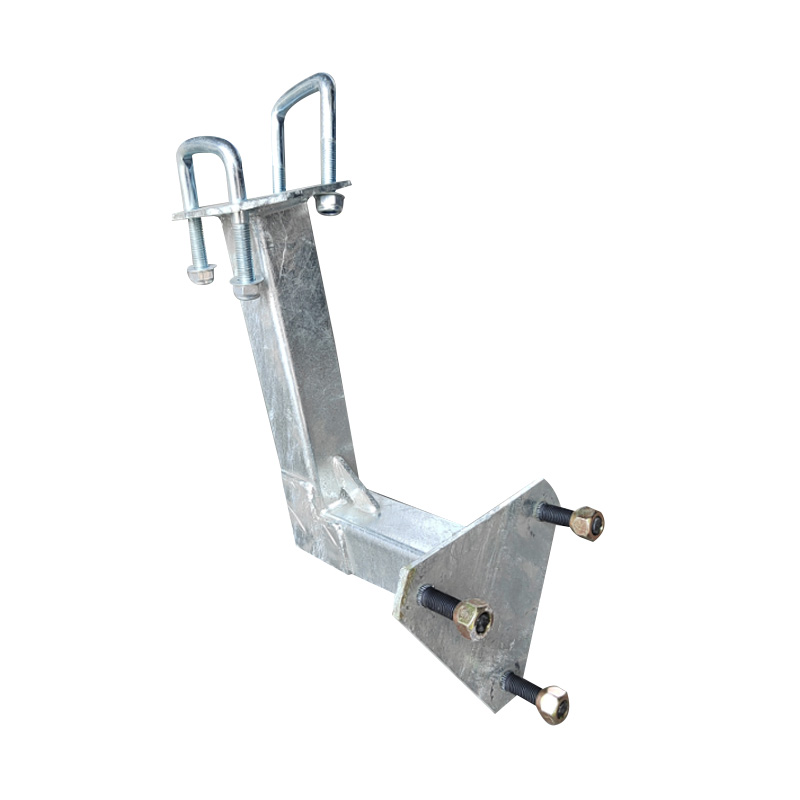
Trailer Spare Wheel Holder
A trailer spare wheel holder is a durable mounting device affixed to the trailer’s frame, drawbar, or sidewall, designed to secure a full-size spare wheel and tyre assembly. Crafted from stamped or fabricated steel, often with reinforced backing plates, the holder employs a clamping mechanism or U-bolt interface that accommodates wheel diameters and rim depths typical of the trailer—commonly 13″ to 16″ units. Mounted either vertically against the trailer face or horizontally under the deck, spare holders are positioned to avoid swinging into other components while preserving ground clearance. When installed on a swing-up jockey wheel or front gate, the holder maintains rear access to the trailer bed. A correctly positioned spare holder reduces downtime by providing immediate access to a replacement wheel and ensures compatibility with the trailer’s suspension and wiring layout.
GET A QUOTE
Give us a call or drop by anytime, we endeavour to answer all enquiries within 24 hours on business days. We will be happy to answer your questions.
Our Certificate
The company has obtained the internationally recognized ISO9001 and other professional factory certifications, and product certifications for professional needs in various markets.





































































































































































































































































 English
English  Español
Español  русский
русский 





